P26618
Gene name |
Pdgfra |
Protein name |
Platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha |
Names |
|
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:18595 |
EC number |
2.7.10.1: Protein-tyrosine kinases |
Protein Class |
|
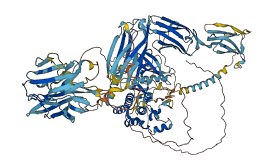
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
593-954 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Ligand binding |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
835-860 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
593-954 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
References
- Hubbard SR (2004) "Juxtamembrane autoinhibition in receptor tyrosine kinases", Nature reviews. Molecular cell biology, 5, 464-71
- Lew ED et al. (2007) "Structural basis for reduced FGFR2 activity in LADD syndrome: Implications for FGFR autoinhibition and activation", Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 104, 19802-7
- Kalinina J et al. (2012) "The alternatively spliced acid box region plays a key role in FGF receptor autoinhibition", Structure (London, England : 1993), 20, 77-88
- Knowles PP et al. (2006) "Structure and chemical inhibition of the RET tyrosine kinase domain", The Journal of biological chemistry, 281, 33577-87
- Mol CD et al. (2004) "Structural basis for the autoinhibition and STI-571 inhibition of c-Kit tyrosine kinase", The Journal of biological chemistry, 279, 31655-63
- Roskoski R Jr (2008) "VEGF receptor protein-tyrosine kinases: structure and regulation", Biochemical and biophysical research communications, 375, 287-91
- Wang X et al. (2020) "Molecular Bases of VEGFR-2-Mediated Physiological Function and Pathological Role", Frontiers in cell and developmental biology, 8, 599281
- Shewchuk LM et al. (2000) "Structure of the Tie2 RTK domain: self-inhibition by the nucleotide binding loop, activation loop, and C-terminal tail", Structure (London, England : 1993), 8, 1105-13
- Stuttfeld E et al. (2009) "Structure and function of VEGF receptors", IUBMB life, 61, 915-22
- Chiara F et al. (2004) "Autoinhibition of the platelet-derived growth factor beta-receptor tyrosine kinase by its C-terminal tail", The Journal of biological chemistry, 279, 19732-8
- Griffith J et al. (2004) "The structural basis for autoinhibition of FLT3 by the juxtamembrane domain", Molecular cell, 13, 169-78
- Reindl C et al. (2006) "From kinases to cancer: leakiness, loss of autoinhibition and leukemia", Cell cycle (Georgetown, Tex.), 5, 599-602
- Jiang J et al. (2004) "Identifying and characterizing a novel activating mutation of the FLT3 tyrosine kinase in AML", Blood, 104, 1855-8
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for P26618
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-P26618-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
1 variants for P26618
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs29589395 | 1005 | G>S | No | Ensembl |
No associated diseases with P26618
15 regional properties for P26618
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Protein kinase domain | 593 - 954 | IPR000719 |
| domain | Serine-threonine/tyrosine-protein kinase, catalytic domain | 594 - 948 | IPR001245 |
| conserved_site | Tyrosine-protein kinase, receptor class III, conserved site | 652 - 665 | IPR001824 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype | 34 - 122 | IPR003599-1 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype | 135 - 206 | IPR003599-2 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype | 220 - 310 | IPR003599-3 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype | 322 - 414 | IPR003599-4 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin-like domain | 1 - 113 | IPR007110-1 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin-like domain | 228 - 306 | IPR007110-2 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin-like domain | 319 - 410 | IPR007110-3 |
| active_site | Tyrosine-protein kinase, active site | 814 - 826 | IPR008266 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin I-set | 221 - 306 | IPR013098-1 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin I-set | 330 - 409 | IPR013098-2 |
| binding_site | Protein kinase, ATP binding site | 599 - 627 | IPR017441 |
| domain | Tyrosine-protein kinase, catalytic domain | 593 - 950 | IPR020635 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.10.1 | Protein-tyrosine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
15 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| axon | The long process of a neuron that conducts nerve impulses, usually away from the cell body to the terminals and varicosities, which are sites of storage and release of neurotransmitter. |
| cell junction | A cellular component that forms a specialized region of connection between two or more cells, or between a cell and the extracellular matrix, or between two membrane-bound components of a cell, such as flagella. |
| cell surface | The external part of the cell wall and/or plasma membrane. |
| cilium | A specialized eukaryotic organelle that consists of a filiform extrusion of the cell surface and of some cytoplasmic parts. Each cilium is largely bounded by an extrusion of the cytoplasmic (plasma) membrane, and contains a regular longitudinal array of microtubules, anchored to a basal body. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| external side of plasma membrane | The leaflet of the plasma membrane that faces away from the cytoplasm and any proteins embedded or anchored in it or attached to its surface. |
