P12931
Gene name |
SRC |
Protein name |
Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src |
Names |
Proto-oncogene c-Src, pp60c-src, p60-Src |
Species |
Homo sapiens (Human) |
KEGG Pathway |
hsa:6714 |
EC number |
2.7.10.2: Protein-tyrosine kinases |
Protein Class |
|
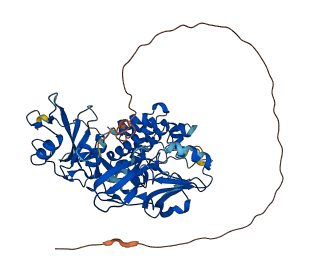
Descriptions
c-Src is a Src family kinase characterized by SH2 and SH3 domains that maintain an inactive conformation through intramolecular interactions. The kinase’s autoinhibition involves the assembly of its regulatory domains and the phosphorylation of Tyr-527, which locks the molecule in an inhibited state. c-Src kinase is maintained in an inactive state through intramolecular interactions of its SH2 and SH3 domains. The autoinhibition is mediated by the assembled regulatory apparatus within the molecule itself, not by intermolecular interactions. The activation loop adopts an inhibitory conformation, blocking the peptide substrate–binding site and preventing Tyr-416 phosphorylation, which is necessary for full catalytic activity. Activation of c-Src requires disassembly of the regulatory domains, induced by SH2 or SH3 ligands, or by dephosphorylation of Tyr-527, leading to exposure and phosphorylation of Tyr-416.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
270-523 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Ligand binding |
Assay |
Structural analysis, Mutagenesis experiment |
Target domain |
270-523 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Ligand binding |
Assay |
Structural analysis, Mutagenesis experiment |
Target domain |
270-523 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
PTM |
Assay |
Structural analysis, Mutagenesis experiment |
Target domain |
270-523 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
PTM |
Assay |
Structural analysis, Mutagenesis experiment |
Accessory elements
406-430 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
270-523 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
Autoinhibited structure
Activated structure

72 structures for P12931
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1A07 | X-ray | 220 A | A/B | 144-249 | PDB |
| 1A08 | X-ray | 220 A | A/B | 144-249 | PDB |
| 1A09 | X-ray | 200 A | A/B | 144-249 | PDB |
| 1A1A | X-ray | 200 A | A/B | 144-249 | PDB |
| 1A1B | X-ray | 220 A | A/B | 144-249 | PDB |
| 1A1C | X-ray | 240 A | A/B | 144-249 | PDB |
| 1A1E | X-ray | 220 A | A/B | 144-249 | PDB |
| 1FMK | X-ray | 150 A | A | 86-536 | PDB |
| 1HCS | NMR | - | B | 144-249 | PDB |
| 1HCT | NMR | - | B | 144-249 | PDB |
| 1KSW | X-ray | 280 A | A | 86-536 | PDB |
| 1O41 | X-ray | 170 A | A | 145-252 | PDB |
| 1O42 | X-ray | 170 A | A | 145-252 | PDB |
| 1O43 | X-ray | 150 A | A | 145-252 | PDB |
| 1O44 | X-ray | 170 A | A | 145-252 | PDB |
| 1O45 | X-ray | 180 A | A | 145-252 | PDB |
| 1O46 | X-ray | 200 A | A | 145-252 | PDB |
| 1O47 | X-ray | 180 A | A | 145-252 | PDB |
| 1O48 | X-ray | 155 A | A | 145-252 | PDB |
| 1O49 | X-ray | 170 A | A | 145-252 | PDB |
| 1O4A | X-ray | 150 A | A | 145-252 | PDB |
| 1O4B | X-ray | 185 A | A | 145-252 | PDB |
| 1O4C | X-ray | 180 A | A | 145-252 | PDB |
| 1O4D | X-ray | 185 A | A | 145-252 | PDB |
| 1O4E | X-ray | 200 A | A | 145-252 | PDB |
| 1O4F | X-ray | 200 A | A | 145-252 | PDB |
| 1O4G | X-ray | 155 A | A | 145-252 | PDB |
| 1O4H | X-ray | 225 A | A | 145-252 | PDB |
| 1O4I | X-ray | 175 A | A | 145-252 | PDB |
| 1O4J | X-ray | 170 A | A | 145-252 | PDB |
| 1O4K | X-ray | 157 A | A | 145-252 | PDB |
| 1O4L | X-ray | 165 A | A | 145-252 | PDB |
| 1O4M | X-ray | 160 A | A | 145-252 | PDB |
| 1O4N | X-ray | 160 A | A | 145-252 | PDB |
| 1O4O | X-ray | 170 A | A | 145-252 | PDB |
| 1O4P | X-ray | 190 A | A | 145-252 | PDB |
| 1O4Q | X-ray | 170 A | A | 145-252 | PDB |
| 1O4R | X-ray | 150 A | A | 145-252 | PDB |
| 1SHD | X-ray | 200 A | A | 144-249 | PDB |
| 1Y57 | X-ray | 191 A | A | 86-536 | PDB |
| 1YI6 | X-ray | 200 A | A/B | 261-536 | PDB |
| 1YOJ | X-ray | 195 A | A/B | 254-536 | PDB |
| 1YOL | X-ray | 230 A | A/B | 254-536 | PDB |
| 1YOM | X-ray | 290 A | A/B | 254-536 | PDB |
| 2BDF | X-ray | 210 A | A/B | 258-536 | PDB |
| 2BDJ | X-ray | 250 A | A | 258-536 | PDB |
| 2H8H | X-ray | 220 A | A | 2-536 | PDB |
| 2SRC | X-ray | 150 A | A | 86-536 | PDB |
| 3VRO | X-ray | 180 A | B | 412-424 | PDB |
| 3ZMP | X-ray | 262 A | C/D | 527-536 | PDB |
| 3ZMQ | X-ray | 330 A | C | 527-536 | PDB |
| 4F59 | X-ray | 171 A | A | 144-252 | PDB |
| 4F5A | X-ray | 180 A | A | 144-252 | PDB |
| 4F5B | X-ray | 157 A | A | 144-252 | PDB |
| 4HXJ | X-ray | 200 A | A/B | 87-144 | PDB |
| 4K11 | X-ray | 230 A | A | 87-534 | PDB |
| 4MXO | X-ray | 210 A | A/B | 254-536 | PDB |
| 4MXX | X-ray | 260 A | A/B | 254-536 | PDB |
| 4MXY | X-ray | 258 A | A/B | 254-536 | PDB |
| 4MXZ | X-ray | 258 A | A/B | 254-536 | PDB |
| 6ATE | X-ray | 240 A | A | 254-536 | PDB |
| 6C4S | X-ray | 150 A | A/B | 87-144 | PDB |
| 6E6E | X-ray | 215 A | A/B/C/D/E/F/G/H | 261-536 | PDB |
| 6EHJ | X-ray | 210 A | D/F | 2-9 | PDB |
| 7NG7 | X-ray | 150 A | A | 254-536 | PDB |
| 7OTE | X-ray | 249 A | A/B | 254-536 | PDB |
| 7T1U | X-ray | 265 A | A/B | 147-251 | PDB |
| 7YQE | X-ray | 350 A | A/B | 85-247 | PDB |
