P25799
Gene name |
Nfkb1 |
Protein name |
Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p105 subunit [Cleaved into: Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p50 subunit] |
Names |
DNA-binding factor KBF1, EBP-1, NF-kappa-B1 p84/NF-kappa-B1 p98, Nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells 1 |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:18033 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
NUCLEAR FACTOR NF-KAPPA-B PROTEIN (PTHR24169) |
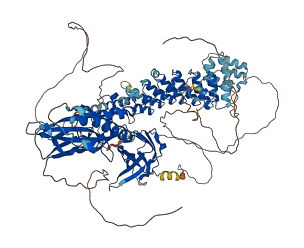
Descriptions
NFκB1 is a nuclear factor NFκB p105 subunit (p50 and its precursor p105), and plays pivotal role in the regulation of the inflammatory response to pathogens, autoimmune diseases, and cancerous cells. The five members of the NF-κB family are normally kept inactive in the cytoplasm by interaction with inhibitors called IκBs or the unprocessed forms of NF-κB1 and NF-κB2. The C-terminal ankyrin repeats of p105 allow it to serve as an IkappaB-like function. The ankyrin repeats interact with and shield the nuclear localization signal located at the end of Rel-homology domain (RHD) domain and DNA binding of Rel/NF-kappaB complexes. RHD domain mediates DNA binding.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
37-350 (Rel-homology domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Cleavage, PTM |
Assay |
Deletion assay |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
References
- Vallabhapurapu S et al. (2009) "Regulation and function of NF-kappaB transcription factors in the immune system", Annual review of immunology, 27, 693-733
- Perkins ND (2007) "Integrating cell-signalling pathways with NF-kappaB and IKK function", Nature reviews. Molecular cell biology, 8, 49-62
- Dorrington MG et al. (2019) "NF-κB Signaling in Macrophages: Dynamics, Crosstalk, and Signal Integration", Frontiers in immunology, 10, 705
- Heusch M et al. (1999) "The generation of nfkb2 p52: mechanism and efficiency", Oncogene, 18, 6201-8
- Savinova OV et al. (2009) "The Nfkb1 and Nfkb2 proteins p105 and p100 function as the core of high-molecular-weight heterogeneous complexes", Molecular cell, 34, 591-602
- Hatada EN et al. (1992) "The ankyrin repeat domains of the NF-kappa B precursor p105 and the protooncogene bcl-3 act as specific inhibitors of NF-kappa B DNA binding", Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 89, 2489-93
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

21 structures for P25799
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1BFS | X-ray | 220 A | A | 245-350 | PDB |
| 1IKN | X-ray | 230 A | C | 245-363 | PDB |
| 1LE5 | X-ray | 275 A | B/F | 39-350 | PDB |
| 1LE9 | X-ray | 300 A | B/F | 39-350 | PDB |
| 1LEI | X-ray | 270 A | B | 39-350 | PDB |
| 1NFK | X-ray | 230 A | A/B | 39-363 | PDB |
| 1OOA | X-ray | 245 A | A/B | 39-363 | PDB |
| 1U36 | X-ray | 189 A | A | 245-350 | PDB |
| 1U3J | X-ray | 190 A | A | 245-350 | PDB |
| 1U3Y | X-ray | 190 A | A | 245-350 | PDB |
| 1U3Z | X-ray | 190 A | A | 245-350 | PDB |
| 1U41 | X-ray | 220 A | A/B/C/D | 245-350 | PDB |
| 1U42 | X-ray | 270 A | A | 245-350 | PDB |
| 1VKX | X-ray | 290 A | B | 39-350 | PDB |
| 2I9T | X-ray | 280 A | B | 39-350 | PDB |
| 2V2T | X-ray | 305 A | B | 38-363 | PDB |
| 3JV4 | X-ray | 315 A | B/D/F | 245-359 | PDB |
| 8TKL | X-ray | 300 A | A/B | 39-350 | PDB |
| 8TKM | X-ray | 280 A | A/B | 39-350 | PDB |
| 8TKN | X-ray | 280 A | A/B | 39-350 | PDB |
| AF-P25799-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
44 variants for P25799
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs1133337474 | 18 | A>P | No | EVA | |
| rs3388665277 | 46 | E>D | No | EVA | |
| rs3388667079 | 67 | L>F | No | EVA | |
| rs3388662711 | 68 | P>T | No | EVA | |
| rs3388667106 | 70 | A>T | No | EVA | |
| rs3388662742 | 82 | V>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3388665310 | 84 | I>T | No | EVA | |
| rs3388660434 | 92 | K>N | No | EVA | |
| rs232176681 | 120 | V>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3388665317 | 126 | G>* | No | EVA | |
| rs3388653075 | 146 | K>T | No | EVA | |
| rs3388660474 | 160 | I>E | No | EVA | |
| rs3388660433 | 176 | L>V | No | EVA | |
| rs3388669918 | 177 | Q>E | No | EVA | |
| rs3388662237 | 179 | E>D | No | EVA | |
| rs3388665675 | 179 | E>V | No | EVA | |
| rs3388653011 | 261 | T>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3410540297 | 262 | G>E | No | EVA | |
| rs3388660518 | 292 | W>G | No | EVA | |
| rs3410332036 | 297 | D>N | No | EVA | |
| rs3388660476 | 309 | I>L | No | EVA | |
| rs3388659441 | 313 | T>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3388666591 | 343 | K>N | No | EVA | |
| rs3388662657 | 387 | G>A | No | EVA | |
| rs262241696 | 405 | S>P | No | EVA | |
| rs234322611 | 406 | N>H | No | EVA | |
| rs218495059 | 421 | V>A | No | EVA | |
| rs263027543 | 450 | E>K | No | EVA | |
| rs3541877264 | 476 | P>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3388659393 | 570 | I>T | No | EVA | |
| rs3388666588 | 581 | P>L | No | EVA | |
| rs3388665280 | 581 | P>T | No | EVA | |
| rs36503768 | 596 | D>E | No | EVA | |
