P16092
Gene name |
Fgfr1 (Flg) |
Protein name |
Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 |
Names |
FGFR-1 , bFGF-R-1 , EC 2.7.10.1 , Basic fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 , MFR , Proto-oncogene c-Fgr , CD antigen CD331 |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:14182 |
EC number |
2.7.10.1: Protein-tyrosine kinases |
Protein Class |
|
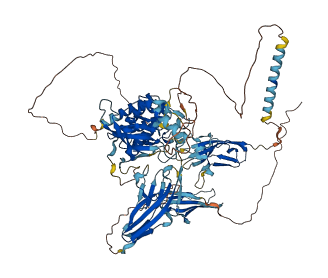
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
478-765 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Ligand binding, PTM |
Assay |
|
Target domain |
478-765 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Ligand binding, PTM |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
640-665 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
464-765 (Catalytic domain of the Protein Tyrosine Kinase, Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 1) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
640-665 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
464-767 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
References
- Yeon JH et al. (2016) "Systems-wide Identification of cis-Regulatory Elements in Proteins", Cell systems, 2, 89-100
- Lew ED et al. (2007) "Structural basis for reduced FGFR2 activity in LADD syndrome: Implications for FGFR autoinhibition and activation", Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 104, 19802-7
- Kalinina J et al. (2012) "The alternatively spliced acid box region plays a key role in FGF receptor autoinhibition", Structure (London, England : 1993), 20, 77-88
- Uchikawa E et al. (2019) "Activation mechanism of the insulin receptor revealed by cryo-EM structure of the fully liganded receptor-ligand complex", eLife, 8,
- Nielsen J et al. (2022) "Structural Investigations of Full-Length Insulin Receptor Dynamics and Signalling", Journal of molecular biology, 434, 167458
- Chen YS et al. (2021) "Insertion of a synthetic switch into insulin provides metabolite-dependent regulation of hormone-receptor activation", Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 118,
- Craddock BP et al. (2007) "Autoinhibition of the insulin-like growth factor I receptor by the juxtamembrane region", FEBS letters, 581, 3235-40
- Klein T et al. (2015) "Structural and dynamic insights into the energetics of activation loop rearrangement in FGFR1 kinase", Nature communications, 6, 7877
- Knowles PP et al. (2006) "Structure and chemical inhibition of the RET tyrosine kinase domain", The Journal of biological chemistry, 281, 33577-87
- Huang X et al. (2009) "Structural insights into the inhibited states of the Mer receptor tyrosine kinase", Journal of structural biology, 165, 88-96
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

2 structures for P16092
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2CKN | NMR | - | A | 25-119 | PDB |
| AF-P16092-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
31 variants for P16092
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs47309288 | 40 | V>A | No | EVA | |
| rs3388959179 | 62 | Q>R | No | EVA | |
| rs3388959161 | 80 | R>H | No | EVA | |
| rs249024346 | 141 | T>A | No | EVA | |
| rs3388970042 | 192 | K>E | No | EVA | |
| rs3388973169 | 233 | E>* | No | EVA | |
| rs3388970063 | 295 | V>M | No | EVA | |
| rs3388970062 | 296 | N>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3388953584 | 306 | P>Q | No | EVA | |
| rs3388976851 | 314 | A>V | No | EVA | |
| rs3388959207 | 319 | T>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3388976788 | 329 | R>Q | No | EVA | |
| rs3388962918 | 345 | N>D | No | EVA | |
| rs3398829139 | 391 | L>VPLFIL* | No | EVA | |
| rs3388962974 | 423 | L>M | No | EVA | |
| rs3388977769 | 477 | R>K | No | EVA | |
| rs3388953549 | 511 | V>L | No | EVA | |
| rs3388977952 | 543 | N>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3388953564 | 564 | A>V | No | EVA | |
| rs3388947175 | 628 | N>K | No | EVA | |
| rs3388977534 | 642 | F>L | No | EVA | |
| rs3388977955 | 653 | Y>F | No | EVA | |
| rs3388930588 | 675 | R>W | No | EVA | |
| rs3388959203 | 686 | F>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3388973164 | 694 | F>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3388969671 | 708 | E>K | No | EVA | |
| rs3399012229 | 737 | W>C | No | EVA | |
| rs3388977476 | 745 | P>L | No | EVA | |
| rs3388969755 | 763 | N>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3388953588 | 778 | P>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3398920766 | 788 | C>G | No | EVA |
No associated diseases with P16092
18 regional properties for P16092
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Protein kinase domain | 478 - 767 | IPR000719 |
| domain | Serine-threonine/tyrosine-protein kinase, catalytic domain | 479 - 754 | IPR001245 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype 2 | 46 - 108 | IPR003598-1 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype 2 | 169 - 237 | IPR003598-2 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype 2 | 268 - 348 | IPR003598-3 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype | 40 - 119 | IPR003599-1 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype | 163 - 248 | IPR003599-2 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype | 262 - 359 | IPR003599-3 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin-like domain | 25 - 119 | IPR007110-1 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin-like domain | 158 - 246 | IPR007110-2 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin-like domain | 255 - 357 | IPR007110-3 |
