P18265
Gene name |
Gsk3a |
Protein name |
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 alpha |
Names |
GSK-3 alpha, Factor A, FA, Serine/threonine-protein kinase GSK3A |
Species |
Rattus norvegicus (Rat) |
KEGG Pathway |
rno:50686 |
EC number |
2.7.11.1: Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
Protein Class |
|
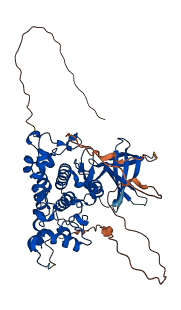
Descriptions
(Annotation based on sequence homology with P49841)
Glycogen synthase kinase 3-beta (GSK3B) is a Ser/Thr protein kinase with key roles in transduction of regulatory and proliferative signals. When the N-terminal peptide is phosphorylated (Ser 9), it autoinhibits GSK-3 by acting as a pseudo-substrate that blocks binding of other substrates. Unique to GSK-3, the binding is associated with a drastic conformational rearrangement of a highly conserved loop that engages the inhibitory peptides in a clamp-like structure. And it shows dose-dependent inhibition of GSK3B kinase activity. In addition, the deletion of the N-terminal residues increased GSK3B catalytic activity by two folds.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
262-284 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
119-403 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for P18265
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-P18265-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for P18265
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for P18265 | |||||
No associated diseases with P18265
4 regional properties for P18265
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Protein kinase domain | 119 - 403 | IPR000719 |
| active_site | Serine/threonine-protein kinase, active site | 240 - 252 | IPR008271 |
| binding_site | Protein kinase, ATP binding site | 125 - 149 | IPR017441 |
| domain | Glycogen synthase kinase 3, catalytic domain | 114 - 406 | IPR039192 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.11.1 | Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
6 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| axon | The long process of a neuron that conducts nerve impulses, usually away from the cell body to the terminals and varicosities, which are sites of storage and release of neurotransmitter. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| microtubule | Any of the long, generally straight, hollow tubes of internal diameter 12-15 nm and external diameter 24 nm found in a wide variety of eukaryotic cells; each consists (usually) of 13 protofilaments of polymeric tubulin, staggered in such a manner that the tubulin monomers are arranged in a helical pattern on the microtubular surface, and with the alpha/beta axes of the tubulin subunits parallel to the long axis of the tubule; exist in equilibrium with pool of tubulin monomers and can be rapidly assembled or disassembled in response to physiological stimuli; concerned with force generation, e.g. in the spindle. |
| mitochondrion | A semiautonomous, self replicating organelle that occurs in varying numbers, shapes, and sizes in the cytoplasm of virtually all eukaryotic cells. It is notably the site of tissue respiration. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
8 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| protein kinase A catalytic subunit binding | Binding to one or both of the catalytic subunits of protein kinase A. |
| protein kinase activity | Catalysis of the phosphorylation of an amino acid residue in a protein, usually according to the reaction: a protein + ATP = a phosphoprotein + ADP. |
| protein kinase binding | Binding to a protein kinase, any enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a protein substrate. |
| protein serine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate. |
| protein serine/threonine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate, and ATP + protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate. |
| signaling receptor binding | Binding to one or more specific sites on a receptor molecule, a macromolecule that undergoes combination with a hormone, neurotransmitter, drug or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell function. |
| tau-protein kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + tau-protein = ADP + O-phospho-tau-protein. |
46 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| aging | A developmental process that is a deterioration and loss of function over time. Aging includes loss of functions such as resistance to disease, homeostasis, and fertility, as well as wear and tear. Aging includes cellular senescence, but is more inclusive. May precede death and may succeed developmental maturation (GO:0021700). |
| cardiac left ventricle morphogenesis | The process in which the left cardiac ventricle is generated and organized. |
| cell migration | The controlled self-propelled movement of a cell from one site to a destination guided by molecular cues. Cell migration is a central process in the development and maintenance of multicellular organisms. |
| cellular response to glucocorticoid stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a glucocorticoid stimulus. Glucocorticoids are hormonal C21 corticosteroids synthesized from cholesterol with the ability to bind with the cortisol receptor and trigger similar effects. Glucocorticoids act primarily on carbohydrate and protein metabolism, and have anti-inflammatory effects. |
| cellular response to insulin stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an insulin stimulus. Insulin is a polypeptide hormone produced by the islets of Langerhans of the pancreas in mammals, and by the homologous organs of other organisms. |
