P23394
Gene name |
PRP28 (YDR243C, YD8419.10C) |
Protein name |
Pre-mRNA-splicing ATP-dependent RNA helicase PRP28 |
Names |
Helicase CA8 |
Species |
Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) |
KEGG Pathway |
sce:YDR243C |
EC number |
3.6.4.13: Acting on ATP; involved in cellular and subcellular movement |
Protein Class |
|
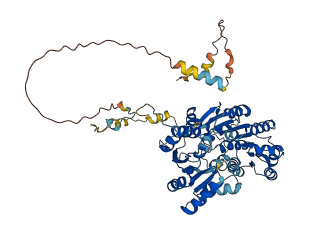
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

3 structures for P23394
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4W7S | X-ray | 254 A | A/B | 127-588 | PDB |
| 5ZWN | EM | 330 A | y | 1-588 | PDB |
| AF-P23394-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
8 variants for P23394
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s04-950115 | 56 | Q>K | No | SGRP | |
| s04-950105 | 59 | S>I | No | SGRP | |
| s04-949923 | 120 | W>R | No | SGRP | |
| s04-949785 | 166 | T>A | No | SGRP | |
| s04-949733 | 183 | D>G | No | SGRP | |
| s04-949446 | 279 | K>E | No | SGRP | |
| s04-948975 | 436 | D>Y | No | SGRP | |
| s04-948674 | 536 | T>S | No | SGRP |
No associated diseases with P23394
4 regional properties for P23394
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| conserved_site | ATP-dependent RNA helicase DEAD-box, conserved site | 265 - 273 | IPR000629 |
| domain | Helicase, C-terminal | 355 - 512 | IPR001650 |
| domain | DEAD/DEAH box helicase domain | 130 - 315 | IPR011545 |
| domain | Helicase superfamily 1/2, ATP-binding domain | 125 - 345 | IPR014001 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 3.6.4.13 | Acting on ATP; involved in cellular and subcellular movement |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
6 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| catalytic step 2 spliceosome | A spliceosomal complex that contains three snRNPs, including U5, bound to a splicing intermediate in which the first catalytic cleavage of the 5' splice site has occurred. The precise subunit composition differs significantly from that of the catalytic step 1, or activated, spliceosome, and includes many proteins in addition to those found in the associated snRNPs. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| spliceosomal complex | Any of a series of ribonucleoprotein complexes that contain snRNA(s) and small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs), and are formed sequentially during the spliceosomal splicing of one or more substrate RNAs, and which also contain the RNA substrate(s) from the initial target RNAs of splicing, the splicing intermediate RNA(s), to the final RNA products. During cis-splicing, the initial target RNA is a single, contiguous RNA transcript, whether mRNA, snoRNA, etc., and the released products are a spliced RNA and an excised intron, generally as a lariat structure. During trans-splicing, there are two initial substrate RNAs, the spliced leader RNA and a pre-mRNA. |
| U4/U6 x U5 tri-snRNP complex | A ribonucleoprotein complex that is formed by the association of the U4/U6 and U5 snRNPs. |
| U5 snRNP | A ribonucleoprotein complex that contains small nuclear RNA U5, a heptameric ring of Sm proteins, as well as several proteins that are unique to the U5 snRNP, most of which remain associated with the U5 snRNA both while the U5 snRNP is free or assembled into a series of spliceosomal complexes. |
5 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| ATP hydrolysis activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + H2O = ADP + H+ phosphate. ATP hydrolysis is used in some reactions as an energy source, for example to catalyze a reaction or drive transport against a concentration gradient. |
| first spliceosomal transesterification activity | Catalysis of the first transesterification reaction of spliceosomal mRNA splicing. The intron branch site adenosine is the nucleophile attacking the 5' splice site, resulting in cleavage at this position. In cis splicing, this is the step that forms a lariat structure of the intron RNA, while it is still joined to the 3' exon. |
| RNA binding | Binding to an RNA molecule or a portion thereof. |
| RNA helicase activity | Unwinding of an RNA helix, driven by ATP hydrolysis. |
2 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| mRNA 5'-splice site recognition | Recognition of the intron 5'-splice site by components of the assembling spliceosome. |
| mRNA splicing, via spliceosome | The joining together of exons from one or more primary transcripts of messenger RNA (mRNA) and the excision of intron sequences, via a spliceosomal mechanism, so that mRNA consisting only of the joined exons is produced. |
4 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q12099 | FAL1 | ATP-dependent RNA helicase FAL1 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) | PR |
| Q07478 | SUB2 | ATP-dependent RNA helicase SUB2 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) | PR |
| P20447 | DBP3 | ATP-dependent RNA helicase DBP3 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) | PR |
| Q9FZ92 | RH44 | Putative DEAD-box ATP-dependent RNA helicase 44 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MARPIDVSQL | IAGINKKKGL | DENTSGKISK | PRFLNKQERS | KQERLKENEE | SLTPTQSDSA |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| KVEIKKVNSR | DDSFFNETND | KKRNPSKQNG | SKFHFSWNES | EDTLSGYDPI | VSTRAIDLLW |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| KGKTPKNAAE | SSYMGKHWTE | KSLHEMNERD | WRILKEDYAI | VTKGGTVENP | LRNWEELNII |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| PRDLLRVIIQ | ELRFPSPTPI | QRITIPNVCN | MKQYRDFLGV | ASTGSGKTLA | FVIPILIKMS |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| RSPPRPPSLK | IIDGPKALIL | APTRELVQQI | QKETQKVTKI | WSKESNYDCK | VISIVGGHSL |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| EEISFSLSEG | CDILVATPGR | LIDSLENHLL | VMKQVETLVL | DEADKMIDLG | FEDQVTNILT |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| KVDINADSAV | NRQTLMFTAT | MTPVIEKIAA | GYMQKPVYAT | IGVETGSEPL | IQQVVEYADN |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| DEDKFKKLKP | IVAKYDPPII | IFINYKQTAD | WLAEKFQKET | NMKVTILHGS | KSQEQREHSL |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| QLFRTNKVQI | MIATNVAARG | LDIPNVSLVV | NFQISKKMDD | YIHRIGRTGR | AANEGTAVSF |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | ||
| VSAAEDESLI | RELYKYVRKH | DPLNSNIFSE | AVKNKYNVGK | QLSNEIIY |