P19812
Gene name |
UBR1 (PTR1, YGR184C, G7168) |
Protein name |
E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase UBR1 |
Names |
N-end-recognizing protein, N-recognin-1, RING-type E3 ubiquitin transferase UBR1 |
Species |
Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) |
KEGG Pathway |
sce:YGR184C |
EC number |
2.3.2.27: Aminoacyltransferases |
Protein Class |
UBIQUITIN LIGASE E3 ALPHA-RELATED (PTHR21497) |
Descriptions
In Saccharomyces cerevisiae, RING domain-containing Ub ligase UBR1 recognizes and binds to proteins bearing specific N-terminal residues that are destabilizing according to the N-end rule, leading to their ubiquitination and subsequent degradation. Binding of dipeptides with destabilizing N-terminal residues to two substrate-binding sites of UBR1 causes dissociation of the C-terminal autoinhibitory domain of UBR1 from its N-terminal region that contains all three substrate-binding sites. This dissociation allows the interaction between UBR1 and CUP9, a transcriptional repressor of the peptide transporter PTR2, thereby accelerating the UBR1-dependent degradation of CUP9 and increasing the cell's capacity to import peptides.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
1-1140 (N-terminal region containing three substrate-binding sites) |
Relief mechanism |
Ligand binding |
Assay |
Deletion assay, Mutagenesis experiment |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
References
- Hu RG et al. (2008) "The N-end rule pathway is a sensor of heme", Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 105, 76-81
- Du F et al. (2002) "Pairs of dipeptides synergistically activate the binding of substrate by ubiquitin ligase through dissociation of its autoinhibitory domain", Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 99, 14110-5
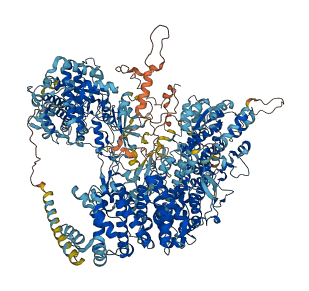
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

13 structures for P19812
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3NIH | X-ray | 210 A | A | 115-194 | PDB |
| 3NII | X-ray | 210 A | A | 115-194 | PDB |
| 3NIJ | X-ray | 210 A | A | 115-194 | PDB |
| 3NIK | X-ray | 185 A | A/B/D/F | 115-194 | PDB |
| 3NIL | X-ray | 175 A | A/B/D/F | 115-194 | PDB |
| 3NIM | X-ray | 200 A | A/B/D/F | 115-194 | PDB |
| 3NIN | X-ray | 210 A | A/B | 115-194 | PDB |
| 3NIS | X-ray | 168 A | A/B/D/F | 115-194 | PDB |
| 3NIT | X-ray | 260 A | A | 107-194 | PDB |
| 6KGI | X-ray | 104 A | B | 113-194 | PDB |
| 7MEX | EM | 335 A | A | 1-1950 | PDB |
| 7MEY | EM | 367 A | A | 1-1950 | PDB |
| AF-P19812-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
40 variants for P19812
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s07-865583 | 59 | S>N | No | SGRP | |
| s07-865523 | 79 | E>G | No | SGRP | |
| s07-865504 | 85 | D>E | No | SGRP | |
| s07-865435 | 108 | D>E | No | SGRP | |
| s07-865099 | 220 | I>M | No | SGRP | |
| s07-864137 | 541 | Q>R | No | SGRP | |
| s07-864006 | 585 | E>K | No | SGRP | |
| s07-863954 | 602 | E>V | No | SGRP | |
| s07-863216 | 848 | R>H | No | SGRP | |
| s07-863214 | 849 | D>N | No | SGRP | |
| s07-863068 | 897 | I>M | No | SGRP | |
| s07-862858 | 967 | L>F | No | SGRP | |
| s07-862620 | 1047 | V>I | No | SGRP | |
| s07-862613 | 1049 | K>R | No | SGRP | |
| s07-862542 | 1073 | I>L | No | SGRP | |
| s07-862496 | 1088 | E>G | No | SGRP | |
| s07-862470 | 1097 | N>H | No | SGRP | |
| s07-862308 | 1151 | D>N | No | SGRP | |
| s07-862076 | 1228 | S>L | No | SGRP | |
| s07-862041 | 1240 | H>Y | No | SGRP | |
| s07-862001 | 1253 | N>S | No | SGRP | |
| s07-861983 | 1259 | W>L | No | SGRP | |
| s07-861915 | 1282 | E>K | No | SGRP | |
| s07-861810 | 1317 | A>T | No | SGRP | |
| s07-861720 | 1347 | M>L | No | SGRP | |