| cellular response to interleukin-3 | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an interleukin-3 stimulus. |
| cellular response to lithium ion | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a lithium (Li+) ion stimulus. |
| cellular response to organic cyclic compound | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an organic cyclic compound stimulus. |
| extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals in which a signal is conveyed from the cell surface to trigger the apoptotic death of a cell. The pathway starts with either a ligand binding to a cell surface receptor, or a ligand being withdrawn from a cell surface receptor (e.g. in the case of signaling by dependence receptors), and ends when the execution phase of apoptosis is triggered. |
| extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in absence of ligand | The series of molecular signals in which a signal is conveyed from the cell surface to trigger the apoptotic death of a cell. The pathway starts with withdrawal of a ligand from a cell surface receptor, and ends when the execution phase of apoptosis is triggered. |
| glycogen metabolic process | The chemical reactions and pathways involving glycogen, a polydisperse, highly branched glucan composed of chains of D-glucose residues in alpha-(1->4) glycosidic linkage, joined together by alpha-(1->6) glycosidic linkages. |
| hypermethylation of CpG island | An increase in the epigenetic methylation of cytosine and adenosine residues in a CpG island in DNA. CpG islands are genomic regions that contain a high frequency of the CG dinucleotide and are often associated with the transcription start site of genes. |
| insulin receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals generated as a consequence of the insulin receptor binding to insulin. |
| negative regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway | Any process that decreases the rate, frequency, or extent of the Wnt signaling pathway through beta-catenin, the series of molecular signals initiated by binding of a Wnt protein to a frizzled family receptor on the surface of the target cell, followed by propagation of the signal via beta-catenin, and ending with a change in transcription of target genes. |
| negative regulation of cell growth involved in cardiac muscle cell development | Any process that decreases the rate, frequency, or extent of the growth of a cardiac muscle cell, where growth contributes to the progression of the cell over time from its initial formation to its mature state. |
| negative regulation of dendrite development | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of dendrite development. |
| negative regulation of glucose import | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the import of the hexose monosaccharide glucose into a cell or organelle. |
| negative regulation of glycogen synthase activity, transferring glucose-1-phosphate | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of glycogen synthase activity, transferring glucose-1-phosphate. |
| negative regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of insulin receptor signaling. |
| negative regulation of TOR signaling | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of TOR signaling. |
| nervous system development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of nervous tissue over time, from its formation to its mature state. |
| peptidyl-serine phosphorylation | The phosphorylation of peptidyl-serine to form peptidyl-O-phospho-L-serine. |
| peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation | The phosphorylation of peptidyl-threonine to form peptidyl-O-phospho-L-threonine. |
| positive regulation of adenylate cyclase-activating adrenergic receptor signaling pathway | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the adenylate cyclase-activating adrenergic receptor protein signaling pathway. An adrenergic receptor signaling pathway is the series of molecular signals generated as a consequence of an adrenergic receptor binding to one of its physiological ligands. |
| positive regulation of adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of an adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway. |
| positive regulation of amyloid-beta formation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of amyloid-beta formation. |
| positive regulation of autophagy | Any process that activates, maintains or increases the rate of autophagy. Autophagy is the process in which cells digest parts of their own cytoplasm. |
| positive regulation of gene expression | Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product (protein or RNA). |
| positive regulation of glycogen (starch) synthase activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of glycogen (starch) synthase activity. |
| positive regulation of heart contraction | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of heart contraction. |
| positive regulation of mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization involved in apoptotic signaling pathway | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization involved in apoptotic signaling pathway. |
| positive regulation of neuron apoptotic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell death of neurons by apoptotic process. |
| positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the phosphorylation of peptidyl-serine. |