| active_site | Tyrosine-protein kinase, active site | 619 - 631 | IPR008266 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin I-set | 168 - 247 | IPR013098-1 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin I-set | 262 - 358 | IPR013098-2 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin-like beta-sandwich domain | 42 - 113 | IPR013151 |
| binding_site | Protein kinase, ATP binding site | 484 - 514 | IPR017441 |
| domain | Tyrosine-protein kinase, catalytic domain | 478 - 754 | IPR020635 |
| domain | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1, catalytic domain | 464 - 765 | IPR028174 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.10.1 | Protein-tyrosine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
6 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytoplasmic vesicle | A vesicle found in the cytoplasm of a cell. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| perinuclear region of cytoplasm | Cytoplasm situated near, or occurring around, the nucleus. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| receptor complex | Any protein complex that undergoes combination with a hormone, neurotransmitter, drug or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell function. |
10 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| cell adhesion molecule binding | Binding to a cell adhesion molecule. |
| fibroblast growth factor binding | Binding to a fibroblast growth factor. |
| fibroblast growth factor receptor activity | Combining with a fibroblast growth factor receptor ligand and transmitting the signal across the plasma membrane to initiate a change in cell activity. |
| heparin binding | Binding to heparin, a member of a group of glycosaminoglycans found mainly as an intracellular component of mast cells and which consist predominantly of alternating alpha-(1->4)-linked D-galactose and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine-6-sulfate residues. |
| protein homodimerization activity | Binding to an identical protein to form a homodimer. |
| protein-containing complex binding | Binding to a macromolecular complex. |
| receptor-receptor interaction | The aggregation, arrangement and bonding together of two or more different receptor complexes that individually undergo combination with a hormone, neurotransmitter, drug or intracellular messenger to form a higher level receptor complex. The formation of the higher level complex initiates a change in cell function. |
| SH2 domain binding | Binding to a SH2 domain (Src homology 2) of a protein, a protein domain of about 100 amino-acid residues and belonging to the alpha + beta domain class. |
| signaling receptor binding | Binding to one or more specific sites on a receptor molecule, a macromolecule that undergoes combination with a hormone, neurotransmitter, drug or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell function. |
80 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| angiogenesis | Blood vessel formation when new vessels emerge from the proliferation of pre-existing blood vessels. |
| auditory receptor cell development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an auditory receptor cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate. |
| blood vessel morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structures of blood vessels are generated and organized. The blood vessel is the vasculature carrying blood. |
| brain development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the brain over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Brain development begins with patterning events in the neural tube and ends with the mature structure that is the center of thought and emotion. The brain is responsible for the coordination and control of bodily activities and the interpretation of information from the senses (sight, hearing, smell, etc.). |
| branching involved in salivary gland morphogenesis | The process in which the branching structure of the salivary gland is generated and organized. |
| calcium ion homeostasis | Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady state of calcium ions within an organism or cell. |
| cardiac muscle cell proliferation | The expansion of a cardiac muscle cell population by cell division. |
| cell maturation | The cellular developmental process, independent of morphogenetic (shape) change, that is required for a specific cell to attain its fully functional state. |
| cell population proliferation | The multiplication or reproduction of cells, resulting in the expansion of a cell population. |
| cell projection assembly | Formation of a prolongation or process extending from a cell, e.g. a flagellum or axon. |
| cementum mineralization | The process in which calcium salts, mainly carbonated hydroxyapatite, are deposited into the initial acellular cementum. |
| central nervous system neuron development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron whose cell body is located in the central nervous system, from initial commitment of the cell to a neuronal fate, to the fully functional differentiated neuron. |
| chondrocyte differentiation | The process in which a chondroblast acquires specialized structural and/or functional features of a chondrocyte. A chondrocyte is a polymorphic cell that forms cartilage. |
| diphosphate metabolic process | The chemical reactions and pathways involving diphosphate, the anion or salt of diphosphoric acid. |
