P22543
Gene name |
VPS34 (END12, PEP15, VPL7, VPT29) |
Protein name |
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase VPS34 |
Names |
PI3-kinase VPS34, PI3K VPS34, PtdIns-3-kinase VPS34, Carboxypeptidase Y-deficient protein 15, Vacuolar protein sorting-associated protein 34, Vacuolar protein-targeting protein 29 |
Species |
Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) |
KEGG Pathway |
sce:YLR240W |
EC number |
2.7.1.137: Phosphotransferases with an alcohol group as acceptor |
Protein Class |
|
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
749-768 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
593-872 (Phosphatidylinositol 3-/4-kinase, catalytic domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
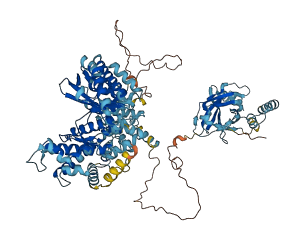
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

3 structures for P22543
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5DFZ | X-ray | 440 A | C | 1-875 | PDB |
| 5KC2 | EM | 2800 A | C | 1-875 | PDB |
| AF-P22543-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
3 variants for P22543
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s12-618201 | 223 | M>L | No | SGRP | |
| s12-618563 | 343 | K>N | No | SGRP | |
| s12-619264 | 577 | R>Q | No | SGRP |
No associated diseases with P22543
5 regional properties for P22543
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Phosphatidylinositol 3-/4-kinase, catalytic domain | 593 - 872 | IPR000403 |
| domain | Phosphoinositide 3-kinase, accessory (PIK) domain | 293 - 535 | IPR001263 |
| domain | C2 phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-type domain | 14 - 188 | IPR002420 |
| conserved_site | Phosphatidylinositol 3/4-kinase, conserved site | 623 - 637 | IPR018936-1 |
| conserved_site | Phosphatidylinositol 3/4-kinase, conserved site | 716 - 736 | IPR018936-2 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.1.137 | Phosphotransferases with an alcohol group as acceptor |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
13 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| endosome | A vacuole to which materials ingested by endocytosis are delivered. |
| endosome membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding an endosome. |
| fungal-type vacuole membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding a vacuole, the shape of which correlates with cell cycle phase. The membrane separates its contents from the cytoplasm of the cell. An example of this structure is found in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. |
| Golgi membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding any of the compartments of the Golgi apparatus. |
| membrane | A lipid bilayer along with all the proteins and protein complexes embedded in it an attached to it. |
| nucleus-vacuole junction | An organelle membrane contact site formed between the vacuole membrane and the outer nuclear membrane. In S. cerevisiae these contacts are mediated through direct physical interaction between Vac8p and Nvj1p. |
| peroxisome | A small organelle enclosed by a single membrane, and found in most eukaryotic cells. Contains peroxidases and other enzymes involved in a variety of metabolic processes including free radical detoxification, lipid catabolism and biosynthesis, and hydrogen peroxide metabolism. |
| phagophore assembly site | Punctate structures proximal to the endoplasmic reticulum which are the sites where the Atg machinery assembles upon autophagy induction. |
| phagophore assembly site membrane | A cellular membrane associated with the phagophore assembly site. |
| phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase complex, class III, type I | A class III phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase complex that is involved in autophagy. In budding yeast, this complex consists of Vps30p, Vps34p, Apg14p and Vps15p. |
| phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase complex, class III, type II | A class III phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase complex that is involved in vacuolar protein sorting (VPS) via endosomes. In budding yeast, this complex consists of Vps30p, Vps34p, Vps38 and Vps15p. |
4 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| 1-phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: 1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol + ATP = a 1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol 3-phosphate + ADP + 2 H(+). |
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| phosphatidylinositol kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + a phosphatidylinositol = ADP + a phosphatidylinositol phosphate. |
| protein kinase activity | Catalysis of the phosphorylation of an amino acid residue in a protein, usually according to the reaction: a protein + ATP = a phosphoprotein + ADP. |
14 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| autophagosome assembly | The formation of a double membrane-bounded structure, the autophagosome, that occurs when a specialized membrane sac, called the isolation membrane, starts to enclose a portion of the cytoplasm. |