| positive regulation of peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation | Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation. Peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation is the phosphorylation of peptidyl-threonine to form peptidyl-O-phospho-L-threonine. |
| positive regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the breakdown of a protein or peptide by hydrolysis of its peptide bonds, initiated by the covalent attachment of ubiquitin, and mediated by the proteasome. |
| positive regulation of protein targeting to mitochondrion | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of protein targeting to mitochondrion. |
| positive regulation of protein ubiquitination | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the addition of ubiquitin groups to a protein. |
| positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription from an RNA polymerase II promoter. |
| proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process | The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of a protein or peptide by hydrolysis of its peptide bonds, initiated by the covalent attachment of ubiquitin, and mediated by the proteasome. |
| protein phosphorylation | The process of introducing a phosphate group on to a protein. |
| regulation of autophagy of mitochondrion | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of mitochondrion degradation by an autophagic process. |
| regulation of gene expression by genomic imprinting | An epigenetic mechanism of regulation of gene expression in which epigenetic modifications (imprints) are established during gametogenesis. For a given gene to show parentally biased expression, the imprint are established exclusively in one of the two parental genomes, thus generating an asymmetry between the maternal and paternal alleles. |
| regulation of neuron projection development | Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of neuron projection development. Neuron projection development is the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron projection over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A neuron projection is any process extending from a neural cell, such as axons or dendrites (collectively called neurites). |
| regulation of systemic arterial blood pressure | The process that modulates the force with which blood travels through the systemic arterial circulatory system. The process is controlled by a balance of processes that increase pressure and decrease pressure. |
| signal transduction | The cellular process in which a signal is conveyed to trigger a change in the activity or state of a cell. Signal transduction begins with reception of a signal (e.g. a ligand binding to a receptor or receptor activation by a stimulus such as light), or for signal transduction in the absence of ligand, signal-withdrawal or the activity of a constitutively active receptor. Signal transduction ends with regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. regulation of transcription or regulation of a metabolic process. Signal transduction covers signaling from receptors located on the surface of the cell and signaling via molecules located within the cell. For signaling between cells, signal transduction is restricted to events at and within the receiving cell. |
| Wnt signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by binding of a Wnt protein to a frizzled family receptor on the surface of the target cell and ending with a change in cell state. |
11 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P18431 | sgg | Protein kinase shaggy | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| P49841 | GSK3B | Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P49840 | GSK3A | Glycogen synthase kinase-3 alpha | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q80YS9 | Stkld1 | Serine/threonine kinase-like domain-containing protein STKLD1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q2NL51 | Gsk3a | Glycogen synthase kinase-3 alpha | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q9WV60 | Gsk3b | Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| P18266 | Gsk3b | Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q09595 | R03D7.5 | Putative serine/threonine-protein kinase R03D7.5 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| Q9U2Q9 | gsk-3 | Glycogen synthase kinase-3 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| Q39019 | ASK10 | Shaggy-related protein kinase kappa | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9FVS6 | ASK4 | Shaggy-related protein kinase delta | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MSGGGPSGGG | PGGSGRARTS | SFAEPGGGGG | GGGGGPGGSA | SGPGGTGGGK | ASVGAMGGGV |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| GASSSGGGPS | GSGGGGSGGP | GAGTSFPPPG | VKLGRDSGKV | TTVVATLGQG | PERSQEVAYT |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| DIKVIGNGSF | GVVYQARLAE | TRELVAIKKV | LQDKRFKNRE | LQIMRKLDHC | NIVRLRYFFY |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| SSGEKKDELY | LNLVLEYVPE | TVYRVARHFT | KAKLIIPIIY | VKVYMYQLFR | SLAYIHSQGV |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| CHRDIKPQNL | LVDPDTAVLK | LCDFGSAKQL | VRGEPNVSYI | CSRYYRAPEL | IFGATDYTSS |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| IDVWSAGCVL | AELLLGQPIF | PGDSGVDQLV | EIIKVLGTPT | REQIREMNPN | YTEFKFPQIK |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| AHPWTKVFKS | RTPPEAIALC | SSLLEYTPSS | RLSPLEACAH | SFFDELRSLG | TQLPNNRPLP |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| PLFNFSPGEL | SIQPSLNAIL | IPPHLRSPSG | PATLTSSSQA | LTETQTGQDW | QAPDATPTLT |
| NSS |