| rs3388662663 | 604 | L>Q | No | EVA | |
| rs3388647956 | 610 | W>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3388662236 | 619 | A>T | No | EVA | |
| rs231728937 | 628 | S>G | No | EVA | |
| rs3388647904 | 686 | H>L | No | EVA | |
| rs3388660502 | 706 | A>T | No | EVA | |
| rs3388647983 | 743 | V>* | No | EVA | |
| rs3388665702 | 757 | E>K | No | EVA | |
| rs3388669302 | 821 | I>N | No | EVA | |
| rs3388665293 | 833 | Q>* | No | EVA | |
| rs3388662129 | 914 | T>S | No | EVA |
No associated diseases with P25799
No regional properties for P25799
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| No domain, repeats, and functional sites for P25799 | |||
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | ||
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | PTHR24169 | NUCLEAR FACTOR NF-KAPPA-B PROTEIN |
| PANTHER Subfamily | PTHR24169:SF9 | NUCLEAR FACTOR NF-KAPPA-B P105 SUBUNIT |
| PANTHER Protein Class |
DNA-binding transcription factor
Rel homology transcription factor immunoglobulin fold transcription factor |
|
| PANTHER Pathway Category |
Inflammation mediated by chemokine and cytokine signaling pathway NFkappaB B cell activation NFkappaB T cell activation NFkappaB Toll receptor signaling pathway NFkappaB Apoptosis signaling pathway NFkappaB |
|
8 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| chromatin | The ordered and organized complex of DNA, protein, and sometimes RNA, that forms the chromosome. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| mitochondrion | A semiautonomous, self replicating organelle that occurs in varying numbers, shapes, and sizes in the cytoplasm of virtually all eukaryotic cells. It is notably the site of tissue respiration. |
| NF-kappaB complex | A protein complex that consists of a homo- or heterodimer of members of a family of structurally related proteins that contain a conserved N-terminal region called the Rel homology domain (RHD). In the nucleus, NF-kappaB complexes act as transcription factors. In unstimulated cells, NF-kappaB dimers are sequestered in the cytoplasm by IkappaB monomers; signals that induce NF-kappaB activity cause degradation of IkappaB, allowing NF-kappaB dimers to translocate to the nucleus and induce gene expression. |
| nucleoplasm | That part of the nuclear content other than the chromosomes or the nucleolus. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| protein-containing complex | A stable assembly of two or more macromolecules, i.e. proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates or lipids, in which at least one component is a protein and the constituent parts function together. |
19 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| actinin binding | Binding to actinin, any member of a family of proteins that crosslink F-actin. |
| chromatin binding | Binding to chromatin, the network of fibers of DNA, protein, and sometimes RNA, that make up the chromosomes of the eukaryotic nucleus during interphase. |
| DNA binding | Any molecular function by which a gene product interacts selectively and non-covalently with DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). |
| DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific | A DNA-binding transcription factor activity that activates or increases transcription of specific gene sets transcribed by RNA polymerase II. |
| DNA-binding transcription factor activity | A transcription regulator activity that modulates transcription of gene sets via selective and non-covalent binding to a specific double-stranded genomic DNA sequence (sometimes referred to as a motif) within a cis-regulatory region. Regulatory regions include promoters (proximal and distal) and enhancers. Genes are transcriptional units, and include bacterial operons. |
| DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific | A DNA-binding transcription factor activity that modulates the transcription of specific gene sets transcribed by RNA polymerase II. |
| DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific | A DNA-binding transcription factor activity that represses or decreases the transcription of specific gene sets transcribed by RNA polymerase II. |
| double-stranded DNA binding | Binding to double-stranded DNA. |
| enzyme binding | Binding to an enzyme, a protein with catalytic activity. |
| heat shock protein binding | Binding to a heat shock protein, a protein synthesized or activated in response to heat shock. |
| identical protein binding | Binding to an identical protein or proteins. |
| protein-containing complex binding | Binding to a macromolecular complex. |
| RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding | Binding to a specific upstream regulatory DNA sequence (transcription factor recognition sequence or binding site) located in cis relative to the transcription start site (i.e., on the same strand of DNA) of a gene transcribed by RNA polymerase II. |
| RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding | Binding to a specific sequence of DNA that is part of a regulatory region that controls the transcription of a gene or cistron by RNA polymerase II. |
