P15442
Gene name |
GCN2 |
Protein name |
eIF-2-alpha kinase GCN2 |
Names |
General control non-derepressible protein 2, Serine/threonine-protein kinase GCN2 |
Species |
Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) |
KEGG Pathway |
sce:YDR283C |
EC number |
2.7.11.1: Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
Protein Class |
EUKARYOTIC TRANSLATION INITIATION FACTOR 2-ALPHA KINASE EIF2-ALPHA KINASE -RELATED (PTHR11042) |
Descriptions
GCN2 is an activator of the general amino acid control (GAAC) pathway initiated for adaptation to nutrient starvation via phosphorylation of the α subunit of eukaryotic initiation factor-2 (eIF-2). The binding region of substrate eIF2 is prevented by binding of the C-terminus to the PK domain, and possibly also by HisRS-N-PK (protein kinase) interaction. Under starvation conditions, uncharged tRNA binds to GCN2 producing conformational changes in both domains that are transmitted to the PK domain, consequently releasing the substrate-binding cleft in the PK domain and allows eIF2 binding and phosphorylation.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
750-999 (PK domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Ligand binding |
Assay |
Mutagenesis experiment, Structural analysis |
Accessory elements
852-889 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
599-981 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
References
- Zhu S et al. (1996) "Histidyl-tRNA synthetase-related sequences in GCN2 protein kinase regulate in vitro phosphorylation of eIF-2", The Journal of biological chemistry, 271, 24989-94
- Wek SA et al. (1995) "The histidyl-tRNA synthetase-related sequence in the eIF-2 alpha protein kinase GCN2 interacts with tRNA and is required for activation in response to starvation for different amino acids", Molecular and cellular biology, 15, 4497-506
- Qiu H et al. (2001) "The tRNA-binding moiety in GCN2 contains a dimerization domain that interacts with the kinase domain and is required for tRNA binding and kinase activation", The EMBO journal, 20, 1425-38
- Padyana AK et al. (2005) "Structural basis for autoinhibition and mutational activation of eukaryotic initiation factor 2alpha protein kinase GCN2", The Journal of biological chemistry, 280, 29289-99
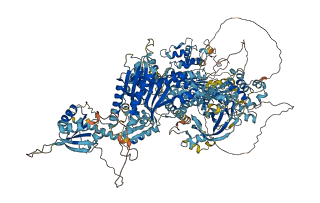
Autoinhibited structure
Activated structure
8 structures for P15442
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1ZXE | X-ray | 260 A | A/B/C/D/E/F | 594-997 | PDB |
| 1ZY4 | X-ray | 195 A | A/B | 594-997 | PDB |
| 1ZY5 | X-ray | 200 A | A/B | 594-997 | PDB |
| 1ZYC | X-ray | 300 A | A/B/C/D | 594-997 | PDB |
| 1ZYD | X-ray | 275 A | A/B | 594-997 | PDB |
| 2YZ0 | NMR | - | A | 1-138 | PDB |
| 4OTM | X-ray | 195 A | A/B | 1519-1659 | PDB |
| AF-P15442-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
13 variants for P15442
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s04-1029985 | 21 | A>T | No | SGRP | |
| s04-1029697 | 117 | I>V | No | SGRP | |
| s04-1029304 | 248 | I>V | No | SGRP | |
| s04-1029099 | 316 | A>V | No | SGRP | |
| s04-1029094 | 318 | H>Y | No | SGRP | |
| s04-1028505 | 514 | K>R | No | SGRP | |
| s04-1028046 | 667 | S>N | No | SGRP | |
| s04-1027792 | 752 | Q>E | No | SGRP | |
| s04-1027227 | 940 | I>T | No | SGRP | |
| s04-1026532 | 1172 | K>E | No | SGRP | |
| s04-1025934 | 1371 | N>S | No | SGRP | |
| s04-1025319 | 1576 | N>S | No | SGRP | |
| s04-1025191 | 1619 | T>A | No | SGRP |
No associated diseases with P15442
7 regional properties for P15442
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Protein kinase domain | 256 - 527 | IPR000719-1 |
| domain | Protein kinase domain | 599 - 981 | IPR000719-2 |
| domain | RWD domain | 13 - 128 | IPR006575 |
| active_site | Serine/threonine-protein kinase, active site | 831 - 843 | IPR008271 |
| binding_site | Protein kinase, ATP binding site | 605 - 629 | IPR017441 |
| domain | Histidyl tRNA synthetase-related domain | 1387 - 1657 | IPR024435 |
| domain | Class II Histidinyl-tRNA synthetase (HisRS)-like catalytic core domain | 1038 - 1362 | IPR041715 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.11.1 | Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | PTHR11042 | EUKARYOTIC TRANSLATION INITIATION FACTOR 2-ALPHA KINASE EIF2-ALPHA KINASE -RELATED |
| PANTHER Subfamily | PTHR11042:SF136 | EUKARYOTIC TRANSLATION INITIATION FACTOR 2-ALPHA KINASE 1 |
| PANTHER Protein Class |
non-receptor serine/threonine protein kinase
protein modifying enzyme |
|
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