| Golgi apparatus | A membrane-bound cytoplasmic organelle of the endomembrane system that further processes the core oligosaccharides (e.g. N-glycans) added to proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum and packages them into membrane-bound vesicles. The Golgi apparatus operates at the intersection of the secretory, lysosomal, and endocytic pathways. |
| integral component of plasma membrane | The component of the plasma membrane consisting of the gene products and protein complexes having at least some part of their peptide sequence embedded in the hydrophobic region of the membrane. |
| intrinsic component of plasma membrane | The component of the plasma membrane consisting of the gene products and protein complexes having either part of their peptide sequence embedded in the hydrophobic region of the membrane or some other covalently attached group such as a GPI anchor that is similarly embedded in the membrane. |
| microvillus | Thin cylindrical membrane-covered projections on the surface of an animal cell containing a core bundle of actin filaments. Present in especially large numbers on the absorptive surface of intestinal cells. |
| nucleoplasm | That part of the nuclear content other than the chromosomes or the nucleolus. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| protein-containing complex | A stable assembly of two or more macromolecules, i.e. proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates or lipids, in which at least one component is a protein and the constituent parts function together. |
| receptor complex | Any protein complex that undergoes combination with a hormone, neurotransmitter, drug or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell function. |
13 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| growth factor binding | Binding to a growth factor, proteins or polypeptides that stimulate a cell or organism to grow or proliferate. |
| phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase binding | Binding to a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, any enzyme that catalyzes the addition of a phosphate group to an inositol lipid at the 3' position of the inositol ring. |
| platelet-derived growth factor alpha-receptor activity | Combining with platelet-derived growth factor isoform PDGF-AA, PDGF-BB or PDGF-AB to initiate a change in cell activity. |
| platelet-derived growth factor binding | Binding to platelet-derived growth factor. |
| platelet-derived growth factor receptor binding | Binding to a platelet-derived growth factor receptor. |
| protein homodimerization activity | Binding to an identical protein to form a homodimer. |
| protein kinase activity | Catalysis of the phosphorylation of an amino acid residue in a protein, usually according to the reaction: a protein + ATP = a phosphoprotein + ADP. |
| protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + a protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate; ATP + a protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate; and ATP + a protein tyrosine = ADP + protein tyrosine phosphate. |
| protein-containing complex binding | Binding to a macromolecular complex. |
| transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity | Combining with a signal and transmitting the signal from one side of the membrane to the other to initiate a change in cell activity by catalysis of the reaction: ATP + a protein-L-tyrosine = ADP + a protein-L-tyrosine phosphate. |
| vascular endothelial growth factor binding | Binding to a vascular endothelial growth factor. |
| vascular endothelial growth factor-activated receptor activity | Combining with a vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptor ligand and transmitting the signal across the plasma membrane to initiate a change in cell activity. |
50 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| adrenal gland development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the adrenal gland over time, from its formation to the mature structure. This gland can either be a discrete structure located bilaterally above each kidney, or a cluster of cells in the head kidney that perform the functions of the adrenal gland. In either case, this organ consists of two cells types, aminergic chromaffin cells and steroidogenic cortical cells. |
| anatomical structure morphogenesis | The process in which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form. |
| animal organ morphogenesis | Morphogenesis of an animal organ. An organ is defined as a tissue or set of tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Morphogenesis is the process in which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions. |
| cardiac myofibril assembly | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the cardiac myofibril over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A cardiac myofibril is a myofibril specific to cardiac muscle cells. |
| cell chemotaxis | The directed movement of a motile cell guided by a specific chemical concentration gradient. Movement may be towards a higher concentration (positive chemotaxis) or towards a lower concentration (negative chemotaxis). |
| cell migration | The controlled self-propelled movement of a cell from one site to a destination guided by molecular cues. Cell migration is a central process in the development and maintenance of multicellular organisms. |