| sequence-specific DNA binding | Binding to DNA of a specific nucleotide composition, e.g. GC-rich DNA binding, or with a specific sequence motif or type of DNA e.g. promotor binding or rDNA binding. |
| sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding | Binding to double-stranded DNA of a specific nucleotide composition, e.g. GC-rich DNA binding, or with a specific sequence motif or type of DNA, e.g. promotor binding or rDNA binding. |
| transcription cis-regulatory region binding | Binding to a specific sequence of DNA that is part of a regulatory region that controls transcription of that section of the DNA. The transcribed region might be described as a gene, cistron, or operon. |
| transcription coactivator binding | Binding to a transcription coactivator, a protein involved in positive regulation of transcription via protein-protein interactions with transcription factors and other proteins that positively regulate transcription. Transcription coactivators do not bind DNA directly, but rather mediate protein-protein interactions between activating transcription factors and the basal transcription machinery. |
| transcription coregulator activity | A transcription regulator activity that modulates the transcription of specific gene sets via binding to a DNA-bound DNA-binding transcription factor, either on its own or as part of a complex. Coregulators often act by altering chromatin structure and modifications. For example, one class of transcription coregulators modifies chromatin structure through covalent modification of histones. A second class remodels the conformation of chromatin in an ATP-dependent fashion. A third class modulates interactions of DNA-bound DNA-binding transcription factors with other transcription coregulators. |
50 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| apoptotic process | A programmed cell death process which begins when a cell receives an internal (e.g. DNA damage) or external signal (e.g. an extracellular death ligand), and proceeds through a series of biochemical events (signaling pathway phase) which trigger an execution phase. The execution phase is the last step of an apoptotic process, and is typically characterized by rounding-up of the cell, retraction of pseudopodes, reduction of cellular volume (pyknosis), chromatin condensation, nuclear fragmentation (karyorrhexis), plasma membrane blebbing and fragmentation of the cell into apoptotic bodies. When the execution phase is completed, the cell has died. |
| B cell receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by the cross-linking of an antigen receptor on a B cell. |
| cellular response to angiotensin | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an angiotensin stimulus. Angiotensin is any of three physiologically active peptides (angiotensin II, III, or IV) processed from angiotensinogen. |
| cellular response to brain-derived neurotrophic factor stimulus | A process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a brain-derived neurotrophic factor stimulus. |
| cellular response to carbohydrate stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a carbohydrate stimulus. |
| cellular response to cytokine stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a cytokine stimulus. |
| cellular response to diterpene | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a diterpene stimulus. |
| cellular response to dsRNA | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a double-stranded RNA stimulus. |
| cellular response to glucoside | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a glucoside stimulus. |
| cellular response to interleukin-1 | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an interleukin-1 stimulus. |
| cellular response to interleukin-17 | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an interleukin-17 stimulus. |
| cellular response to interleukin-6 | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an interleukin-6 stimulus. |
| cellular response to lipopolysaccharide | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a lipopolysaccharide stimulus; lipopolysaccharide is a major component of the cell wall of gram-negative bacteria. |
| cellular response to mechanical stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a mechanical stimulus. |
| cellular response to nicotine | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a nicotine stimulus. |
| cellular response to organic cyclic compound | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an organic cyclic compound stimulus. |
| cellular response to peptide | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a peptide stimulus. |
| cellular response to tumor necrosis factor | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a tumor necrosis factor stimulus. |
| cellular response to virus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus from a virus. |
| gene expression | The process in which a gene's sequence is converted into a mature gene product (protein or RNA). This includes the production of an RNA transcript and its processing, translation and maturation for protein-coding genes. |
