P17289
Gene name |
TH |
Protein name |
Tyrosine 3-monooxygenase |
Names |
Tyrosine 3-hydroxylase, TH |
Species |
Bos taurus (Bovine) |
KEGG Pathway |
bta:280707 |
EC number |
1.14.16.2: With reduced pteridine as one donor, and incorporation of one atom of oxygen |
Protein Class |
|
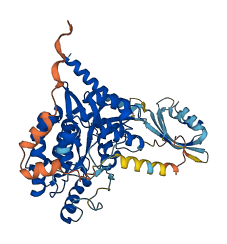
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for P17289
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-P17289-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for P17289
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for P17289 | |||||
No associated diseases with P17289
4 regional properties for P17289
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Aromatic amino acid hydroxylase, C-terminal | 145 - 491 | IPR019774 |
| conserved_site | Tyrosine hydroxylase, conserved site | 2 - 26 | IPR021164-1 |
| conserved_site | Tyrosine hydroxylase, conserved site | 31 - 49 | IPR021164-2 |
| domain | Tyrosine 3-monooxygenase, catalytic domain | 159 - 456 | IPR041903 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 1.14.16.2 | With reduced pteridine as one donor, and incorporation of one atom of oxygen |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
7 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| anchoring junction | A cell junction that mechanically attaches a cell (and its cytoskeleton) to neighboring cells or to the extracellular matrix. |
| axon | The long process of a neuron that conducts nerve impulses, usually away from the cell body to the terminals and varicosities, which are sites of storage and release of neurotransmitter. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| perikaryon | The portion of the cell soma (neuronal cell body) that excludes the nucleus. |
| perinuclear region of cytoplasm | Cytoplasm situated near, or occurring around, the nucleus. |
| synaptic vesicle | A secretory organelle, typically 50 nm in diameter, of presynaptic nerve terminals; accumulates in high concentrations of neurotransmitters and secretes these into the synaptic cleft by fusion with the 'active zone' of the presynaptic plasma membrane. |
2 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| iron ion binding | Binding to an iron (Fe) ion. |
| tyrosine 3-monooxygenase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: L-tyrosine + tetrahydrobiopterin + O2 = 3,4-dihydroxy-L-phenylalanine + 4-alpha-hydroxytetrahydrobiopterin + H2O. |
6 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| dopamine biosynthetic process from tyrosine | The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of dopamine (3,4-dihydroxyphenylethylamine) from L-tyrosine, via the metabolic precursor 3,4-dihydroxy-L-phenylalanine (L-dopa). Dopamine is a catecholamine neurotransmitter and a metabolic precursor of norepinephrine and epinephrine. |
| heart development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the heart over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The heart is a hollow, muscular organ, which, by contracting rhythmically, keeps up the circulation of the blood. |
| hyaloid vascular plexus regression | The developmental process in which the hyaloid vascular plexus is destroyed as a part of its normal progression. |
| neurotransmitter biosynthetic process | The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of any of a group of substances that are released on excitation from the axon terminal of a presynaptic neuron of the central or peripheral nervous system and travel across the synaptic cleft to either excite or inhibit the target cell. |
| response to ethanol | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an ethanol stimulus. |
| response to hypoxia | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating lowered oxygen tension. Hypoxia, defined as a decline in O2 levels below normoxic levels of 20.8 - 20.95%, results in metabolic adaptation at both the cellular and organismal level. |
4 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q2KIH7 | PAH | Phenylalanine-4-hydroxylase | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| P00439 | PAH | Phenylalanine-4-hydroxylase | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P16331 | Pah | Phenylalanine-4-hydroxylase | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P04176 | Pah | Phenylalanine-4-hydroxylase | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | EV |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MPTPNAASPQ | AKGFRRAVSE | LDAKQAEAIM | SPRFVGRRQS | LIQDARKERE | KAEAAASSSE |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| SAEAAAWLER | DGEAVLTLLF | ALPPTRPPAL | TRAIKVFETF | EAHLHHLETR | PAQPLRAGSP |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| PLECFVRCEV | PGPVVPALLS | ALRRVAEDVR | AAGESKVLWF | PRKVSELDKC | HHLVTKFDPD |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| LDLDHPGFSD | QAYRQRRKLI | AEIAFQYKQG | DPIPHVEYTA | EETATWKEVY | STLRGLYPTH |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| ACREHLEAFE | LLERFCGYRE | DRIPQLEDVS | RFLKERTGFQ | LRPAAGLLSA | RDFLASLAFR |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| VFQCTQYIRH | ASSPMHSPEP | ECCHELLGHV | PMLADRTFAQ | FSQDIGLASL | GVSDEEIEKL |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| STLYWFTVEF | GLCKQNGEVK | AYGAGLLSSY | GELLHSLSEE | PEIRAFDPDA | AAVQPYQDQT |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| YQPVYFVSES | FSDAKDKLRS | YASRIQRPFS | VKFDPYTLAI | DVLDSPHAIR | HALDGVQDEM |
| 490 | |||||
| QALAHALNAI | S |