| cellular response to amino acid stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an amino acid stimulus. An amino acid is a carboxylic acids containing one or more amino groups. |
| cellular response to reactive oxygen species | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a reactive oxygen species stimulus. Reactive oxygen species include singlet oxygen, superoxide, and oxygen free radicals. |
| embryonic cranial skeleton morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structures of the cranial skeleton are generated and organized during the embryonic phase. |
| embryonic digestive tract morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structures of the digestive tract are generated and organized during embryonic development. The digestive tract is the anatomical structure through which food passes and is processed. |
| estrogen metabolic process | The chemical reactions and pathways involving estrogens, C18 steroid hormones that can stimulate the development of female sexual characteristics. Also found in plants. |
| extracellular matrix organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of an extracellular matrix. |
| face morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structures of the face are generated and organized. The face is the ventral division of the head. |
| female gonad development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the female gonad over time, from its formation to the mature structure. |
| hematopoietic progenitor cell differentiation | The process in which precursor cell type acquires the specialized features of a hematopoietic progenitor cell, a class of cell types including myeloid progenitor cells and lymphoid progenitor cells. |
| in utero embryonic development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the embryo in the uterus over time, from formation of the zygote in the oviduct, to birth. An example of this process is found in Mus musculus. |
| Leydig cell differentiation | The process in which a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized structural and/or functional features of a Leydig cell. A Leydig cell is a testosterone-secreting cell in the interstitial area, between the seminiferous tubules, in the testis. |
| lung development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the lung over time, from its formation to the mature structure. In all air-breathing vertebrates the lungs are developed from the ventral wall of the oesophagus as a pouch which divides into two sacs. In amphibians and many reptiles the lungs retain very nearly this primitive sac-like character, but in the higher forms the connection with the esophagus becomes elongated into the windpipe and the inner walls of the sacs become more and more divided, until, in the mammals, the air spaces become minutely divided into tubes ending in small air cells, in the walls of which the blood circulates in a fine network of capillaries. In mammals the lungs are more or less divided into lobes, and each lung occupies a separate cavity in the thorax. |
| lung growth | The increase in size or mass of a lung. In all air-breathing vertebrates the lungs are developed from the ventral wall of the oesophagus as a pouch which divides into two sacs. In amphibians and many reptiles the lungs retain very nearly this primitive sac-like character, but in the higher forms the connection with the esophagus becomes elongated into the windpipe and the inner walls of the sacs become more and more divided, until, in the mammals, the air spaces become minutely divided into tubes ending in small air cells, in the walls of which the blood circulates in a fine network of capillaries. In mammals the lungs are more or less divided into lobes, and each lung occupies a separate cavity in the thorax. |
| luteinization | The set of processes resulting in differentiation of theca and granulosa cells into luteal cells and in the formation of a corpus luteum after ovulation. |
| male genitalia development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the male genitalia over time, from its formation to the mature structure. |
| metanephric glomerular capillary formation | The process that gives rise to a metanephric glomerular capillary. This process pertains to the initial formation of a structure from unspecified parts. |
| negative regulation of platelet activation | Any process that decreases the rate or frequency of platelet activation. Platelet activation is a series of progressive, overlapping events triggered by exposure of the platelets to subendothelial tissue. |
| odontogenesis of dentin-containing tooth | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a dentin-containing tooth over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A dentin-containing tooth is a hard, bony organ borne on the jaw or other bone of a vertebrate, and is composed mainly of dentin, a dense calcified substance, covered by a layer of enamel. |
| peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation | The phosphorylation of peptidyl-tyrosine to form peptidyl-O4'-phospho-L-tyrosine. |
| phosphatidylinositol-mediated signaling | The series of molecular signals in which a cell uses a phosphatidylinositol-mediated signaling to convert a signal into a response. Phosphatidylinositols include phosphatidylinositol (PtdIns) and its phosphorylated derivatives. |