5 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| cytosolic ribosome | A ribosome located in the cytosol. |
| large ribosomal subunit | The larger of the two subunits of a ribosome. Two sites on the ribosomal large subunit are involved in translation, namely the aminoacyl site (A site) and peptidyl site (P site). |
| polysomal ribosome | A ribosome bound to mRNA that forms part of a polysome. |
| small ribosomal subunit | The smaller of the two subunits of a ribosome. |
13 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| double-stranded RNA binding | Binding to double-stranded RNA. |
| eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2alpha kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP |
| protein homodimerization activity | +Binding to an identical protein to form a homodimer. |
| protein kinase activity | Catalysis of the phosphorylation of an amino acid residue in a protein, usually according to the reaction: a protein + ATP = a phosphoprotein + ADP. |
| protein kinase inhibitor activity | Binds to and stops, prevents or reduces the activity of a protein kinase, an enzyme which phosphorylates a protein. |
| protein self-association | Binding to a domain within the same polypeptide. |
| protein serine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate. |
| protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + a protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate; ATP + a protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate; and ATP + a protein tyrosine = ADP + protein tyrosine phosphate. |
| ribosomal large subunit binding | Binding to a large ribosomal subunit. |
| ribosome binding | Binding to a ribosome. |
| translation initiation factor binding | Binding to a translation initiation factor, any polypeptide factor involved in the initiation of ribosome-mediated translation. |
| tRNA binding | Binding to a transfer RNA. |
17 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cellular response to amino acid starvation | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of deprivation of amino acids. |
| cellular response to benomyl | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a benomyl stimulus. |
| cellular response to histidine | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a histidine stimulus. |
| cellular response to hydrogen peroxide | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) stimulus. |
| cellular stress response to acidic pH | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a disturbance in the homeostasis of organismal or cellular pH (with pH < 7). pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution. |
| DNA damage checkpoint signaling | A signal transduction process that contributes to a DNA damage checkpoint. |
| GCN2-mediated signaling | A series of reactions in which a signal is passed on to downstream proteins within the cell via GCN2 (also known as EIF2AK4), an intracellular protein kinase that is activated by stress signals, such as amino acid starvation. |
| intracellular signal transduction | The process in which a signal is passed on to downstream components within the cell, which become activated themselves to further propagate the signal and finally trigger a change in the function or state of the cell. |
| negative regulation of protein kinase activity by protein phosphorylation | Any protein phosphorylation process that negatively regulates protein kinase activity. |
| negative regulation of TORC1 signaling | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of TORC1 signaling. |
| positive regulation of cellular response to amino acid starvation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cellular response to amino acid starvation. |
| positive regulation of macroautophagy | Any process, such as recognition of nutrient depletion, that activates or increases the rate of macroautophagy to bring cytosolic macromolecules to the vacuole/lysosome for degradation. |
| positive regulation of translational initiation in response to starvation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of translation initiation, as a result of deprivation of nourishment. |
| protein autophosphorylation | The phosphorylation by a protein of one or more of its own amino acid residues (cis-autophosphorylation), or residues on an identical protein (trans-autophosphorylation). |
| protein phosphorylation | The process of introducing a phosphate group on to a protein. |
