P14646
Gene name |
Pde4b |
Protein name |
cAMP-specific 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase 4B |
Names |
DPDE4 |
Species |
Rattus norvegicus (Rat) |
KEGG Pathway |
rno:24626 |
EC number |
3.1.4.53: Phosphoric diester hydrolases |
Protein Class |
|
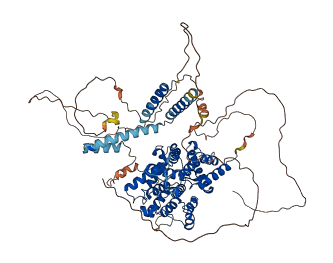
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
330-659 (3'5'-cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase, catalytic domain) |
Relief mechanism |
PTM |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
References
- Houslay MD et al. (2010) "Putting the lid on phosphodiesterase 4", Nature biotechnology, 28, 38-40
- Burgin AB et al. (2010) "Design of phosphodiesterase 4D (PDE4D) allosteric modulators for enhancing cognition with improved safety", Nature biotechnology, 28, 63-70
- Beard MB et al. (2000) "UCR1 and UCR2 domains unique to the cAMP-specific phosphodiesterase family form a discrete module via electrostatic interactions", The Journal of biological chemistry, 275, 10349-58
- Zoraghi R et al. (2005) "Structural and functional features in human PDE5A1 regulatory domain that provide for allosteric cGMP binding, dimerization, and regulation", The Journal of biological chemistry, 280, 12051-63
- Francis SH et al. (2011) "Mammalian cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases: molecular mechanisms and physiological functions", Physiological reviews, 91, 651-90
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for P14646
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-P14646-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for P14646
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for P14646 | |||||
No associated diseases with P14646
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 3.1.4.53 | Phosphoric diester hydrolases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
14 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cell periphery | The part of a cell encompassing the cell cortex, the plasma membrane, and any external encapsulating structures. |
| centrosome | A structure comprised of a core structure (in most organisms, a pair of centrioles) and peripheral material from which a microtubule-based structure, such as a spindle apparatus, is organized. Centrosomes occur close to the nucleus during interphase in many eukaryotic cells, though in animal cells it changes continually during the cell-division cycle. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| dendritic spine | A small, membranous protrusion from a dendrite that forms a postsynaptic compartment, typically receiving input from a single presynapse. They function as partially isolated biochemical and an electrical compartments. Spine morphology is variable:they can be thin, stubby, mushroom, or branched, with a continuum of intermediate morphologies. They typically terminate in a bulb shape, linked to the dendritic shaft by a restriction. Spine remodeling is though to be involved in synaptic plasticity. |
| excitatory synapse | A synapse in which an action potential in the presynaptic cell increases the probability of an action potential occurring in the postsynaptic cell. |
| gamma-tubulin complex | A multiprotein complex composed of gamma-tubulin and other non-tubulin proteins. Gamma-tubulin complexes are localized to microtubule organizing centers, and play an important role in the nucleation of microtubules. The number and complexity of non-tubulin proteins associated with these complexes varies between species. |
| membrane | A lipid bilayer along with all the proteins and protein complexes embedded in it an attached to it. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| perinuclear region of cytoplasm | Cytoplasm situated near, or occurring around, the nucleus. |
| postsynaptic density | An electron dense network of proteins within and adjacent to the postsynaptic membrane of an asymmetric, neuron-neuron synapse. Its major components include neurotransmitter receptors and the proteins that spatially and functionally organize them such as anchoring and scaffolding molecules, signaling enzymes and cytoskeletal components. |
| synaptic vesicle | A secretory organelle, typically 50 nm in diameter, of presynaptic nerve terminals; accumulates in high concentrations of neurotransmitters and secretes these into the synaptic cleft by fusion with the 'active zone' of the presynaptic plasma membrane. |
| voltage-gated calcium channel complex | A protein complex that forms a transmembrane channel through which calcium ions may pass in response to changes in membrane potential. |
| Z disc | Platelike region of a muscle sarcomere to which the plus ends of actin filaments are attached. |
6 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| 3',5'-cyclic-AMP phosphodiesterase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: 3',5'-cyclic AMP + H2O = AMP + H+. |
| 3',5'-cyclic-nucleotide phosphodiesterase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: a nucleoside 3',5'-cyclic phosphate + H2O = a nucleoside 5'-phosphate. |
