P14772
Gene name |
BPT1 (YLL015W, L1313) |
Protein name |
Bile pigment transporter 1 |
Names |
|
Species |
Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) |
KEGG Pathway |
sce:YLL015W |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
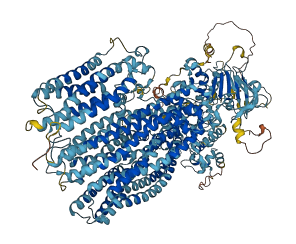
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for P14772
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-P14772-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
32 variants for P14772
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s12-116598 | 56 | N>K | No | SGRP | |
| s12-116612 | 61 | R>I | No | SGRP | |
| s12-116635 | 69 | P>S | No | SGRP | |
| s12-116934 | 168 | E>D | No | SGRP | |
| s12-116959 | 177 | T>A | No | SGRP | |
| s12-117243 | 271 | L>F | No | SGRP | |
| s12-117390 | 320 | L>F | No | SGRP | |
| s12-117589 | 387 | E>K | No | SGRP | |
| s12-117706 | 426 | T>A | No | SGRP | |
| s12-118242 | 604 | D>E | No | SGRP | |
| s12-118321 | 631 | T>A | No | SGRP | |
| s12-118336 | 636 | G>R | No | SGRP | |
| s12-118517 | 696 | R>K | No | SGRP | |
| s12-118639 | 737 | D>N | No | SGRP | |
| s12-118657 | 743 | I>V | No | SGRP | |
| s12-118664 | 745 | A>V | No | SGRP | |
| s12-118864 | 812 | V>I | No | SGRP | |
| s12-118975 | 849 | I>V | No | SGRP | |
| s12-118984 | 852 | Q>K | No | SGRP | |
| s12-119011 | 861 | R>G | No | SGRP | |
| s12-119099 | 890 | E>G | No | SGRP | |
| s12-119170 | 914 | V>I | No | SGRP | |
| s12-119275 | 949 | K>Q | No | SGRP | |
| s12-119290 | 954 | K>E | No | SGRP | |
| s12-119329 | 967 | I>V | No | SGRP | |
| s12-119422 | 998 | N>D | No | SGRP | |
| s12-119509 | 1027 | I>L | No | SGRP | |
| s12-120194 | 1255 | W>* | No | SGRP | |
| s12-120215 | 1262 | T>M | No | SGRP | |
| s12-120271 | 1281 | P>S | No | SGRP | |
| s12-120325 | 1299 | K>E | No | SGRP | |
| s12-120493 | 1355 | P>A | No | SGRP |
No associated diseases with P14772
3 regional properties for P14772
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| conserved_site | 14-3-3 protein, conserved site | 43 - 53 | IPR023409-1 |
| conserved_site | 14-3-3 protein, conserved site | 216 - 235 | IPR023409-2 |
| domain | 14-3-3 domain | 5 - 247 | IPR023410 |
5 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| endoplasmic reticulum | The irregular network of unit membranes, visible only by electron microscopy, that occurs in the cytoplasm of many eukaryotic cells. The membranes form a complex meshwork of tubular channels, which are often expanded into slitlike cavities called cisternae. The ER takes two forms, rough (or granular), with ribosomes adhering to the outer surface, and smooth (with no ribosomes attached). |
| fungal-type vacuole | A vacuole that has both lytic and storage functions. The fungal vacuole is a large, membrane-bounded organelle that functions as a reservoir for the storage of small molecules (including polyphosphate, amino acids, several divalent cations (e.g. calcium), other ions, and other small molecules) as well as being the primary compartment for degradation. It is an acidic compartment, containing an ensemble of acid hydrolases. At least in S. cerevisiae, there are indications that the morphology of the vacuole is variable and correlated with the cell cycle, with logarithmically growing cells having a multilobed, reticulated vacuole, while stationary phase cells contain a single large structure. |
| fungal-type vacuole membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding a vacuole, the shape of which correlates with cell cycle phase. The membrane separates its contents from the cytoplasm of the cell. An example of this structure is found in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. |