| ear development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the ear over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The ear is the sense organ in vertebrates that is specialized for the detection of sound, and the maintenance of balance. Includes the outer ear and middle ear, which collect and transmit sound waves; and the inner ear, which contains the organs of balance and (except in fish) hearing. Also includes the pinna, the visible part of the outer ear, present in some mammals. |
| embryonic limb morphogenesis | The process, occurring in the embryo, by which the anatomical structures of the limb are generated and organized. A limb is an appendage of an animal used for locomotion or grasping. |
| epithelial to mesenchymal transition | A transition where an epithelial cell loses apical/basolateral polarity, severs intercellular adhesive junctions, degrades basement membrane components and becomes a migratory mesenchymal cell. |
| fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals generated as a consequence of a fibroblast growth factor receptor binding to one of its physiological ligands. |
| fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway involved in orbitofrontal cortex development | The series of molecular signals generated as a consequence of a fibroblast growth factor-type receptor binding to one of its physiological ligands, which contributes to the progression of the orbitofrontal cortex over time from its initial formation until its mature state. |
| gene expression | The process in which a gene's sequence is converted into a mature gene product (protein or RNA). This includes the production of an RNA transcript and its processing, translation and maturation for protein-coding genes. |
| generation of neurons | The process in which nerve cells are generated. This includes the production of neuroblasts and their differentiation into neurons. |
| in utero embryonic development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the embryo in the uterus over time, from formation of the zygote in the oviduct, to birth. An example of this process is found in Mus musculus. |
| inner ear morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structures of the inner ear are generated and organized. The inner ear is the structure in vertebrates that contains the organs of balance and hearing. It consists of soft hollow sensory structures (the membranous labyrinth) containing fluid (endolymph) surrounded by fluid (perilymph) and encased in a bony cavity (the bony labyrinth). It consists of two chambers, the sacculus and utriculus, from which arise the cochlea and semicircular canals respectively. |
| lung development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the lung over time, from its formation to the mature structure. In all air-breathing vertebrates the lungs are developed from the ventral wall of the oesophagus as a pouch which divides into two sacs. In amphibians and many reptiles the lungs retain very nearly this primitive sac-like character, but in the higher forms the connection with the esophagus becomes elongated into the windpipe and the inner walls of the sacs become more and more divided, until, in the mammals, the air spaces become minutely divided into tubes ending in small air cells, in the walls of which the blood circulates in a fine network of capillaries. In mammals the lungs are more or less divided into lobes, and each lung occupies a separate cavity in the thorax. |
| lung-associated mesenchyme development | The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a lung-associated mesenchyme from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of lung-associated mesenchyme and ends with the mature structure. Lung-associated mesenchyme is the tissue made up of loosely connected mesenchymal cells in the lung. |
| mesenchymal cell differentiation | The process in which a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a mesenchymal cell. A mesenchymal cell is a loosely associated cell that is part of the connective tissue in an organism. Mesenchymal cells give rise to more mature connective tissue cell types. |
| mesenchymal cell proliferation | The multiplication or reproduction of cells, resulting in the expansion of a mesenchymal cell population. A mesenchymal cell is a cell that normally gives rise to other cells that are organized as three-dimensional masses, rather than sheets. |
| midbrain development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the midbrain over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The midbrain is the middle division of the three primary divisions of the developing chordate brain or the corresponding part of the adult brain (in vertebrates, includes a ventral part containing the cerebral peduncles and a dorsal tectum containing the corpora quadrigemina and that surrounds the aqueduct of Sylvius connecting the third and fourth ventricles). |
| middle ear morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structures of the middle ear are generated and organized. The middle ear is the air-filled cavity within the skull of vertebrates that lies between the outer ear and the inner ear. It is linked to the pharynx (and therefore to outside air) via the Eustachian tube and in mammals contains the three ear ossicles, which transmit auditory vibrations from the outer ear (via the tympanum) to the inner ear (via the oval window). |
| motogenic signaling involved in postnatal olfactory bulb interneuron migration | The signaling that results in the stimulation of cell movement in the rostral migratory stream. |
