P18653
Gene name |
Rps6ka1 (Mapkapk1a, Rsk1) |
Protein name |
Ribosomal protein S6 kinase alpha-1 |
Names |
S6K-alpha-1, 90 kDa ribosomal protein S6 kinase 1, p90-RSK 1, p90RSK1, p90S6K, MAP kinase-activated protein kinase 1a, MAPK-activated protein kinase 1a, MAPKAP kinase 1a, MAPKAPK-1a, Ribosomal S6 kinase 1, RSK-1 |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:20111 |
EC number |
2.7.11.1: Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
Protein Class |
|
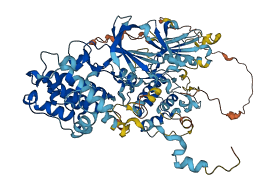
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
407-664 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
PTM |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
204-227 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
66-371 (N-terminal catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, 90 kDa ribosomal protein S6 kinase) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
545-568 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
407-664 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
References
- Li D et al. (2012) "Structural basis for the autoinhibition of the C-terminal kinase domain of human RSK1", Acta crystallographica. Section D, Biological crystallography, 68, 680-5
- Malakhova M et al. (2008) "Structural basis for activation of the autoinhibitory C-terminal kinase domain of p90 RSK2", Nature structural & molecular biology, 15, 112-3
- Poteet-Smith CE et al. (1999) "Generation of constitutively active p90 ribosomal S6 kinase in vivo. Implications for the mitogen-activated protein kinase-activated protein kinase family", The Journal of biological chemistry, 274, 22135-8
- Li D et al. (2013) "The prometastatic ribosomal S6 kinase 2-cAMP response element-binding protein (RSK2-CREB) signaling pathway up-regulates the actin-binding protein fascin-1 to promote tumor metastasis", The Journal of biological chemistry, 288, 32528-32538
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for P18653
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-P18653-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
3 variants for P18653
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs13459957 | 535 | E>* | No | Ensembl | |
| rs221060815 | 616 | T>S | No | Ensembl | |
| rs251507991 | 700 | T>S | No | Ensembl |
No associated diseases with P18653
9 regional properties for P18653
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Protein kinase domain | 62 - 310 | IPR000719-1 |
| domain | Protein kinase domain | 407 - 664 | IPR000719-2 |
| domain | AGC-kinase, C-terminal | 311 - 380 | IPR000961 |
| active_site | Serine/threonine-protein kinase, active site | 183 - 195 | IPR008271-1 |
| active_site | Serine/threonine-protein kinase, active site | 520 - 532 | IPR008271-2 |
| binding_site | Protein kinase, ATP binding site | 68 - 94 | IPR017441-1 |
| binding_site | Protein kinase, ATP binding site | 413 - 436 | IPR017441-2 |
| domain | Protein kinase, C-terminal | 333 - 370 | IPR017892 |
| domain | Ribosomal S6 kinase, N-terminal catalytic domain | 66 - 371 | IPR041906 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.11.1 | Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
5 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| nucleoplasm | That part of the nuclear content other than the chromosomes or the nucleolus. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| spindle | The array of microtubules and associated molecules that forms between opposite poles of a eukaryotic cell during mitosis or meiosis and serves to move the duplicated chromosomes apart. |
9 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| cysteine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity involved in apoptotic process | Binds to and stops, prevents or reduces the activity of a cysteine-type endopeptidase involved in the apoptotic process. |
| DNA-binding transcription factor binding | Binding to a DNA-binding transcription factor, a protein that interacts with a specific DNA sequence (sometimes referred to as a motif) within the regulatory region of a gene to modulate transcription. |
| kinase activity | Catalysis of the transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a substrate molecule. |
| magnesium ion binding | Binding to a magnesium (Mg) ion. |
| protein serine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate. |
| protein serine/threonine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate, and ATP + protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate. |
| protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + a protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate; ATP + a protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate; and ATP + a protein tyrosine = ADP + protein tyrosine phosphate. |
| ribosomal protein S6 kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ribosomal protein S6 + ATP = ribosomal protein S6 phosphate + ATP. |