| platelet aggregation | The adhesion of one platelet to one or more other platelets via adhesion molecules. |
| platelet-derived growth factor receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by a ligand binding to a platelet-derived growth factor receptor on the surface of a target cell, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| platelet-derived growth factor receptor-alpha signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated a ligand binding to an alpha-type platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFalpha) on the surface of a target cell, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| positive regulation of branching involved in lung morphogenesis | Any process that increases the rate, frequency, or extent of the process in which a highly ordered sequence of patterning events generates the branched structures of the lung, consisting of reiterated combinations of bud outgrowth, elongation, and dichotomous subdivision of terminal units. |
| positive regulation of cell migration | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell migration. |
| positive regulation of cell population proliferation | Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of cell proliferation. |
| positive regulation of cell proliferation by VEGF-activated platelet derived growth factor receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) binding to a platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR) on the surface of a cell, which activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell proliferation. |
| positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration | Any process that increases the concentration of calcium ions in the cytosol. |
| positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction mediated by the ERK1 and ERK2 cascade. |
| positive regulation of fibroblast proliferation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of multiplication or reproduction of fibroblast cells. |
| positive regulation of kinase activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of kinase activity, the catalysis of the transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a substrate molecule. |
| positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the phosphorylation of peptidyl-tyrosine. |
| positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity. |
| positive regulation of phospholipase C activity | Any process that increases the rate of phospholipase C activity. |
| protein autophosphorylation | The phosphorylation by a protein of one or more of its own amino acid residues (cis-autophosphorylation), or residues on an identical protein (trans-autophosphorylation). |
| regulation of chemotaxis | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the directed movement of a motile cell or organism in response to a specific chemical concentration gradient. |
| regulation of mesenchymal stem cell differentiation | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of mesenchymal stem cell differentiation. |
| retina vasculature development in camera-type eye | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the vasculature of the retina over time, from its formation to the mature structure. |
| roof of mouth development | The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of the roof of the mouth from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure. The roof of the mouth is the partition that separates the nasal and oral cavities. |
| signal transduction involved in regulation of gene expression | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression as a consequence of a process in which a signal is released and/or conveyed from one location to another. |
| skeletal system morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structures of the skeleton are generated and organized. |
| transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by an extracellular ligand binding to a receptor on the surface of the target cell where the receptor possesses tyrosine kinase activity, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| white fat cell differentiation | The process in which a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a white adipocyte, an animal connective tissue cell involved in energy storage. White adipocytes have cytoplasmic lipids arranged in a unique vacuole. |
| wound healing | The series of events that restore integrity to a damaged tissue, following an injury. |
101 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P43481 | KIT | Mast/stem cell growth factor receptor Kit | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| Q06805 | TIE1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor Tie-1 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| Q06807 | TEK | Angiopoietin-1 receptor | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| Q28889 | KIT | Mast/stem cell growth factor receptor Kit | Felis catus (Cat) (Felis silvestris catus) | SS |
| P13369 | CSF1R | Macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor | Felis catus (Cat) (Felis silvestris catus) | SS |
| P18460 | FGFR3 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P21804 | FGFR1 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q08156 | KIT | Mast/stem cell growth factor receptor Kit | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q8QHL3 | FLT1 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P18461 | FGFR2 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q9PUF6 | PDGFRA | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q07407 | htl | Fibroblast growth factor receptor homolog 1 | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | PR |