| cAMP binding | Binding to cAMP, the nucleotide cyclic AMP (adenosine 3',5'-cyclophosphate). |
| gamma-tubulin binding | Binding to the microtubule constituent protein gamma-tubulin. |
| metal ion binding | Binding to a metal ion. |
| transmembrane transporter binding | Binding to a transmembrane transporter, a protein or protein complex that enables the transfer of a substance, usually a specific substance or a group of related substances, from one side of a membrane to the other. |
16 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cAMP catabolic process | The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of the nucleotide cAMP (cyclic AMP, adenosine 3',5'-cyclophosphate). |
| cellular response to epinephrine stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an epinephrine stimulus. Epinephrine is a catecholamine that has the formula C9H13NO3; it is secreted by the adrenal medulla to act as a hormone, and released by certain neurons to act as a neurotransmitter active in the central nervous system. |
| cellular response to lipopolysaccharide | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a lipopolysaccharide stimulus; lipopolysaccharide is a major component of the cell wall of gram-negative bacteria. |
| cellular response to xenobiotic stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus from a xenobiotic, a compound foreign to the organism exposed to it. It may be synthesized by another organism (like ampicilin) or it can be a synthetic chemical. |
| leukocyte migration | The movement of a leukocyte within or between different tissues and organs of the body. |
| negative regulation of adenylate cyclase-activating adrenergic receptor signaling pathway involved in heart process | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of an adenylate cyclase-activating adrenergic receptor signaling pathway involved in some heart process. |
| negative regulation of relaxation of cardiac muscle | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of relaxation of cardiac muscle. |
| neutrophil chemotaxis | The directed movement of a neutrophil cell, the most numerous polymorphonuclear leukocyte found in the blood, in response to an external stimulus, usually an infection or wounding. |
| neutrophil homeostasis | The process of regulating the proliferation and elimination of neutrophils such that the total number of neutrophils within a whole or part of an organism is stable over time in the absence of an outside stimulus. |
| positive regulation of interferon-gamma production | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of interferon-gamma production. Interferon-gamma is also known as type II interferon. |
| positive regulation of interleukin-2 production | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of interleukin-2 production. |
| regulation of cardiac muscle cell contraction | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cardiac muscle cell contraction. |
| regulation of high voltage-gated calcium channel activity | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of high voltage-gated calcium channel activity. |
| response to heat | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a heat stimulus, a temperature stimulus above the optimal temperature for that organism. |
| signal transduction | The cellular process in which a signal is conveyed to trigger a change in the activity or state of a cell. Signal transduction begins with reception of a signal (e.g. a ligand binding to a receptor or receptor activation by a stimulus such as light), or for signal transduction in the absence of ligand, signal-withdrawal or the activity of a constitutively active receptor. Signal transduction ends with regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. regulation of transcription or regulation of a metabolic process. Signal transduction covers signaling from receptors located on the surface of the cell and signaling via molecules located within the cell. For signaling between cells, signal transduction is restricted to events at and within the receiving cell. |
| T cell receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by the cross-linking of an antigen receptor on a T cell. |
32 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q28156 | PDE5A | cGMP-specific 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| P23439 | PDE6B | Rod cGMP-specific 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase subunit beta | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| P52731 | PDE6C | Cone cGMP-specific 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase subunit alpha' | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | PR |
| H2QL32 | PDE9A | High affinity cGMP-specific 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase 9A | Pan troglodytes (Chimpanzee) | PR |
