P14681
Gene name |
KSS1 (YGR040W) |
Protein name |
Mitogen-activated protein kinase KSS1 |
Names |
MAP kinase KSS1 , EC 2.7.11.24 , Kinase suppressor of SST2 |
Species |
Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) |
KEGG Pathway |
sce:YGR040W |
EC number |
2.7.11.24: Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
Protein Class |
|
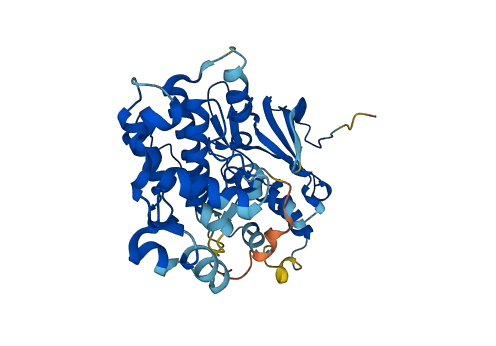
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
13-313 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
PTM |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
References
- Yeon JH et al. (2016) "Systems-wide Identification of cis-Regulatory Elements in Proteins", Cell systems, 2, 89-100
- Emrick MA et al. (2006) "The gatekeeper residue controls autoactivation of ERK2 via a pathway of intramolecular connectivity", Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 103, 18101-6
- Emrick MA et al. (2001) "Constitutive activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2 by synergistic point mutations", The Journal of biological chemistry, 276, 46469-79
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for P14681
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-P14681-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
2 variants for P14681
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s07-576033 | 211 | S>* | No | SGRP | |
| s07-576469 | 356 | K>N | No | SGRP |
No associated diseases with P14681
4 regional properties for P14681
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Protein kinase domain | 13 - 313 | IPR000719 |
| conserved_site | Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase, conserved site | 47 - 155 | IPR003527 |
| active_site | Serine/threonine-protein kinase, active site | 139 - 151 | IPR008271 |
| binding_site | Protein kinase, ATP binding site | 19 - 43 | IPR017441 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.11.24 | Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
4 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cellular bud neck | The constriction between the mother cell and daughter cell (bud) in an organism that reproduces by budding. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| periplasmic space | The region between the inner (cytoplasmic) and outer membrane (Gram-negative Bacteria) or cytoplasmic membrane and cell wall (Fungi and Gram-positive Bacteria). |
5 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| MAP kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction |
| protein kinase activity | Catalysis of the phosphorylation of an amino acid residue in a protein, usually according to the reaction |
| protein serine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions |
| protein serine/threonine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions |
7 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cell cycle | The progression of biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur in a cell during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events. Canonically, the cell cycle comprises the replication and segregation of genetic material followed by the division of the cell, but in endocycles or syncytial cells nuclear replication or nuclear division may not be followed by cell division. |
| intracellular signal transduction | The process in which a signal is passed on to downstream components within the cell, which become activated themselves to further propagate the signal and finally trigger a change in the function or state of the cell. |
| invasive growth in response to glucose limitation | A growth pattern exhibited by budding haploid cells under certain growth conditions, in which cells retain the typical axial budding pattern of haploids, but become elongated and fail to separate after division; during growth on a solid substrate, this results in penetration of cells into the agar medium. An example of this process is found in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. |
| pheromone-dependent signal transduction involved in conjugation with cellular fusion | A signal transduction process resulting in the relay, amplification or dampening of a signal generated in response to pheromone exposure in organisms that undergo conjugation with cellular fusion. An example of this process is found in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. |
| phosphorylation | The process of introducing a phosphate group into a molecule, usually with the formation of a phosphoric ester, a phosphoric anhydride or a phosphoric amide. |
| positive regulation of division septum assembly | Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of division septum formation. division septum formation is the assembly and arrangement of a septum that spans the plasma membrane interface between progeny cells following cytokinesis. |
| signal transduction involved in filamentous growth | Relaying of environmental signals promoting filamentous growth. |
32 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P16892 | FUS3 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase FUS3 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) | SS |
| P41808 | SMK1 | Sporulation-specific mitogen-activated protein kinase SMK1 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) | PR |
| Q00772 | SLT2 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase SLT2/MPK1 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) | PR |
| P32485 | HOG1 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase HOG1 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) | PR |
| P46196 | MAPK1 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| Q5F3W3 | MAPK6 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 6 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P40417 | rl | Mitogen-activated protein kinase ERK-A | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| P31152 | MAPK4 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 4 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q16659 | MAPK6 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 6 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P28482 | MAPK1 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P27361 | MAPK3 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q6P5G0 | Mapk4 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 4 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q61532 | Mapk6 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 6 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P63085 | Mapk1 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q63844 | Mapk3 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P27704 | Mapk6 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 6 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P63086 | Mapk1 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P21708 | Mapk3 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 3 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q63454 | Mapk4 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 4 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q336X9 | MPK6 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 6 | Oryza sativa subsp. japonica (Rice) | SS |
| Q5J4W4 | MPK2 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 2 | Oryza sativa subsp. japonica (Rice) | SS |
| Q84UI5 | MPK1 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 | Oryza sativa subsp. japonica (Rice) | SS |
| Q10N20 | MPK5 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 5 | Oryza sativa subsp. japonica (Rice) | SS |
| P39745 | mpk-1 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase mpk-1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| Q39023 | MPK3 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 3 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| Q39026 | MPK6 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 6 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| Q39025 | MPK5 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 5 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| Q8GYQ5 | MPK12 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 12 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| Q9LMM5 | MPK11 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 11 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| Q39024 | MPK4 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 4 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| Q9LQQ9 | MPK13 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 13 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| Q9M1Z5 | MPK10 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 10 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MARTITFDIP | SQYKLVDLIG | EGAYGTVCSA | IHKPSGIKVA | IKKIQPFSKK | LFVTRTIREI |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| KLLRYFHEHE | NIISILDKVR | PVSIDKLNAV | YLVEELMETD | LQKVINNQNS | GFSTLSDDHV |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| QYFTYQILRA | LKSIHSAQVI | HRDIKPSNLL | LNSNCDLKVC | DFGLARCLAS | SSDSRETLVG |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| FMTEYVATRW | YRAPEIMLTF | QEYTTAMDIW | SCGCILAEMV | SGKPLFPGRD | YHHQLWLILE |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| VLGTPSFEDF | NQIKSKRAKE | YIANLPMRPP | LPWETVWSKT | DLNPDMIDLL | DKMLQFNPDK |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| RISAAEALRH | PYLAMYHDPS | DEPEYPPLNL | DDEFWKLDNK | IMRPEEEEEV | PIEMLKDMLY |
| DELMKTME |