9 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| hepatocyte proliferation | The multiplication or reproduction of hepatocytes, resulting in the expansion of a cell population. Hepatocytes form the main structural component of the liver. They are specialized epithelial cells that are organized into interconnected plates called lobules. |
| intracellular signal transduction | The process in which a signal is passed on to downstream components within the cell, which become activated themselves to further propagate the signal and finally trigger a change in the function or state of the cell. |
| negative regulation of apoptotic process | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cell death by apoptotic process. |
| negative regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in the apoptotic process. |
| peptidyl-serine phosphorylation | The phosphorylation of peptidyl-serine to form peptidyl-O-phospho-L-serine. |
| positive regulation of hepatic stellate cell activation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of hepatic stellate cell activation. |
| positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription from an RNA polymerase II promoter. |
| positive regulation of transcription, DNA-templated | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cellular DNA-templated transcription. |
| protein phosphorylation | The process of introducing a phosphate group on to a protein. |
19 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q5F3L1 | RPS6KA5 | Ribosomal protein S6 kinase alpha-5 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P18652 | RPS6KA | Ribosomal protein S6 kinase 2 alpha | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q9UK32 | RPS6KA6 | Ribosomal protein S6 kinase alpha-6 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| O75676 | RPS6KA4 | Ribosomal protein S6 kinase alpha-4 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q96S38 | RPS6KC1 | Ribosomal protein S6 kinase delta-1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P51812 | RPS6KA3 | Ribosomal protein S6 kinase alpha-3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q15349 | RPS6KA2 | Ribosomal protein S6 kinase alpha-2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| O75582 | RPS6KA5 | Ribosomal protein S6 kinase alpha-5 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q15418 | RPS6KA1 | Ribosomal protein S6 kinase alpha-1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q8BLK9 | Rps6kc1 | Ribosomal protein S6 kinase delta-1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P18654 | Rps6ka3 | Ribosomal protein S6 kinase alpha-3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q9WUT3 | Rps6ka2 | Ribosomal protein S6 kinase alpha-2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q9Z2B9 | Rps6ka4 | Ribosomal protein S6 kinase alpha-4 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q8C050 | Rps6ka5 | Ribosomal protein S6 kinase alpha-5 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9Z1M4 | Rps6kb2 | Ribosomal protein S6 kinase beta-2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q8BSK8 | Rps6kb1 | Ribosomal protein S6 kinase beta-1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q63531 | Rps6ka1 | Ribosomal protein S6 kinase alpha-1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q18846 | rskn-2 | Putative ribosomal protein S6 kinase alpha-2 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| Q21734 | rskn-1 | Putative ribosomal protein S6 kinase alpha-1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MPLAQLKEPW | PLMELVPLDP | ENGQTSGEEA | GLQPSKDEAI | LKEISITHHV | KAGSEKADPS |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| QFELLKVLGQ | GSFGKVFLVR | KVTRPDSGHL | YAMKVLKKAT | LKVRDRVRTK | MERDILADVN |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| HPFVVKLHYA | FQTEGKLYLI | LDFLRGGDLF | TRLSKEVMFT | EEDVKFYLAE | LALGLDHLHS |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| LGIIYRDLKP | ENILLDEEGH | IKLTDFGLSK | EAIDHEKKAY | SFCGTVEYMA | PEVVNRQGHT |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| HSADWWSYGV | LMGKDRKETM | TLILKAKLGM | PQFLSTEAQS | LLRALFKRNP | ANRLGSGPDG |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| AEEIKRHIFY | STIDWNKLYR | REIKPPFKPA | VAQPDDTFYF | DTEFTSRTPR | DSPGIPPSAG |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| AHQLFRGFSF | VATGLMEDDG | KPRTTQAPLH | SVVQQLHGKN | LVFSDGYVVK | ETIGVGSYSV |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| CKRCVHKATN | MEYAVKVIDK | SKRDPSEEIE | ILLRYGQHPN | IITLKDVYDD | GKHVYLVTEL |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| MRGGELLDKI | LRQKFFSERE | ASFVLHTISK | TVEYLHSQGV | VHRDLKPSNI | LYVDESGNPE |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| CLRICDFGFA | KQLRAENGLL | MTPCYTANFV | APEVLKRQGY | DEGCDIWSLG | ILLYTMLAGY |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| TPFANGPSDT | PEEILTRIGS | GKFTLSGGNW | NTVSETAKDL | VSKMLHVDPH | QRLTAKQVLQ |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| HPWITQKDKL | PQSQLSHQDL | QLVKGAMAAT | YSALNSSKPT | PQLKPIESSI | LAQRRVRKLP |
| STTL |