| negative regulation of fibroblast growth factor production | Any process that decreases the rate, frequency or extent of the appearance of a fibroblast growth factor due to biosynthesis or secretion following a cellular stimulus, resulting in an increase in its intracellular or extracellular levels. |
| negative regulation of gene expression | Any process that decreases the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product (protein or RNA). |
| negative regulation of osteoblast differentiation | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of osteoblast differentiation. |
| negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of transcription mediated by RNA polymerase II. |
| neuron projection development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron projection over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A neuron projection is any process extending from a neural cell, such as axons or dendrites (collectively called neurites). |
| orbitofrontal cortex development | The progression of the orbitofrontal cortex over time from its initial formation until its mature state. The orbitofrontal cortex is a cerebral cortex region located in the frontal lobe. |
| organ induction | The interaction of two or more cells or tissues that causes them to change their fates and specify the development of an organ. |
| outer ear morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structures of the outer ear are generated and organized. The outer ear is the part of the ear external to the tympanum (eardrum). It consists of a tube (the external auditory meatus) that directs sound waves on to the tympanum, and may also include the external pinna, which extends beyond the skull. |
| paraxial mesoderm development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the paraxial mesoderm over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The paraxial mesoderm is the mesoderm located bilaterally adjacent to the notochord and neural tube. |
| peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation | The phosphorylation of peptidyl-tyrosine to form peptidyl-O4'-phospho-L-tyrosine. |
| positive regulation of blood vessel endothelial cell migration | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the migration of the endothelial cells of blood vessels. |
| positive regulation of cardiac muscle cell proliferation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cardiac muscle cell proliferation. |
| positive regulation of cell cycle | Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of progression through the cell cycle. |
| positive regulation of cell differentiation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation. |
| positive regulation of cell population proliferation | Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of cell proliferation. |
| positive regulation of endothelial cell chemotaxis to fibroblast growth factor | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of endothelial cell chemotaxis to fibroblast growth factor. |
| positive regulation of fibroblast migration | Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of fibroblast cell migration. Fibroblast cell migration is accomplished by extension and retraction of a pseudopodium. |
| positive regulation of hepatic stellate cell activation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of hepatic stellate cell activation. |
| positive regulation of MAP kinase activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of MAP kinase activity. |
| positive regulation of MAPKKK cascade by fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals generated as a consequence of a fibroblast growth factor receptor binding to one of its physiological ligands resulting in an increase in the rate or frequency of a MAPKKK cascade. |
| positive regulation of mesenchymal cell proliferation | The process of activating or increasing the rate or extent of mesenchymal cell proliferation. Mesenchymal cells are loosely organized embryonic cells. |
| positive regulation of mitotic cell cycle DNA replication | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of mitotic cell cycle DNA replication. |
| positive regulation of neuron differentiation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of neuron differentiation. |
| positive regulation of neuron projection development | Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of neuron projection development. Neuron projection development is the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron projection over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A neuron projection is any process extending from a neural cell, such as axons or dendrites (collectively called neurites). |
| positive regulation of parathyroid hormone secretion | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of parathyroid hormone secretion. |
| positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B signal transduction | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of protein kinase B signaling, a series of reactions mediated by the intracellular serine/threonine kinase protein kinase B. |
| positive regulation of phospholipase C activity | Any process that increases the rate of phospholipase C activity. |
| positive regulation of stem cell proliferation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of stem cell proliferation. |
| positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription from an RNA polymerase II promoter. |
| positive regulation of vascular endothelial cell proliferation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of vascular endothelial cell proliferation. |