| s07-861480 | 1427 | Y>H | No | SGRP | |
| s07-861459 | 1434 | S>G | No | SGRP | |
| s07-861420 | 1447 | V>L | No | SGRP | |
| s07-861392 | 1456 | I>T | No | SGRP | |
| s07-861252 | 1503 | T>A | No | SGRP | |
| s07-861221 | 1513 | F>S | No | SGRP | |
| s07-861195 | 1522 | Q>E | No | SGRP | |
| s07-861047 | 1571 | F>S | No | SGRP | |
| s07-860867 | 1631 | E>G | No | SGRP | |
| s07-860841 | 1640 | T>A | No | SGRP | |
| s07-860826 | 1645 | I>V | No | SGRP | |
| s07-860817 | 1648 | H>Y | No | SGRP | |
| s07-860602 | 1719 | M>I | No | SGRP | |
| s07-860352 | 1803 | V>I | No | SGRP | |
| s07-860140 | 1873 | E>D | No | SGRP |
No associated diseases with P19812
No regional properties for P19812
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| No domain, repeats, and functional sites for P19812 | |||
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.3.2.27 | Aminoacyltransferases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | PTHR21497 | UBIQUITIN LIGASE E3 ALPHA-RELATED |
| PANTHER Subfamily | PTHR21497:SF26 | E3 UBIQUITIN-PROTEIN LIGASE UBR1 |
| PANTHER Protein Class |
ubiquitin-protein ligase
protein modifying enzyme |
|
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
4 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| proteasome regulatory particle, base subcomplex | The subcomplex of the proteasome regulatory particle that directly associates with the proteasome core complex. |
| ubiquitin ligase complex | A protein complex that includes a ubiquitin-protein ligase and enables ubiquitin protein ligase activity. The complex also contains other proteins that may confer substrate specificity on the complex. |
| UBR1-RAD6 ubiquitin ligase complex | A ubiquitin ligase complex consisting of UBR1 and RAD6 components. It polyubiquitinates proteins containing non-acetylated N-terminal residues causing their subsequent degradation by the proteasome as part of the Ac/N-End Rule pathway. It recognizes non-acetylated N-terminal methionine if it is followed by a hydrophobic residue. Additionally, it acts in an N-end rule independent manner as a component of a novel quality control pathway for proteins synthesized on cytosolic ribosomes. |
4 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| proteasome regulatory particle binding | Binding to a proteasome regulatory particle. |
| ubiquitin protein ligase activity | Catalysis of the transfer of ubiquitin to a substrate protein via the reaction X-ubiquitin + S -> X + S-ubiquitin, where X is either an E2 or E3 enzyme, the X-ubiquitin linkage is a thioester bond, and the S-ubiquitin linkage is an amide bond |
| ubiquitin-protein transferase activity | Catalysis of the transfer of ubiquitin from one protein to another via the reaction X-Ub + Y --> Y-Ub + X, where both X-Ub and Y-Ub are covalent linkages. |
| zinc ion binding | Binding to a zinc ion (Zn). |
10 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytoplasm protein quality control by the ubiquitin-proteasome system | The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of misfolded proteins in the cytoplasm, which are targeted to cytoplasmic proteasomes for degradation. |
| mitochondria-associated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process | The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of proteins transported from mitochondria and targeted to cytoplasmic proteasomes for degradation as a response to oxidative stress conditions. |
| protein monoubiquitination | Addition of a single ubiquitin group to a protein. |
| protein polyubiquitination | Addition of multiple ubiquitin groups to a protein, forming a ubiquitin chain. |
| protein ubiquitination | The process in which one or more ubiquitin groups are added to a protein. |