| regulation of translational initiation | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of translational initiation. |
| translation | The cellular metabolic process in which a protein is formed, using the sequence of a mature mRNA or circRNA molecule to specify the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain. Translation is mediated by the ribosome, and begins with the formation of a ternary complex between aminoacylated initiator methionine tRNA, GTP, and initiation factor 2, which subsequently associates with the small subunit of the ribosome and an mRNA or circRNA. Translation ends with the release of a polypeptide chain from the ribosome. |
4 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P32944 | SWE1 | Mitosis inhibitor protein kinase SWE1 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) | PR |
| Q9P2K8 | EIF2AK4 | eIF-2-alpha kinase GCN2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q9QZ05 | Eif2ak4 | eIF-2-alpha kinase GCN2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV SS |
| D4A7V9 | Eif2ak4 | eIF-2-alpha kinase GCN2 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MSLSHLTLDQ | YYEIQCNELE | AIRSIYMDDF | TDLTKRKSSW | DKQPQIIFEI | TLRSVDKEPV |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| ESSITLHFAM | TPMYPYTAPE | IEFKNVQNVM | DSQLQMLKSE | FKKIHNTSRG | QEIIFEITSF |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| TQEKLDEFQN | VVNTQSLEDD | RLQRIKETKE | QLEKEEREKQ | QETIKKRSDE | QRRIDEIVQR |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| ELEKRQDDDD | DLLFNRTTQL | DLQPPSEWVA | SGEAIVFSKT | IKAKLPNNSM | FKFKAVVNPK |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| PIKLTSDIFS | FSKQFLVKPY | IPPESPLADF | LMSSEMMENF | YYLLSEIELD | NSYFNTSNGK |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| KEIANLEKEL | ETVLKAKHDN | VNRLFGYTVE | RMGRNNATFV | WKIRLLTEYC | NYYPLGDLIQ |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| SVGFVNLATA | RIWMIRLLEG | LEAIHKLGIV | HKCINLETVI | LVKDADFGST | IPKLVHSTYG |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| YTVLNMLSRY | PNKNGSSVEL | SPSTWIAPEL | LKFNNAKPQR | LTDIWQLGVL | FIQIISGSDI |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| VMNFETPQEF | LDSTSMDETL | YDLLSKMLNN | DPKKRLGTLE | LLPMKFLRTN | IDSTINRFNL |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| VSESVNSNSL | ELTPGDTITV | RGNGGRTLSQ | SSIRRRSFNV | GSRFSSINPA | TRSRYASDFE |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| EIAVLGQGAF | GQVVKARNAL | DSRYYAIKKI | RHTEEKLSTI | LSEVMLLASL | NHQYVVRYYA |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| AWLEEDSMDE | NVFESTDEES | DLSESSSDFE | ENDLLDQSSI | FKNRTNHDLD | NSNWDFISGS |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| GYPDIVFENS | SRDDENEDLD | HDTSSTSSSE | SQDDTDKESK | SIQNVPRRRN | FVKPMTAVKK |
| 790 | 800 | 810 | 820 | 830 | 840 |
| KSTLFIQMEY | CENRTLYDLI | HSENLNQQRD | EYWRLFRQIL | EALSYIHSQG | IIHRDLKPMN |
| 850 | 860 | 870 | 880 | 890 | 900 |
| IFIDESRNVK | IGDFGLAKNV | HRSLDILKLD | SQNLPGSSDN | LTSAIGTAMY | VATEVLDGTG |
| 910 | 920 | 930 | 940 | 950 | 960 |
| HYNEKIDMYS | LGIIFFEMIY | PFSTGMERVN | ILKKLRSVSI | EFPPDFDDNK | MKVEKKIIRL |
| 970 | 980 | 990 | 1000 | 1010 | 1020 |
| LIDHDPNKRP | GARTLLNSGW | LPVKHQDEVI | KEALKSLSNP | SSPWQQQVRE | SLFNQSYSLT |
| 1030 | 1040 | 1050 | 1060 | 1070 | 1080 |
| NDILFDNSVP | TSTPFANILR | SQMTEEVVKI | FRKHGGIENN | APPRIFPKAP | IYGTQNVYEV |
| 1090 | 1100 | 1110 | 1120 | 1130 | 1140 |
| LDKGGTVLQL | QYDLTYPMAR | YLSKNPSLIS | KQYRMQHVYR | PPDHSRSSLE | PRKFGEIDFD |
| 1150 | 1160 | 1170 | 1180 | 1190 | 1200 |
| IISKSSSESG | FYDAESLKII | DEILTVFPVF | EKTNTFFILN | HADILESVFN | FTNIDKAQRP |
| 1210 | 1220 | 1230 | 1240 | 1250 | 1260 |
| LVSRMLSQVG | FARSFKEVKN | ELKAQLNISS | TALNDLELFD | FRLDFEAAKK | RLYKLMIDSP |
| 1270 | 1280 | 1290 | 1300 | 1310 | 1320 |
| HLKKIEDSLS | HISKVLSYLK | PLEVARNVVI | SPLSNYNSAF | YKGGIMFHAV | YDDGSSRNMI |
| 1330 | 1340 | 1350 | 1360 | 1370 | 1380 |
| AAGGRYDTLI | SFFARPSGKK | SSNTRKAVGF | NLAWETIFGI | AQNYFKLASG | NRIKKRNRFL |
| 1390 | 1400 | 1410 | 1420 | 1430 | 1440 |
| KDTAVDWKPS | RCDVLISSFS | NSLLDTIGVT | ILNTLWKQNI | KADMLRDCSS | VDDVVTGAQQ |
| 1450 | 1460 | 1470 | 1480 | 1490 | 1500 |
| DGIDWILLIK | QQAYPLTNHK | RKYKPLKIKK | LSTNVDIDLD | LDEFLTLYQQ | ETGNKSLIND |
| 1510 | 1520 | 1530 | 1540 | 1550 | 1560 |
| SLTLGDKADE | FKRWDENSSA | GSSQEGDIDD | VVAGSTNNQK | VIYVPNMATR | SKKANKREKW |
| 1570 | 1580 | 1590 | 1600 | 1610 | 1620 |
| VYEDAARNSS | NMILHNLSNA | PIITVDALRD | ETLEIISITS | LAQKEEWLRK | VFGSGNNSTP |
| 1630 | 1640 | 1650 | |||
| RSFATSIYNN | LSKEAHKGNR | WAILYCHKTG | KSSVIDLQR |