P23611
Gene name |
Irf8 |
Protein name |
Interferon regulatory factor 8 |
Names |
IRF-8, Interferon consensus sequence-binding protein, ICSBP |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:15900 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
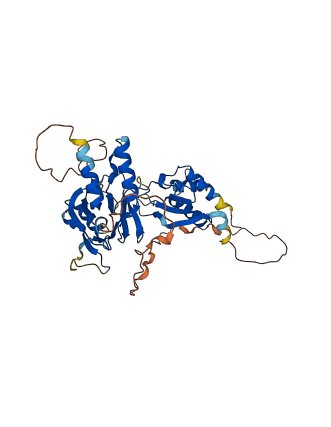
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for P23611
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-P23611-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
23 variants for P23611
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs3389009335 | 15 | I>N | No | EVA | |
| rs3389016295 | 43 | A>T | No | EVA | |
| rs3389014933 | 44 | G>D | No | EVA | |
| rs3389014932 | 47 | D>E | No | EVA | |
| rs3389017566 | 54 | A>G | No | EVA | |
| rs3388991217 | 63 | F>L | No | EVA | |
| rs3399804539 | 120 | C>* | No | EVA | |
| rs3389009324 | 140 | R>L | No | EVA | |
| rs263012755 | 156 | M>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3389021112 | 161 | R>K | No | EVA | |
| rs3389021995 | 237 | P>H | No | EVA | |
| rs3389021142 | 240 | Y>* | No | EVA | |
| rs3388984875 | 248 | V>M | No | EVA | |
| rs3388967228 | 265 | T>N | No | EVA | |
| rs3389010161 | 273 | E>G | No | EVA | |
| rs3389004164 | 313 | R>W | No | EVA | |
| rs3389017329 | 331 | Q>R | No | EVA | |
| rs3389017582 | 339 | L>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3388996842 | 355 | T>N | No | EVA | |
| rs3388991305 | 363 | I>N | No | EVA | |
| rs3388996796 | 387 | S>P | No | EVA | |
| rs3399947097 | 394 | E>A | No | EVA | |
| rs37379799 | 400 | A>T | No | EVA |
No associated diseases with P23611
3 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| nucleoplasm | That part of the nuclear content other than the chromosomes or the nucleolus. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
7 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| DNA binding | Any molecular function by which a gene product interacts selectively and non-covalently with DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). |
| DNA-binding transcription factor activity | A transcription regulator activity that modulates transcription of gene sets via selective and non-covalent binding to a specific double-stranded genomic DNA sequence (sometimes referred to as a motif) within a cis-regulatory region. Regulatory regions include promoters (proximal and distal) and enhancers. Genes are transcriptional units, and include bacterial operons. |
| DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific | A DNA-binding transcription factor activity that modulates the transcription of specific gene sets transcribed by RNA polymerase II. |
| DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific | A DNA-binding transcription factor activity that represses or decreases the transcription of specific gene sets transcribed by RNA polymerase II. |
| RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding | Binding to a specific upstream regulatory DNA sequence (transcription factor recognition sequence or binding site) located in cis relative to the transcription start site (i.e., on the same strand of DNA) of a gene transcribed by RNA polymerase II. |
| RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding | Binding to a specific sequence of DNA that is part of a regulatory region that controls the transcription of a gene or cistron by RNA polymerase II. |
| sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding | Binding to double-stranded DNA of a specific nucleotide composition, e.g. GC-rich DNA binding, or with a specific sequence motif or type of DNA, e.g. promotor binding or rDNA binding. |
22 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| autophagy | The cellular catabolic process in which cells digest parts of their own cytoplasm; allows for both recycling of macromolecular constituents under conditions of cellular stress and remodeling the intracellular structure for cell differentiation. |
| cellular response to interferon-gamma | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an interferon-gamma stimulus. Interferon gamma is the only member of the type II interferon found so far. |
| cellular response to lipopolysaccharide | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a lipopolysaccharide stimulus; lipopolysaccharide is a major component of the cell wall of gram-negative bacteria. |
| defense response to bacterium | Reactions triggered in response to the presence of a bacterium that act to protect the cell or organism. |
| defense response to protozoan | Reactions triggered in response to the presence of a protozoan that act to protect the cell or organism. |