| autophagy | The cellular catabolic process in which cells digest parts of their own cytoplasm; allows for both recycling of macromolecular constituents under conditions of cellular stress and remodeling the intracellular structure for cell differentiation. |
| autophagy of peroxisome | The process in which peroxisomes are delivered to a type of vacuole and degraded in response to changing nutrient conditions. |
| endocytosis | A vesicle-mediated transport process in which cells take up external materials or membrane constituents by the invagination of a small region of the plasma membrane to form a new membrane-bounded vesicle. |
| late endosome to vacuole transport | The directed movement of substances from late endosomes to the vacuole. In yeast, after transport to the prevacuolar compartment, endocytic content is delivered to the late endosome and on to the vacuole. This pathway is analogous to endosome to lysosome transport. |
| macroautophagy | The major inducible pathway for the general turnover of cytoplasmic constituents in eukaryotic cells, it is also responsible for the degradation of active cytoplasmic enzymes and organelles during nutrient starvation. Macroautophagy involves the formation of double-membrane-bounded autophagosomes which enclose the cytoplasmic constituent targeted for degradation in a membrane-bounded structure. Autophagosomes then fuse with a lysosome (or vacuole) releasing single-membrane-bounded autophagic bodies that are then degraded within the lysosome (or vacuole). Some types of macroautophagy, e.g. pexophagy, mitophagy, involve selective targeting of the targets to be degraded. |
| phosphatidylinositol phosphate biosynthetic process | The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of phosphatidylinositol phosphate. |
| phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate biosynthetic process | The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate, a phosphatidylinositol monophosphate carrying the phosphate group at the 3-position. |
| phosphatidylinositol-mediated signaling | The series of molecular signals in which a cell uses a phosphatidylinositol-mediated signaling to convert a signal into a response. Phosphatidylinositols include phosphatidylinositol (PtdIns) and its phosphorylated derivatives. |
| phosphorylation | The process of introducing a phosphate group into a molecule, usually with the formation of a phosphoric ester, a phosphoric anhydride or a phosphoric amide. |
| positive regulation of macroautophagy | Any process, such as recognition of nutrient depletion, that activates or increases the rate of macroautophagy to bring cytosolic macromolecules to the vacuole/lysosome for degradation. |
| positive regulation of transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription elongation, the extension of an RNA molecule after transcription initiation and promoter clearance by the addition of ribonucleotides, catalyzed by RNA polymerase II. |
| protein transport | The directed movement of proteins into, out of or within a cell, or between cells, by means of some agent such as a transporter or pore. |
| regulation of protein localization by the Cvt pathway | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of protein localization by the Cvt pathway. |
1 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P39104 | PIK1 | Phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase PIK1 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MSLNNITFCV | SQDLDVPLKV | KIKSLEGHKP | LLKPSQKILN | PELMLIGSNV | FPSSDLIVSL |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| QVFDKERNRN | LTLPIYTPYI | PFRNSRTWDY | WLTLPIRIKQ | LTFSSHLRII | LWEYNGSKQI |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| PFFNLETSIF | NLKDCTLKRG | FESLKFRYDV | IDHCEVVTDN | KDQENLNKYF | QGEFTRLPWL |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| DEITISKLRK | QRENRTWPQG | TFVLNLEFPM | LELPVVFIER | EIMNTQMNIP | TLKNNPGLST |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| DLREPNRNDP | QIKISLGDKY | HSTLKFYDPD | QPNNDPIEEK | YRRLERASKN | ANLDKQVKPD |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| IKKRDYLNKI | INYPPGTKLT | AHEKGSIWKY | RYYLMNNKKA | LTKLLQSTNL | REESERVEVL |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| ELMDSWAEID | IDDALELLGS | TFKNLSVRSY | AVNRLKKASD | KELELYLLQL | VEAVCFENLS |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| TFSDKSNSEF | TIVDAVSSQK | LSGDSMLLST | SHANQKLLKS | ISSESETSGT | ESLPIVISPL |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| AEFLIRRALV | NPRLGSFFYW | YLKSESEDKP | YLDQILSSFW | SRLDKKSRNI | LNDQVRLINV |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| LRECCETIKR | LKDTTAKKME | LLVHLLETKV | RPLVKVRPIA | LPLDPDVLIC | DVCPETSKVF |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| KSSLSPLKIT | FKTTLNQPYH | LMFKVGDDLR | QDQLVVQIIS | LMNELLKNEN | VDLKLTPYKI |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| LATGPQEGAI | EFIPNDTLAS | ILSKYHGILG | YLKLHYPDEN | ATLGVQGWVL | DNFVKSCAGY |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| CVITYILGVG | DRHLDNLLVT | PDGHFFHADF | GYILGQDPKP | FPPLMKLPPQ | IIEAFGGAES |
| 790 | 800 | 810 | 820 | 830 | 840 |
| SNYDKFRSYC | FVAYSILRRN | AGLILNLFEL | MKTSNIPDIR | IDPNGAILRV | RERFNLNMSE |
| 850 | 860 | 870 | |||
| EDATVHFQNL | INDSVNALLP | IVIDHLHNLA | QYWRT |