| I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling | The process in which a signal is passed on to downstream components within the cell through the I-kappaB-kinase (IKK)-dependent activation of NF-kappaB. The cascade begins with activation of a trimeric IKK complex (consisting of catalytic kinase subunits IKKalpha and/or IKKbeta, and the regulatory scaffold protein NEMO) and ends with the regulation of transcription of target genes by NF-kappaB. In a resting state, NF-kappaB dimers are bound to I-kappaB proteins, sequestering NF-kappaB in the cytoplasm. Phosphorylation of I-kappaB targets I-kappaB for ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation, thus releasing the NF-kappaB dimers, which can translocate to the nucleus to bind DNA and regulate transcription. |
| inflammatory response | The immediate defensive reaction (by vertebrate tissue) to infection or injury caused by chemical or physical agents. The process is characterized by local vasodilation, extravasation of plasma into intercellular spaces and accumulation of white blood cells and macrophages. |
| innate immune response | Innate immune responses are defense responses mediated by germline encoded components that directly recognize components of potential pathogens. |
| JNK cascade | An intracellular protein kinase cascade containing at least a JNK (a MAPK), a JNKK (a MAPKK) and a JUN3K (a MAP3K). The cascade can also contain an additional tier |
| lymph node development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of lymph nodes over time, from their formation to the mature structure. A lymph node is a round, oval, or bean shaped structure localized in clusters along the lymphatic vessels, with a distinct internal structure including specialized vasculature and B- and T-zones for the activation of lymphocytes. |
| mammary gland involution | The tissue remodeling that removes differentiated mammary epithelia during weaning. |
| MAPK cascade | An intracellular protein kinase cascade containing at least a MAPK, a MAPKK and a MAP3K. The cascade can also contain an additional tiers |
| negative regulation of apoptotic process | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cell death by apoptotic process. |
| negative regulation of calcidiol 1-monooxygenase activity | Any process that decreases the rate, frequency or extent of calcidiol 1-monooxygenase activity. Calcidiol 1-monooxygenase activity is the catalysis of the reaction |
| negative regulation of cytokine production | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the rate of production of a cytokine. |
| negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cellular DNA-templated transcription. |
| negative regulation of gene expression | Any process that decreases the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product (protein or RNA). |
| negative regulation of inflammatory response | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the inflammatory response. |
| negative regulation of interleukin-12 production | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate, or extent of interleukin-12 production. |
| negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of transcription mediated by RNA polymerase II. |
| NIK/NF-kappaB signaling | The process in which a signal is passed on to downstream components within the cell through the NIK-dependent processing and activation of NF-KappaB. Begins with activation of the NF-KappaB-inducing kinase (NIK), which in turn phosphorylates and activates IkappaB kinase alpha (IKKalpha). IKKalpha phosphorylates the NF-Kappa B2 protein (p100) leading to p100 processing and release of an active NF-KappaB (p52). |
| positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway | Any process that increases the rate, frequency, or extent of the Wnt signaling pathway through beta-catenin, the series of molecular signals initiated by binding of a Wnt protein to a frizzled family receptor on the surface of the target cell, followed by propagation of the signal via beta-catenin, and ending with a change in transcription of target genes. |
| positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cellular DNA-templated transcription. |
| positive regulation of gene expression | Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product (protein or RNA). |
| positive regulation of hyaluronan biosynthetic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of hyaluronan biosynthetic process. |
| positive regulation of miRNA metabolic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of miRNA metabolic process. |
| positive regulation of miRNA transcription | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of microRNA (miRNA) gene transcription. |
| positive regulation of miRNA-mediated gene silencing | A process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of gene silencing by a microRNA (miRNA). |
| positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription from an RNA polymerase II promoter. |