| protein autophosphorylation | The phosphorylation by a protein of one or more of its own amino acid residues (cis-autophosphorylation), or residues on an identical protein (trans-autophosphorylation). |
| regulation of branching involved in salivary gland morphogenesis by mesenchymal-epithelial signaling | Any process that modulates the rate, frequency, or extent of branching involved in salivary gland morphogenesis as a result of signals being generated by the mesenchyme and received and interpreted by the salivary gland epithelium. |
| regulation of cell population proliferation | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell proliferation. |
| regulation of epithelial cell proliferation | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of epithelial cell proliferation. |
| regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in absence of ligand | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in absence of ligand. |
| regulation of gene expression | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product (protein or RNA). |
| regulation of lateral mesodermal cell fate specification | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of lateral mesoderm cell fate specification. |
| regulation of phosphate transport | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of phosphate transport. Phosphate transport is the directed movement of phosphate into, out of or within a cell, or between cells, by means of some agent such as a transporter or pore. |
| regulation of phosphorus metabolic process | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving phosphorus or compounds containing phosphorus. |
| regulation of stem cell proliferation | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of stem cell proliferation. A stem cell is a cell that retains the ability to divide and proliferate throughout life to provide progenitor cells that can differentiate into specialized cells. |
| response to sodium phosphate | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a sodium phosphate stimulus. |
| salivary gland morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structures of the salivary gland are generated and organized. |
| sensory perception of sound | The series of events required for an organism to receive an auditory stimulus, convert it to a molecular signal, and recognize and characterize the signal. Sonic stimuli are detected in the form of vibrations and are processed to form a sound. |
| stem cell differentiation | The process in which a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a stem cell. A stem cell is a cell that retains the ability to divide and proliferate throughout life to provide progenitor cells that can differentiate into specialized cells. |
| stem cell population maintenance | The process by which an organism or tissue maintains a population of stem cells of a single type. This can be achieved by a number of mechanisms |
| stem cell proliferation | The multiplication or reproduction of stem cells, resulting in the expansion of a stem cell population. A stem cell is a cell that retains the ability to divide and proliferate throughout life to provide progenitor cells that can differentiate into specialized cells. |
| ureteric bud development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the ureteric bud over time, from its formation to the mature structure. |
| vasculogenesis involved in coronary vascular morphogenesis | The differentiation of endothelial cells from progenitor cells that contributes to blood vessel development in the heart, and the de novo formation of blood vessels and tubes. |
| ventricular zone neuroblast division | The proliferation of neuroblasts in the ventricular zone of the cerebral cortex. The neuronal progenitors of these cells will migrate radially. |
| vitamin D3 metabolic process | The chemical reactions and pathways involving vitamin D3, (3S,5Z,7E)-9,10-secocholesta-5,7,10(19)-trien-3-ol. |
112 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P43481 | KIT | Mast/stem cell growth factor receptor Kit | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| Q06805 | TIE1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor Tie-1 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| Q06807 | TEK | Angiopoietin-1 receptor | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| Q28889 | KIT | Mast/stem cell growth factor receptor Kit | Felis catus (Cat) (Felis silvestris catus) | SS |
| P13369 | CSF1R | Macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor | Felis catus (Cat) (Felis silvestris catus) | SS |
| Q9PUF6 | PDGFRA | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q08156 | KIT | Mast/stem cell growth factor receptor Kit | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q8QHL3 | FLT1 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P18460 | FGFR3 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P18461 | FGFR2 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P21804 | FGFR1 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q07407 | htl | Fibroblast growth factor receptor homolog 1 | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | PR |
