P23625
Gene name |
Galphaq |
Protein name |
G protein alpha q subunit |
Names |
Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(q) subunit alpha, Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-q, dGQalpha |
Species |
Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) |
KEGG Pathway |
dme:Dmel_CG17759 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
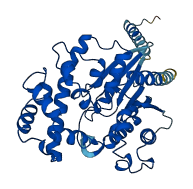
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for P23625
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-P23625-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for P23625
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for P23625 | |||||
No associated diseases with P23625
No regional properties for P23625
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| No domain, repeats, and functional sites for P23625 | |||
4 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| heterotrimeric G-protein complex | Any of a family of heterotrimeric GTP-binding and hydrolyzing proteins; they belong to a superfamily of GTPases that includes monomeric proteins such as EF-Tu and RAS. Heterotrimeric G-proteins consist of three subunits; the alpha subunit contains the guanine nucleotide binding site and possesses GTPase activity; the beta and gamma subunits are tightly associated and function as a beta-gamma heterodimer; extrinsic plasma membrane proteins (cytoplasmic face) that function as a complex to transduce signals from G protein-coupled receptors to an effector protein. |
| inaD signaling complex | A complex of proteins that are involved in phototransduction and attached to the transient receptor potential (TRP) channel. The protein connections are mediated through inaD. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| rhabdomere | The specialized microvilli-containing organelle on the apical surfaces of a photoreceptor cell containing the visual pigment rhodopsin and most of the proteins involved in phototransduction. |
5 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| G protein-coupled receptor binding | Binding to a G protein-coupled receptor. |
| G-protein beta/gamma-subunit complex binding | Binding to a complex of G-protein beta/gamma subunits. |
| GTP binding | Binding to GTP, guanosine triphosphate. |
| GTPase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: GTP + H2O = GDP + H+ + phosphate. |
| metal ion binding | Binding to a metal ion. |
17 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| activation of phospholipase C activity | The initiation of the activity of the inactive enzyme phospolipase C as the result of The series of molecular signals generated as a consequence of a G protein-coupled receptor binding to its physiological ligand. |
| adenylate cyclase-modulating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway | A G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway in which the signal is transmitted via the activation or inhibition of adenylyl cyclase activity and a subsequent change in the intracellular concentration of cyclic AMP (cAMP). |
| axon midline choice point recognition | The recognition of molecules at the central nervous system midline choice point by an axon growth cone; this choice point determines whether the growth cone will cross the midline. |
| cellular response to carbon dioxide | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a carbon dioxide (CO2) stimulus. |
| flight behavior | The response to external or internal stimuli that results in the locomotory process of flight. Flight is the self-propelled movement of an organism through the air. |
| metarhodopsin inactivation | The process in which metarhodopsin is prevented from generating molecular signals. Activated rhodopsin (R*) is inactivated by a two-step process: first, R* is phosphorylated by rhodopsin kinase which lowers the activity of R*. Second, the protein arrestin binds to phosphorylated R* to de-activate it. |
| mucosal immune response | An immune response taking place in mucosal tissues, including those of the intestinal tract, nasal and upper respiratory tract, and genital tract. |
| negative regulation of compound eye retinal cell programmed cell death | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of programmed cell death that occurs in the compound eye retina. |
| neuron cellular homeostasis | The cellular homeostatic process that preserves a neuron in a stable, differentiated functional and structural state. |
| phospholipase C-activating dopamine receptor signaling pathway | A phospholipase C-activating receptor G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway initiated by dopamine binding to its receptor on the surface of a target cell, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| phototransduction | The sequence of reactions within a cell required to convert absorbed photons into a molecular signal. |
| regulation of neuromuscular synaptic transmission | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of neuromuscular synaptic transmission. |
| rhodopsin mediated signaling pathway | A G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway initiated by the excitation of rhodopsin by a photon, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process. |
| sensory perception of smell | The series of events required for an organism to receive an olfactory stimulus, convert it to a molecular signal, and recognize and characterize the signal. Olfaction involves the detection of chemical composition of an organism's ambient medium by chemoreceptors. This is a neurological process. |
| stabilization of membrane potential | The accomplishment of a non-fluctuating membrane potential, the electric potential existing across any membrane arising from charges in the membrane itself and from the charges present in the media on either side of the membrane. |
| thermotaxis | The directed movement of a motile cell or organism in response to a temperature gradient. Movement may be towards either a higher or lower temperature. |
| visual perception | The series of events required for an organism to receive a visual stimulus, convert it to a molecular signal, and recognize and characterize the signal. Visual stimuli are detected in the form of photons and are processed to form an image. |
22 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P38408 | GNA14 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit alpha-14 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| Q28294 | GNAQ | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(q) subunit alpha | Canis lupus familiaris (Dog) (Canis familiaris) | PR |
| P25157 | cta | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit alpha homolog | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| P20353 | Galphai | G protein alpha i subunit | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| P16378 | Galphao | G protein alpha o subunit | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| P50148 | GNAQ | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P29992 | GNA11 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit alpha-11 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| O95837 | GNA14 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit alpha-14 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P30679 | GNA15 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit alpha-15 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P21279 | Gnaq | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(q) subunit alpha | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P30678 | Gna15 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit alpha-15 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q2PKF4 | GNAQ | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(q) subunit alpha | Sus scrofa (Pig) | PR |
| P93564 | GPA1 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-1 subunit | Solanum tuberosum (Potato) | SS |
| Q9JID2 | Gna11 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit alpha-11 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P82471 | Gnaq | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| O88302 | Gna15 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit alpha-15 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q0DJ33 | GPA1 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-1 subunit | Oryza sativa subsp. japonica (Rice) | SS |
| P49084 | GPA1 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-1 subunit | Glycine max (Soybean) (Glycine hispida) | SS |
| P93163 | GPA2 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-2 subunit | Glycine max (Soybean) (Glycine hispida) | SS |
| P18064 | GPA1 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-1 subunit | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| O80462 | XLG1 | Extra-large guanine nucleotide-binding protein 1 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| P26981 | GPA1 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-1 subunit | Solanum lycopersicum (Tomato) (Lycopersicon esculentum) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MECCLSEEAK | EQKRINQEIE | KQLRRDKRDA | RRELKLLLLG | TGESGKSTFI | KQMRIIHGSG |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| YSDEDKRGYI | KLVFQNIFMA | MQSMIKAMDM | LKISYGQGEH | SELADLVMSI | DYETVTTFED |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| PYLNAIKTLW | DDAGIQECYD | RRREYQLTDS | AKYYLSDLAR | IEQADYLPTE | QDILRARVPT |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| TGILEYPFDL | DGIVFRMVDV | GGQRSERRKW | IHCFENVTSI | IFLVALSEYD | QILFESDNEN |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| RMEESKALFR | TIITYPWFQN | SSVILFLNKK | DLLEEKIMYS | HLVDYFPEYD | GPKQDHAAAK |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | |
| QFVLKKYLAC | NPDPERQCYS | HFTTATDTEN | IKLVFCAVKD | TIMQNALKEF | NLG |