| integral component of membrane | The component of a membrane consisting of the gene products and protein complexes having at least some part of their peptide sequence embedded in the hydrophobic region of the membrane. |
| membrane | A lipid bilayer along with all the proteins and protein complexes embedded in it an attached to it. |
5 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ABC-type peptide transporter activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + H2O + peptide(in) = ADP + phosphate + peptide(out). Peptides exported include alpha-hemolysin, cyclolysin, colicin V and siderophores from Gram-negative bacteria, and bacteriocin, subtilin, competence factor and pediocin from Gram-positive bacteria. |
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| ATPase-coupled transmembrane transporter activity | Primary active transporter of a solute across a membrane, via the reaction: ATP + H2O = ADP + phosphate, to directly drive the transport of a substance across a membrane. The transport protein may be transiently phosphorylated (P-type transporters), or not (ABC-type transporters and other families of transporters). Primary active transport occurs up the solute's concentration gradient and is driven by a primary energy source. |
| bilirubin transmembrane transporter activity | Enables the transfer of bilirubin from one side of a membrane to the other. Bilirubin is a linear tetrapyrrole produced in the reticuloendothelial system from biliverdin and transported to the liver as a complex with serum albumin. In the liver, bilirubin is converted to bilirubin bisglucuronide, which is excreted in the bile. |
| cadmium ion transmembrane transporter activity | Enables the transfer of cadmium (Cd) ions from one side of a membrane to the other. |
4 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| bilirubin transport | The directed movement of bilirubin into, out of or within a cell, or between cells, by means of some agent such as a transporter or pore. |
| cadmium ion transport | The directed movement of cadmium (Cd) ions into, out of or within a cell, or between cells, by means of some agent such as a transporter or pore. |
| transmembrane transport | The process in which a solute is transported across a lipid bilayer, from one side of a membrane to the other. |
| vacuole fusion, non-autophagic | The fusion of two vacuole membranes to form a single vacuole. |
13 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P38735 | VMR1 | ABC transporter ATP-binding protein/permease VMR1 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) | PR |
| P0CE68 | NFT1 | ABC transporter NFT1 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) | PR |
| Q8HXQ5 | ABCC1 | Multidrug resistance-associated protein 1 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| Q6UR05 | ABCC1 | Multidrug resistance-associated protein 1 | Canis lupus familiaris (Dog) (Canis familiaris) | PR |
| Q92887 | ABCC2 | ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| O15438 | ABCC3 | ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| O95255 | ABCC6 | ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 6 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P33527 | ABCC1 | Multidrug resistance-associated protein 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q8VI47 | Abcc2 | ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| B2RX12 | Abcc3 | ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| O35379 | Abcc1 | Multidrug resistance-associated protein 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q63120 | Abcc2 | ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 2 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | EV |