| Q6J9G0 | STYK1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase STYK1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P36888 | FLT3 | Receptor-type tyrosine-protein kinase FLT3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P09619 | PDGFRB | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P35916 | FLT4 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P35968 | KDR | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P17948 | FLT1 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P07333 | CSF1R | Macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P10721 | KIT | Mast/stem cell growth factor receptor Kit | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P22455 | FGFR4 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P22607 | FGFR3 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P07949 | RET | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase receptor Ret | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P35590 | TIE1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor Tie-1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q02763 | TEK | Angiopoietin-1 receptor | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P11362 | FGFR1 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P21802 | FGFR2 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P16234 | PDGFRA | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q91V87 | Fgfrl1 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor-like 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q6J9G1 | Styk1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase STYK1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P35546 | Ret | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase receptor Ret | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q61006 | Musk | Muscle, skeletal receptor tyrosine-protein kinase | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q9Z138 | Ror2 | Tyrosine-protein kinase transmembrane receptor ROR2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q9Z139 | Ror1 | Inactive tyrosine-protein kinase transmembrane receptor ROR1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q62371 | Ddr2 | Discoidin domain-containing receptor 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q03146 | Ddr1 | Epithelial discoidin domain-containing receptor 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P15209 | Ntrk2 | BDNF/NT-3 growth factors receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q3UFB7 | Ntrk1 | High affinity nerve growth factor receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q6VNS1 | Ntrk3 | NT-3 growth factor receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P35917 | Flt4 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P35969 | Flt1 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P35918 | Kdr | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q03145 | Epha2 | Ephrin type-A receptor 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q60750 | Epha1 | Ephrin type-A receptor 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P54761 | Ephb4 | Ephrin type-B receptor 4 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q60629 | Epha5 | Ephrin type-A receptor 5 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P97793 | Alk | ALK tyrosine kinase receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q9WTL4 | Insrr | Insulin receptor-related protein | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q60751 | Igf1r | Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P15208 | Insr | Insulin receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P16092 | Fgfr1 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P21803 | Fgfr2 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q03142 | Fgfr4 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q60805 | Mertk | Tyrosine-protein kinase Mer | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q62190 | Mst1r | Macrophage-stimulating protein receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q00993 | Axl | Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor UFO | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P55144 | Tyro3 | Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor TYRO3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P70424 | Erbb2 | Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q61527 | Erbb4 | Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-4 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q61526 | Erbb3 | Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q01279 | Egfr | Epidermal growth factor receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q01887 | Ryk | Tyrosine-protein kinase RYK | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q02858 | Tek | Angiopoietin-1 receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q06806 | Tie1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor Tie-1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P05532 | Kit | Mast/stem cell growth factor receptor Kit | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P05622 | Pdgfrb | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P09581 | Csf1r | Macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q00342 | Flt3 | Receptor-type tyrosine-protein kinase FLT3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q61851 | Fgfr3 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P16056 | Met | Hepatocyte growth factor receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q2HWD6 | KIT | Mast/stem cell growth factor receptor Kit | Sus scrofa (Pig) | SS |