| Q9VJ79 | Pde11 | Dual 3',5'-cyclic-AMP and -GMP phosphodiesterase 11 | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| Q9W4T4 | dnc | 3',5'-cyclic-AMP phosphodiesterase, isoform I | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| Q9HCR9 | PDE11A | Dual 3',5'-cyclic-AMP and -GMP phosphodiesterase 11A | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| O76083 | PDE9A | High affinity cGMP-specific 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase 9A | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q08499 | PDE4D | cAMP-specific 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase 4D | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| O76074 | PDE5A | cGMP-specific 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q08493 | PDE4C | cAMP-specific 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase 4C | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV SS |
| P51160 | PDE6C | Cone cGMP-specific 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase subunit alpha' | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P27815 | PDE4A | cAMP-specific 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase 4A | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV SS |
| P35913 | PDE6B | Rod cGMP-specific 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase subunit beta | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9Y233 | PDE10A | cAMP and cAMP-inhibited cGMP 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase 10A | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q07343 | PDE4B | cAMP-specific 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase 4B | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV SS |
| P23440 | Pde6b | Rod cGMP-specific 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase subunit beta | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| O89084 | Pde4a | 3',5'-cyclic-AMP phosphodiesterase 4A | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| O70628 | Pde9a | High affinity cGMP-specific 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase 9A | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q8CG03 | Pde5a | cGMP-specific 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q8CA95 | Pde10a | cAMP and cAMP-inhibited cGMP 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase 10A | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P0C1Q2 | Pde11a | Dual 3',5'-cyclic-AMP and -GMP phosphodiesterase 11A | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q3UEI1 | Pde4c | cAMP-specific 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase 4C | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q01063 | Pde4d | 3',5'-cyclic-AMP phosphodiesterase 4D | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P54748 | Pde4a | 3',5'-cyclic-AMP phosphodiesterase 4A | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P14270 | Pde4d | cAMP-specific 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase 4D | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q8QZV1 | Pde9a | High affinity cGMP-specific 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase 9A | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q9QYJ6 | Pde10a | cAMP and cAMP-inhibited cGMP 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase 10A | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q8VID6 | Pde11a | Dual 3',5'-cyclic-AMP and -GMP phosphodiesterase 11A | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| O54735 | Pde5a | cGMP-specific 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P14644 | Pde4c | cAMP-specific 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase 4C | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q22000 | pde-4 | Probable 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase pde-4 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MKKSRSVMAV | TADDNLKDYF | ECSLSKSYSS | SSYTLGIDLW | RGRRCCSGNL | QLPPLSQRQS |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| ERARTPEGDG | ISRPTTLPLT | TLPSIAITTV | SQECFDVENG | PSPGRSPLDP | QASSSSGLVL |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| HAAFPGHSQR | RESFLYRSDS | DYDLSPKAMS | RNSSLPSEQH | GDDLIVTPFA | QVLASLRIVR |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| NNFTLLTNLH | GAPNKRSPAA | SQAPVTRVSL | QEESYQKLAM | ETLEELDWCL | DQLETIQTYR |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| SVSEMASNKF | KRMLNRELTH | LSEMSRSGNQ | VSEYISNTFL | DKQNDVEIPS | PTQKDREKKK |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| KQQLMTQISG | VKKLMHSSSL | NNTSISRFGV | NTENEDHLAK | ELEDLNKWGL | NIFNVAGYSH |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| NRPLTCIMYA | IFQERDLLKT | FKISSDTFVT | YMMTLEDHYH | SDVAYHNSLH | AADVAQSTHV |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| LLSTPALDAV | FTDLEILAAI | FAAAIHDVDH | PGVSNQFLIN | TNSELALMYN | DESVLENHHL |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| AVGFKLLQEE | HCDIFQNLTK | KQRQTLRKMV | IDMVLATDMS | KHMSLLADLK | TMVETKKVTS |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| SGVLLLDNYT | DRIQVLRNMV | HCADLSNPTK | SLELYRQWTD | RIMEEFFQQG | DKERERGMEI |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| SPMCDKHTAS | VEKSQVGFID | YIVHPLWETW | ADLVQPDAQD | ILDTLEDNRN | WYQSMIPQSP |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| SPPLDERSRD | CQGLMEKFQF | ELTLEEEDSE | GPEKEGEGPN | YFSSTKTLCV | IDPENRDSLE |
| 730 | |||||
| ETDIDIATED | KSLIDT |