| regulation of dipeptide transport | Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of dipeptide transport. Dipeptide transport is the directed movement of a dipeptide, a combination of two amino acids by means of a peptide (-CO-NH-) link, into, out of or within a cell, or between cells, by means of some agent such as a transporter or pore. |
| ribosome-associated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process | The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of a protein or peptide encoded by an aberrant message and associated with a stalled ribosome. Degradation is initiated by the covalent attachment of a ubiquitin group, or multiple ubiquitin groups, to the ribosome-associated protein. |
| stress-induced homeostatically regulated protein degradation pathway | A stress-inducible protein catabolic pathway that promotes protein quality control by accelerating the degradation of misfolded ER membrane and cytosolic proteins, as well as native proteins. The pathway starts with the activation, by stress, of the Nma111p/Ynm3p serine protease, which cleaves the stress-induced hydrophilin Roq1p, resulting in the generation of a Roq1p cleavage product that selectively interacts with Ubr1p, an E3 ubiquitin ligase. Interaction with the Ubr1p type-1 substrate binding site reprograms the substrate specificity of this ubiquitin ligase resulting in the selective proteasome-mediated degradation of misfolded and native proteins. The pathway ends with degradation of the protein by the cytoplasmic proteasome. Currently, NMA111, ROQ1, UBR1, RAD6, and CDC48 are considered to be involved in this quality control pathway. |
| ubiquitin-dependent ERAD pathway | The series of steps necessary to target endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-resident proteins for degradation by the cytoplasmic proteasome. Begins with recognition of the ER-resident protein, includes retrotranslocation (dislocation) of the protein from the ER to the cytosol, protein ubiquitination necessary for correct substrate transfer, transport of the protein to the proteasome, and ends with degradation of the protein by the cytoplasmic proteasome. |
| ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process via the N-end rule pathway | The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of a protein or peptide covalently tagged with ubiquitin, via the N-end rule pathway. In the N-end rule pathway, destabilizing N-terminal residues (N-degrons) in substrates are recognized by E3 ligases (N-recognins), whereupon the substrates are linked to ubiquitin and then delivered to the proteasome for degradation. |
5 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q9VX91 | Ubr1 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase UBR1 | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | PR |
| Q8IWV7 | UBR1 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase UBR1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q8IWV8 | UBR2 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase UBR2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| O70481 | Ubr1 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase UBR1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| Q6WKZ8 | Ubr2 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase UBR2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MSVADDDLGS | LQGHIRRTLR | SIHNLPYFRY | TRGPTERADM | SRALKEFIYR | YLYFVISNSG |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| ENLPTLFNAH | PKQKLSNPEL | TVFPDSLEDA | VDIDKITSQQ | TIPFYKIDES | RIGDVHKHTG |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| RNCGRKFKIG | EPLYRCHECG | CDDTCVLCIH | CFNPKDHVNH | HVCTDICTEF | TSGICDCGDE |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| EAWNSPLHCK | AEEQENDISE | DPATNADIKE | EDVWNDSVNI | ALVELVLAEV | FDYFIDVFNQ |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| NIEPLPTIQK | DITIKLREMT | QQGKMYERAQ | FLNDLKYEND | YMFDGTTTAK | TSPSNSPEAS |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| PSLAKIDPEN | YTVIIYNDEY | HNYSQATTAL | RQGVPDNVHI | DLLTSRIDGE | GRAMLKCSQD |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| LSSVLGGFFA | VQTNGLSATL | TSWSEYLHQE | TCKYIILWIT | HCLNIPNSSF | QTTFRNMMGK |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| TLCSEYLNAT | ECRDMTPVVE | KYFSNKFDKN | DPYRYIDLSI | LADGNQIPLG | HHKILPESST |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| HSLSPLINDV | ETPTSRTYSN | TRLQHILYFD | NRYWKRLRKD | IQNVIIPTLA | SSNLYKPIFC |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| QQVVEIFNHI | TRSVAYMDRE | PQLTAIRECV | VQLFTCPTNA | KNIFENQSFL | DIVWSIIDIF |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| KEFCKVEGGV | LIWQRVQKSN | LTKSYSISFK | QGLYTVETLL | SKVHDPNIPL | RPKEIISLLT |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| LCKLFNGAWK | IKRKEGEHVL | HEDQNFISYL | EYTTSIYSII | QTAEKVSEKS | KDSIDSKLFL |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| NAIRIISSFL | GNRSLTYKLI | YDSHEVIKFS | VSHERVAFMN | PLQTMLSFLI | EKVSLKDAYE |
| 790 | 800 | 810 | 820 | 830 | 840 |
| ALEDCSDFLK | ISDFSLRSVV | LCSQIDVGFW | VRNGMSVLHQ | ASYYKNNPEL | GSYSRDIHLN |
| 850 | 860 | 870 | 880 | 890 | 900 |
| QLAILWERDD | IPRIIYNILD | RWELLDWFTG | EVDYQHTVYE | DKISFIIQQF | IAFIYQILTE |
| 910 | 920 | 930 | 940 | 950 | 960 |
| RQYFKTFSSL | KDRRMDQIKN | SIIYNLYMKP | LSYSKLLRSV | PDYLTEDTTE | FDEALEEVSV |
| 970 | 980 | 990 | 1000 | 1010 | 1020 |
| FVEPKGLADN | GVFKLKASLY | AKVDPLKLLN | LENEFESSAT | IIKSHLAKDK | DEIAKVVLIP |
| 1030 | 1040 | 1050 | 1060 | 1070 | 1080 |
| QVSIKQLDKD | ALNLGAFTRN | TVFAKVVYKL | LQVCLDMEDS | TFLNELLHLV | HGIFRDDELI |
| 1090 | 1100 | 1110 | 1120 | 1130 | 1140 |
| NGKDSIPEAY | LSKPICNLLL | SIANAKSDVF | SESIVRKADY | LLEKMIMKKP | NELFESLIAS |
| 1150 | 1160 | 1170 | 1180 | 1190 | 1200 |
| FGNQYVNDYK | DKKLRQGVNL | QETEKERKRR | LAKKHQARLL | AKFNNQQTKF | MKEHESEFDE |
| 1210 | 1220 | 1230 | 1240 | 1250 | 1260 |
| QDNDVDMVGE | KVYESEDFTC | ALCQDSSSTD | FFVIPAYHDH | SPIFRPGNIF | NPNEFMPMWD |
| 1270 | 1280 | 1290 | 1300 | 1310 | 1320 |
| GFYNDDEKQA | YIDDDVLEAL | KENGSCGSRK | VFVSCNHHIH | HNCFKRYVQK | KRFSSNAFIC |
| 1330 | 1340 | 1350 | 1360 | 1370 | 1380 |
| PLCQTFSNCT | LPLCQTSKAN | TGLSLDMFLE | SELSLDTLSR | LFKPFTEENY | RTINSIFSLM |
| 1390 | 1400 | 1410 | 1420 | 1430 | 1440 |
| ISQCQGFDKA | VRKRANFSHK | DVSLILSVHW | ANTISMLEIA | SRLEKPYSIS | FFRSREQKYK |
| 1450 | 1460 | 1470 | 1480 | 1490 | 1500 |
| TLKNILVCIM | LFTFVIGKPS | MEFEPYPQQP | DTVWNQNQLF | QYIVRSALFS | PVSLRQTVTE |
| 1510 | 1520 | 1530 | 1540 | 1550 | 1560 |
| ALTTFSRQFL | RDFLQGLSDA | EQVTKLYAKA | SKIGDVLKVS | EQMLFALRTI | SDVRMEGLDS |
| 1570 | 1580 | 1590 | 1600 | 1610 | 1620 |
| ESIIYDLAYT | FLLKSLLPTI | RRCLVFIKVL | HELVKDSENE | TLVINGHEVE | EELEFEDTAE |
| 1630 | 1640 | 1650 | 1660 | 1670 | 1680 |
| FVNKALKMIT | EKESLVDLLT | TQESIVSHPY | LENIPYEYCG | IIKLIDLSKY | LNTYVTQSKE |
| 1690 | 1700 | 1710 | 1720 | 1730 | 1740 |
| IKLREERSQH | MKNADNRLDF | KICLTCGVKV | HLRADRHEMT | KHLNKNCFKP | FGAFLMPNSS |
| 1750 | 1760 | 1770 | 1780 | 1790 | 1800 |
| EVCLHLTQPP | SNIFISAPYL | NSHGEVGRNA | MRRGDLTTLN | LKRYEHLNRL | WINNEIPGYI |
| 1810 | 1820 | 1830 | 1840 | 1850 | 1860 |
| SRVMGDEFRV | TILSNGFLFA | FNREPRPRRI | PPTDEDDEDM | EEGEDGFFTE | GNDEMDVDDE |
| 1870 | 1880 | 1890 | 1900 | 1910 | 1920 |
| TGQAANLFGV | GAEGIAGGGV | RDFFQFFENF | RNTLQPQGNG | DDDAPQNPPP | ILQFLGPQFD |
| 1930 | 1940 | ||||
| GATIIRNTNP | RNLDEDDSDD | NDDSDEREIW |