| Q7TQM3 | Fgfrl1 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor-like 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P53767 | Flt1 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q91ZT1 | Flt4 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q04589 | Fgfr1 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| G3V9H8 | Ret | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase receptor Ret | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q498D6 | Fgfr4 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q05030 | Pdgfrb | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| O08775 | Kdr | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P20786 | Pdgfra | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q17833 | old-1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor old-1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| Q19238 | F09A5.2 | Putative tyrosine-protein kinase F09A5.2 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| Q10656 | egl-15 | Myoblast growth factor receptor egl-15 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| P34892 | kin-16 | Receptor-like tyrosine-protein kinase kin-16 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| G5ED65 | ver-1 | Protein ver-1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| Q9S9M2 | WAKL4 | Wall-associated receptor kinase-like 4 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q7X8C5 | WAKL2 | Wall-associated receptor kinase-like 2 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q8VYA3 | WAKL10 | Wall-associated receptor kinase-like 10 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9C9L5 | WAKL9 | Wall-associated receptor kinase-like 9 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9M092 | WAKL17 | Wall-associated receptor kinase-like 17 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q0WNY5 | WAKL18 | Wall-associated receptor kinase-like 18 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q8AXB3 | kdrl | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor kdr-like | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q5GIT4 | kdr | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| O73791 | tek | Angiopoietin-1 receptor | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q90Z00 | fgfr1a | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1-A | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q8JG38 | fgfr2 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q9I8N6 | csf1r | Macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q90413 | fgfr4 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q8JFR5 | kita | Mast/stem cell growth factor receptor kita | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q5MD89 | flt4 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q9DE49 | pdgfra | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MGTSHQVFLV | LSCLLTGPGL | ISCQLLLPSI | LPNENEKIVQ | LNSSFSLRCV | GESEVSWQHP |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| MSEEDDPNVE | IRSEENNSGL | FVTVLEVVNA | SAAHTGWYTC | YYNHTQTDES | EIEGRHIYIY |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| VPDPDMAFVP | LGMTDSLVIV | EEDDSAIIPC | RTTDPETQVT | LHNNGRLVPA | SYDSRQGFNG |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| TFSVGPYICE | ATVKGRTFKT | SEFNVYALKA | TSELNLEMDA | RQTVYKAGET | IVVTCAVFNN |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| EVVDLQWTYP | GEVRNKGITM | LEEIKLPSIK | LVYTLTVPKA | TVKDSGEYEC | AARQATKEVK |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| EMKRVTISVH | EKGFVEIEPT | FGQLEAVNLH | EVREFVVEVQ | AYPTPRISWL | KDNLTLIENL |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| TEITTDVQKS | QETRYQSKLK | LIRAKEEDSG | HYTIIVQNED | DVKSYTFELS | TLVPASILDL |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| VDDHHGSGGG | QTVRCTAEGT | PLPEIDWMIC | KHIKKCNNDT | SWTVLASNVS | NIITELPRRG |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| RSTVEGRVSF | AKVEETIAVR | CLAKNNLSVV | ARELKLVAPT | LRSELTVAAA | VLVLLVIVIV |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| SLIVLVVIWK | QKPRYEIRWR | VIESISPDGH | EYIYVDPMQL | PYDSRWEFPR | DGLVLGRILG |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| SGAFGKVVEG | TAYGLSRSQP | VMKVAVKMLK | PTARSSEKQA | LMSELKIMTH | LGPHLNIVNL |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| LGACTKSGPI | YIITEYCFYG | DLVNYLHKNR | DSFMSQHPEK | PKKDLDIFGL | NPADESTRSY |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| VILSFENNGD | YMDMKQADTT | QYVPMLERKE | VSKYSDIQRS | LYDRPASYKK | KSMLDSEVKN |
| 790 | 800 | 810 | 820 | 830 | 840 |
| LLSDDDSEGL | TLLDLLSFTY | QVARGMEFLA | SKNCVHRDLA | ARNVLLAQGK | IVKICDFGLA |
| 850 | 860 | 870 | 880 | 890 | 900 |
| RDIMHDSNYV | SKGSTFLPVK | WMAPESIFDN | LYTTLSDVWS | YGILLWEIFS | LGGTPYPGMM |
| 910 | 920 | 930 | 940 | 950 | 960 |
| VDSTFYNKIK | SGYRMAKPDH | ATSEVYEIMV | QCWNSEPEKR | PSFYHLSEIV | ENLLPGQYKK |
| 970 | 980 | 990 | 1000 | 1010 | 1020 |
| SYEKIHLDFL | KSDHPAVARM | RVDSDNAYIG | VTYKNEEDKL | KDWEGGLDEQ | RLSADSGYII |
| 1030 | 1040 | 1050 | 1060 | 1070 | 1080 |
| PLPDIDPVPE | EEDLGKRNRH | SSQTSEESAI | ETGSSSSTFI | KREDETIEDI | DMMDDIGIDS |
| SDLVEDSFL |