| Q6J9G0 | STYK1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase STYK1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P36888 | FLT3 | Receptor-type tyrosine-protein kinase FLT3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P16234 | PDGFRA | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P09619 | PDGFRB | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P35916 | FLT4 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P35968 | KDR | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P17948 | FLT1 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P07333 | CSF1R | Macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P10721 | KIT | Mast/stem cell growth factor receptor Kit | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P07949 | RET | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase receptor Ret | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P35590 | TIE1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor Tie-1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q02763 | TEK | Angiopoietin-1 receptor | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P21802 | FGFR2 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P22455 | FGFR4 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P22607 | FGFR3 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P11362 | FGFR1 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q91V87 | Fgfrl1 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor-like 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q6J9G1 | Styk1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase STYK1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P35546 | Ret | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase receptor Ret | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q61006 | Musk | Muscle, skeletal receptor tyrosine-protein kinase | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q9Z138 | Ror2 | Tyrosine-protein kinase transmembrane receptor ROR2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q9Z139 | Ror1 | Inactive tyrosine-protein kinase transmembrane receptor ROR1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q62371 | Ddr2 | Discoidin domain-containing receptor 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q03146 | Ddr1 | Epithelial discoidin domain-containing receptor 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P15209 | Ntrk2 | BDNF/NT-3 growth factors receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q3UFB7 | Ntrk1 | High affinity nerve growth factor receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q6VNS1 | Ntrk3 | NT-3 growth factor receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P35917 | Flt4 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P35969 | Flt1 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P35918 | Kdr | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q03145 | Epha2 | Ephrin type-A receptor 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q60750 | Epha1 | Ephrin type-A receptor 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P54761 | Ephb4 | Ephrin type-B receptor 4 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q60629 | Epha5 | Ephrin type-A receptor 5 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P97793 | Alk | ALK tyrosine kinase receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q9WTL4 | Insrr | Insulin receptor-related protein | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q60751 | Igf1r | Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P15208 | Insr | Insulin receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P21803 | Fgfr2 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q03142 | Fgfr4 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q60805 | Mertk | Tyrosine-protein kinase Mer | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q62190 | Mst1r | Macrophage-stimulating protein receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q00993 | Axl | Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor UFO | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P55144 | Tyro3 | Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor TYRO3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P70424 | Erbb2 | Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q61527 | Erbb4 | Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-4 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q61526 | Erbb3 | Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q01279 | Egfr | Epidermal growth factor receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q01887 | Ryk | Tyrosine-protein kinase RYK | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q02858 | Tek | Angiopoietin-1 receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q06806 | Tie1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor Tie-1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P05532 | Kit | Mast/stem cell growth factor receptor Kit | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P05622 | Pdgfrb | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P09581 | Csf1r | Macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P26618 | Pdgfra | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q00342 | Flt3 | Receptor-type tyrosine-protein kinase FLT3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q61851 | Fgfr3 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P16056 | Met | Hepatocyte growth factor receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q2HWD6 | KIT | Mast/stem cell growth factor receptor Kit | Sus scrofa (Pig) | SS |