| positive regulation of transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II | Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of a process involved in starting transcription from an RNA polymerase II promoter. |
| regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of transcription mediated by RNA polymerase II. |
| response to cytokine | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a cytokine stimulus. |
| response to muscle stretch | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a myofibril being extended beyond its slack length. |
| response to organic cyclic compound | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an organic cyclic compound stimulus. |
| response to oxidative stress | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of oxidative stress, a state often resulting from exposure to high levels of reactive oxygen species, e.g. superoxide anions, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), and hydroxyl radicals. |
17 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P98150 | NFKB2 | Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p100 subunit | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q04861 | NFKB1 | Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p105 subunit | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q6F3J0 | NFKB1 | Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p105 subunit | Canis lupus familiaris (Dog) (Canis familiaris) | SS |
| Q94527 | Rel | Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p110 subunit | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | EV |
| Q99549 | MPHOSPH8 | M-phase phosphoprotein 8 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q8N9B4 | ANKRD42 | Ankyrin repeat domain-containing protein 42 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q6ZVZ8 | ASB18 | Ankyrin repeat and SOCS box protein 18 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q00653 | NFKB2 | Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p100 subunit | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P19838 | NFKB1 | Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p105 subunit | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q04206 | RELA | Transcription factor p65 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q9CZK6 | Anks3 | Ankyrin repeat and SAM domain-containing protein 3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q8VHA6 | Asb18 | Ankyrin repeat and SOCS box protein 18 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q04207 | Rela | Transcription factor p65 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q9WTK5 | Nfkb2 | Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p100 subunit [Cleaved into: Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p52 subunit] | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| Q9TZM3 | lrk-1 | Leucine-rich repeat serine/threonine-protein kinase 1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| O22265 | CAO | Signal recognition particle 43 kDa protein, chloroplastic | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9SZI3 | NPR2 | Regulatory protein NPR2 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MADDDPYGTG | QMFHLNTALT | HSIFNAELYS | PEIPLSTDGP | YLQILEQPKQ | RGFRFRYVCE |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| GPSHGGLPGA | SSEKNKKSYP | QVKICNYVGP | AKVIVQLVTN | GKNIHLHAHS | LVGKHCEDGV |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| CTVTAGPKDM | VVGFANLGIL | HVTKKKVFET | LEARMTEACI | RGYNPGLLVH | SDLAYLQAEG |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| GGDRQLTDRE | KEIIRQAAVQ | QTKEMDLSVV | RLMFTAFLPD | STGSFTRRLE | PVVSDAIYDS |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| KAPNASNLKI | VRMDRTAGCV | TGGEEIYLLC | DKVQKDDIQI | RFYEEEENGG | VWEGFGDFSP |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| TDVHRQFAIV | FKTPKYKDVN | ITKPASVFVQ | LRRKSDLETS | EPKPFLYYPE | IKDKEEVQRK |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| RQKLMPNFSD | SFGGGSGAGA | GGGGMFGSGG | GGGSTGSPGP | GYGYSNYGFP | PYGGITFHPG |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| VTKSNAGVTH | GTINTKFKNG | PKDCAKSDDE | ESLTLPEKET | EGEGPSLPMA | CTKTEPIALA |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| STMEDKEQDM | GFQDNLFLEK | ALQLARRHAN | ALFDYAVTGD | VKMLLAVQRH | LTAVQDENGD |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| SVLHLAIIHL | HAQLVRDLLE | VTSGLISDDI | INMRNDLYQT | PLHLAVITKQ | EDVVEDLLRV |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| GADLSLLDRW | GNSVLHLAAK | EGHDRILSIL | LKSRKAAPLI | DHPNGEGLNA | IHIAVMSNSL |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| PCLLLLVAAG | AEVNAQEQKS | GRTALHLAVE | YDNISLAGCL | LLEGDAHVDS | TTYDGTTPLH |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| IAAGRGSTRL | AALLKAAGAD | PLVENFEPLY | DLDDSWEKAG | EDEGVVPGTT | PLDMAANWQV |
| 790 | 800 | 810 | 820 | 830 | 840 |
| FDILNGKPYE | PVFTSDDILP | QGDMKQLTED | TRLQLCKLLE | IPDPDKNWAT | LAQKLGLGIL |
| 850 | 860 | 870 | 880 | 890 | 900 |
| NNAFRLSPAP | SKTLMDNYEV | SGGTIKELME | ALQQMGYTEA | IEVIQAAFRT | PATTASSPVT |
| 910 | 920 | 930 | 940 | 950 | 960 |
| TAQVHCLPLS | SSSTRQHIDE | LRDSDSVCDS | GVETSFRKLS | FTESLTGDSP | LLSLNKMPHG |
| 970 | |||||
| YGQEGPIEGK | I |