| Q8CG09 | Abcc1 | Multidrug resistance-associated protein 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MSSLEVVDGC | PYGYRPYPDS | GTNALNPCFI | SVISAWQAVF | FLLIGSYQLW | KLYKNNKVPP |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| RFKNFPTLPS | KINSRHLTHL | TNVCFQSTLI | ICELALVSQS | SDRVYPFILK | KALYLNLLFN |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| LGISLPTQYL | AYFKSTFSMG | NQLFYYMFQI | LLQLFLILQR | YYHGSSNERL | TVISGQTAMI |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| LEVLLLFNSV | AIFIYDLCIF | EPINELSEYY | KKNGWYPPVH | VLSYITFIWM | NKLIVETYRN |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| KKIKDPNQLP | LPPVDLNIKS | ISKEFKANWE | LEKWLNRNSL | WRAIWKSFGR | TISVAMLYET |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| TSDLLSVVQP | QFLRIFIDGL | NPETSSKYPP | LNGVFIALTL | FVISVVSVFL | TNQFYIGIFE |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| AGLGIRGSLA | SLVYQKSLRL | TLAERNEKST | GDILNLMSVD | VLRIQRFFEN | AQTIIGAPIQ |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| IIVVLTSLYW | LLGKAVIGGL | VTMAIMMPIN | AFLSRKVKKL | SKTQMKYKDM | RIKTITELLN |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| AIKSIKLYAW | EEPMMARLNH | VRNDMELKNF | RKIGIVSNLI | YFAWNCVPLM | VTCSTFGLFS |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| LFSDSPLSPA | IVFPSLSLFN | ILNSAIYSVP | SMINTIIETS | VSMERLKSFL | LSDEIDDSFI |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| ERIDPSADER | ALPAIEMNNI | TFLWKSKEVL | TSSQSGDNLR | TDEESIIGSS | QIALKNIDHF |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| EAKRGDLVCV | VGRVGAGKST | FLKAILGQLP | CMSGSRDSIP | PKLIIRSSSV | AYCSQESWIM |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| NASVRENILF | GHKFDQDYYD | LTIKACQLLP | DLKILPDGDE | TLVGEKGISL | SGGQKARLSL |
| 790 | 800 | 810 | 820 | 830 | 840 |
| ARAVYSRADI | YLLDDILSAV | DAEVSKNIIE | YVLIGKTALL | KNKTIILTTN | TVSILKHSQM |
| 850 | 860 | 870 | 880 | 890 | 900 |
| IYALENGEIV | EQGNYEDVMN | RKNNTSKLKK | LLEEFDSPID | NGNESDVQTE | HRSESEVDEP |
| 910 | 920 | 930 | 940 | 950 | 960 |
| LQLKVTESET | EDEVVTESEL | ELIKANSRRA | SLATLRPRPF | VGAQLDSVKK | TAQKAEKTEV |
| 970 | 980 | 990 | 1000 | 1010 | 1020 |
| GRVKTKIYLA | YIKACGVLGV | VLFFLFMILT | RVFDLAENFW | LKYWSESNEK | NGSNERVWMF |
| 1030 | 1040 | 1050 | 1060 | 1070 | 1080 |
| VGVYSLIGVA | SAAFNNLRSI | MMLLYCSIRG | SKKLHESMAK | SVIRSPMTFF | ETTPVGRIIN |
| 1090 | 1100 | 1110 | 1120 | 1130 | 1140 |
| RFSSDMDAVD | SNLQYIFSFF | FKSILTYLVT | VILVGYNMPW | FLVFNMFLVV | IYIYYQTFYI |
| 1150 | 1160 | 1170 | 1180 | 1190 | 1200 |
| VLSRELKRLI | SISYSPIMSL | MSESLNGYSI | IDAYDHFERF | IYLNYEKIQY | NVDFVFNFRS |
| 1210 | 1220 | 1230 | 1240 | 1250 | 1260 |
| TNRWLSVRLQ | TIGATIVLAT | AILALATMNT | KRQLSSGMVG | LLMSYSLEVT | GSLTWIVRTT |
| 1270 | 1280 | 1290 | 1300 | 1310 | 1320 |
| VTIETNIVSV | ERIVEYCELP | PEAQSINPEK | RPDENWPSKG | GIEFKNYSTK | YRENLDPVLN |
| 1330 | 1340 | 1350 | 1360 | 1370 | 1380 |
| NINVKIEPCE | KVGIVGRTGA | GKSTLSLALF | RILEPTEGKI | IIDGIDISDI | GLFDLRSHLA |
| 1390 | 1400 | 1410 | 1420 | 1430 | 1440 |
| IIPQDAQAFE | GTVKTNLDPF | NRYSEDELKR | AVEQAHLKPH | LEKMLHSKPR | GDDSNEEDGN |
| 1450 | 1460 | 1470 | 1480 | 1490 | 1500 |
| VNDILDVKIN | ENGSNLSVGQ | RQLLCLARAL | LNRSKILVLD | EATASVDMET | DKIIQDTIRR |
| 1510 | 1520 | 1530 | 1540 | 1550 | |
| EFKDRTILTI | AHRIDTVLDS | DKIIVLDQGS | VREFDSPSKL | LSDKTSIFYS | LCEKGGYLK |