| Q7TQM3 | Fgfrl1 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor-like 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P53767 | Flt1 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P20786 | Pdgfra | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q91ZT1 | Flt4 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| G3V9H8 | Ret | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase receptor Ret | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q05030 | Pdgfrb | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| O08775 | Kdr | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q498D6 | Fgfr4 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q04589 | Fgfr1 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q17833 | old-1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor old-1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| Q19238 | F09A5.2 | Putative tyrosine-protein kinase F09A5.2 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| P34892 | kin-16 | Receptor-like tyrosine-protein kinase kin-16 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| G5ED65 | ver-1 | Protein ver-1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| Q10656 | egl-15 | Myoblast growth factor receptor egl-15 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| O64556 | At2g19230 | Putative leucine-rich repeat receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At2g19230 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| C0LGI2 | At1g67720 | Probable LRR receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g67720 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q6XAT2 | ERL2 | LRR receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase ERL2 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q3E991 | PRK6 | Pollen receptor-like kinase 6 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q94C77 | At4g34220 | Receptor protein kinase-like protein At4g34220 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q94AG2 | SERK1 | Somatic embryogenesis receptor kinase 1 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q8LPS5 | SERK5 | Somatic embryogenesis receptor kinase 5 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9XIC7 | SERK2 | Somatic embryogenesis receptor kinase 2 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| C0LGJ1 | At1g74360 | Probable LRR receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g74360 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q93ZS4 | NIK3 | Protein NSP-INTERACTING KINASE 3 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| P43298 | TMK1 | Receptor protein kinase TMK1 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9LRP3 | At3g17420 | Probable receptor-like protein kinase At3g17420 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| C0LGQ4 | MDIS2 | Protein MALE DISCOVERER 2 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9LFG1 | At3g53590 | Putative leucine-rich repeat receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At3g53590 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q0WR59 | At5g10020 | Probable inactive receptor kinase At5g10020 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| C0LGX1 | At5g65240 | Probable LRR receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At5g65240 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9FXF2 | RKF1 | Probable LRR receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase RFK1 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q8AXB3 | kdrl | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor kdr-like | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q5GIT4 | kdr | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| O73791 | tek | Angiopoietin-1 receptor | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q8JG38 | fgfr2 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q9I8N6 | csf1r | Macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q90413 | fgfr4 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q9DE49 | pdgfra | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q8JFR5 | kita | Mast/stem cell growth factor receptor kita | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q5MD89 | flt4 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q90Z00 | fgfr1a | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1-A | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MWGWKCLLFW | AVLVTATLCT | ARPAPTLPEQ | AQPWGVPVEV | ESLLVHPGDL | LQLRCRLRDD |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| VQSINWLRDG | VQLVESNRTR | ITGEEVEVRD | SIPADSGLYA | CVTSSPSGSD | TTYFSVNVSD |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| ALPSSEDDDD | DDDSSSEEKE | TDNTKPNRRP | VAPYWTSPEK | MEKKLHAVPA | AKTVKFKCPS |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| SGTPNPTLRW | LKNGKEFKPD | HRIGGYKVRY | ATWSIIMDSV | VPSDKGNYTC | IVENEYGSIN |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| HTYQLDVVER | SPHRPILQAG | LPANKTVALG | SNVEFMCKVY | SDPQPHIQWL | KHIEVNGSKI |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| GPDNLPYVQI | LKTAGVNTTD | KEMEVLHLRN | VSFEDAGEYT | CLAGNSIGLS | HHSAWLTVLE |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| ALEERPAVMT | SPLYLEIIIY | CTGAFLISCM | LGSVIIYKMK | SGTKKSDFHS | QMAVHKLAKS |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| IPLRRQVTVS | ADSSASMNSG | VLLVRPSRLS | SSGTPMLAGV | SEYELPEDPR | WELPRDRLVL |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| GKPLGEGCFG | QVVLAEAIGL | DKDKPNRVTK | VAVKMLKSDA | TEKDLSDLIS | EMEMMKMIGK |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| HKNIINLLGA | CTQDGPLYVI | VEYASKGNLR | EYLQARRPPG | LEYCYNPSHN | PEEQLSSKDL |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| VSCAYQVARG | MEYLASKKCI | HRDLAARNVL | VTEDNVMKIA | DFGLARDIHH | IDYYKKTTNG |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| RLPVKWMAPE | ALFDRIYTHQ | SDVWSFGVLL | WEIFTLGGSP | YPGVPVEELF | KLLKEGHRMD |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| KPSNCTNELY | MMMRDCWHAV | PSQRPTFKQL | VEDLDRIVAL | TSNQEYLDLS | IPLDQYSPSF |
| 790 | 800 | 810 | 820 | ||
| PDTRSSTCSS | GEDSVFSHEP | LPEEPCLPRH | PTQLANSGLK | RR |