P17609
Gene name |
ypt2 (SPAC9E9.07c) |
Protein name |
GTP-binding protein ypt2 |
Names |
SEC4 homolog |
Species |
Schizosaccharomyces pombe (strain 972 / ATCC 24843) (Fission yeast) |
KEGG Pathway |
spo:SPAC9E9.07c |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
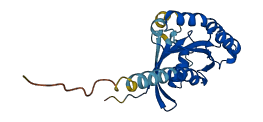
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for P17609
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-P17609-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for P17609
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for P17609 | |||||
No associated diseases with P17609
1 regional properties for P17609
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Small GTP-binding protein domain | 8 - 163 | IPR005225 |
7 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| endosome | A vacuole to which materials ingested by endocytosis are delivered. |
| intracellular membrane-bounded organelle | Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane. |
| meiotic spindle pole body | The microtubule organizing center that forms as part of the meiotic cell cycle; functionally homologous to the animal cell centrosome. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| prospore membrane | The prospore membrane is a double-membraned structure that extends from the cytoplasmic face of the spindle pole bodies to encompass the spindle pole bodies and the four nuclear lobes that are formed during meiosis. It helps isolate the meiotic nuclei from the cytoplasm during spore formation and serves as a foundation for the formation of the spore walls. An example of this component is found in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. |
2 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| GTP binding | Binding to GTP, guanosine triphosphate. |
| GTPase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: GTP + H2O = GDP + H+ + phosphate. |
9 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| exocytosis | A process of secretion by a cell that results in the release of intracellular molecules (e.g. hormones, matrix proteins) contained within a membrane-bounded vesicle. Exocytosis can occur either by full fusion, when the vesicle collapses into the plasma membrane, or by a kiss-and-run mechanism that involves the formation of a transient contact, a pore, between a granule (for exemple of chromaffin cells) and the plasma membrane. The latter process most of the time leads to only partial secretion of the granule content. Exocytosis begins with steps that prepare vesicles for fusion with the membrane (tethering and docking) and ends when molecules are secreted from the cell. |
| Golgi to plasma membrane transport | The directed movement of substances from the Golgi to the plasma membrane in transport vesicles that move from the trans-Golgi network to the plasma membrane, where they fuse and release their contents by exocytosis. |
| intracellular protein transport | The directed movement of proteins in a cell, including the movement of proteins between specific compartments or structures within a cell, such as organelles of a eukaryotic cell. |
| protein localization to plasma membrane | A process in which a protein is transported to, or maintained in, a specific location in the plasma membrane. |
| protein secretion | The controlled release of proteins from a cell. |
| regulation of exocytosis | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of exocytosis. |
| signaling | The entirety of a process in which information is transmitted within a biological system. This process begins with an active signal and ends when a cellular response has been triggered. |
| vesicle docking involved in exocytosis | The initial attachment of a vesicle membrane to a target membrane, mediated by proteins protruding from the membrane of the vesicle and the target membrane, that contributes to exocytosis. |
| vesicle fusion | Fusion of the membrane of a transport vesicle with its target membrane. |
No homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No homologous proteins | ||||
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MSTKSYDYLI | KLLLIGDSGV | GKSCLLLRFS | EDSFTPSFIT | TIGIDFKIRT | IELDGKRIKL |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| QIWDTAGQER | FRTITTAYYR | GAMGILLLYD | VTDKKSFDNV | RTWFSNVEQH | ASENVYKILI |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| GNKCDCEDQR | QVSFEQGQAL | ADELGVKFLE | ASAKTNVNVD | EAFFTLAREI | KKQKIDAENE |
| 190 | |||||
| FSNQANNVDL | GNDRTVKRCC |