| dendritic cell differentiation | The process in which a precursor cell type acquires the specialized features of a dendritic cell. A dendritic cell is a leukocyte of dendritic lineage specialized in the uptake, processing, and transport of antigens to lymph nodes for the purpose of stimulating an immune response via T cell activation. |
| follicular B cell differentiation | The process in which a B cell in the spleen acquires the specialized features of a follicular B cell. Follicular B cells are major population of mature recirculating B cells in the spleen and are located in the B-cell follicle region. |
| germinal center B cell differentiation | The process in which a B cell in the spleen acquires the specialized features of a germinal center B cell. Germinal center B cells are rapidly cycling B cells which have downregulated IgD expression and exhibit high levels of binding by peanut agglutinin (PNA). |
| immune response | Any immune system process that functions in the calibrated response of an organism to a potential internal or invasive threat. |
| immune system process | Any process involved in the development or functioning of the immune system, an organismal system for calibrated responses to potential internal or invasive threats. |
| myeloid cell differentiation | The process in which a relatively unspecialized myeloid precursor cell acquires the specialized features of any cell of the myeloid leukocyte, megakaryocyte, thrombocyte, or erythrocyte lineages. |
| negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of transcription mediated by RNA polymerase II. |
| phagocytosis | A vesicle-mediated transport process that results in the engulfment of external particulate material by phagocytes and their delivery to the lysosome. The particles are initially contained within phagocytic vacuoles (phagosomes), which then fuse with primary lysosomes to effect digestion of the particles. |
| plasmacytoid dendritic cell differentiation | The process in which a relatively unspecialized hemopoietic precursor cell acquires the specialized features of a plasmacytoid dendritic cell. |
| positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cellular DNA-templated transcription. |
| positive regulation of interferon-gamma production | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of interferon-gamma production. Interferon-gamma is also known as type II interferon. |
| positive regulation of interleukin-12 production | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of interleukin-12 production. |
| positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription from an RNA polymerase II promoter. |
| regulation of DNA-templated transcription | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cellular DNA-templated transcription. |
| regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of transcription mediated by RNA polymerase II. |
| regulation of type I interferon production | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of interferon type I production. Type I interferons include the interferon-alpha, beta, delta, episilon, zeta, kappa, tau, and omega gene families. |
| response to bacterium | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus from a bacterium. |
7 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q90871 | IRF8 | Interferon regulatory factor 8 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | PR |
| Q02556 | IRF8 | Interferon regulatory factor 8 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q61179 | Irf9 | Interferon regulatory factor 9 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P56477 | Irf5 | Interferon regulatory factor 5 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q64287 | Irf4 | Interferon regulatory factor 4 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| P70671 | Irf3 | Interferon regulatory factor 3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P70434 | Irf7 | Interferon regulatory factor 7 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MCDRNGGRRL | RQWLIEQIDS | SMYPGLIWEN | DEKTMFRIPW | KHAGKQDYNQ | EVDASIFKAW |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| AVFKGKFKEG | DKAEPATWKT | RLRCALNKSP | DFEEVTDRSQ | LDISEPYKVY | RIVPEEEQKC |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| KLGVAPAGCM | SEVPEMECGR | SEIEELIKEP | SVDEYMGMTK | RSPSPPEACR | SQILPDWWVQ |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| QPSAGLPLVT | GYAAYDTHHS | AFSQMVISFY | YGGKLVGQAT | TTCLEGCRLS | LSQPGLPKLY |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| GPDGLEPVCF | PTADTIPSER | QRQVTRKLFG | HLERGVLLHS | NRKGVFVKRL | CQGRVFCSGN |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| AVVCKGRPNK | LERDEVVQVF | DTNQFIRELQ | QFYATQSRLP | DSRVVLCFGE | EFPDTVPLRS |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| KLILVQVEQL | YARQLVEEAG | KSCGAGSLMP | ALEEPQPDQA | FRMFPDICTS | HQRPFFRENQ |
| QITV |