| 8GWH | X-ray | 200 A | E | 527-531 | PDB |
| 8HAQ | X-ray | 227 A | A/B | 260-536 | PDB |
| 8JF3 | X-ray | 285 A | A/B | 254-536 | PDB |
| AF-P12931-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
292 variants for P12931
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
CA10576055 RCV001003535 rs879255268 VAR_076919 RCV000211002 |
527 | E>K | Myelofibrosis Thrombocytopenia 6 THC6; increased protein tyrosine kinase activity; increased autophosphorylation at Y-419; causes defective megakaryopoiesis associated with increased overall tyrosine phosphorylation in megakaryocytes [ClinVar, UniProt] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar UniProt Ensembl dbSNP |
|
CA122517 RCV000428592 rs121913314 RCV000013401 |
531 | Q>* | Neoplasm Colon cancer, advanced [ClinVar] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar Ensembl dbSNP |
|
rs767602518 CA9847672 |
3 | S>T | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA408926375 rs1320051629 |
4 | N>H | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA408926401 rs1262407930 |
5 | K>N | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA408926461 rs1251001677 |
10 | D>N | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1318197870 CA408926476 |
11 | A>T | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1212841399 CA408926487 |
11 | A>V | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA408926513 rs1250842919 |
13 | Q>R | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1162867836 CA408926579 |
19 | E>Q | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA9847673 rs753143221 |
20 | P>A | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs367543238 RCV000084815 CA226013 |
21 | A>T | No |
ClinGen ClinVar Ensembl dbSNP |
|
|
rs1416764320 CA408926622 |
22 | E>K | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA9847675 rs764712270 |
23 | N>T | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1188439975 CA408926682 |
25 | H>D | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA9847678 rs779676153 |
26 | G>R | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA9847679 rs750998052 |
28 | G>S | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA226015 RCV000084816 rs367543239 |
29 | G>W | No |
ClinGen ClinVar TOPMed dbSNP |
|
|
rs1437496392 CA408926785 |
31 | A>T | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs754705008 CA9847680 |
32 | F>S | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1371352984 CA408926821 |
33 | P>A | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA408926863 rs1447509893 |
34 | A>D | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1288993928 CA408926852 |
34 | A>P | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1288993928 CA408926842 |
34 | A>T | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1232549534 CA408926872 |
35 | S>A | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs55962640 CA408926914 |
36 | Q>H | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs769523302 CA9847683 |
37 | T>I | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs911387445 CA314453745 |
37 | T>P | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs777533514 CA408926969 |
38 | P>L | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs777533514 CA9847684 |
38 | P>R | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA408926991 rs1479413147 |
39 | S>N | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1269537486 CA408927028 |
41 | P>A | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1475181251 CA408927078 |
43 | S>W | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA408927092 rs1420527845 |
44 | A>D | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA408927091 rs1420527845 |
44 | A>G | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA408927083 rs1186378528 |
44 | A>S | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA408927094 rs1406297899 |
45 | D>N | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1406297899 CA408927097 |
45 | D>Y | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs770744364 CA9847687 |
46 | G>C | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs770744364 CA9847686 |
46 | G>S | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA408927146 rs1352982585 |
47 | H>Y | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA408927179 rs1354854561 |
48 | R>G | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA408927230 rs1414132534 |
51 | S>G | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1291332754 CA408927236 |
51 | S>N | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1228673150 CA408927246 |
52 | A>T | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1600996596 CA408927281 |
53 | A>G | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs1235559294 CA408927263 |
53 | A>T | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1206123440 CA408927310 |
55 | A>D | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1568634641 CA408927322 |
56 | P>L | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs1270136897 CA408927317 |
56 | P>S | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1432190943 CA408927323 |
57 | A>T | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1260223338 CA408927346 |
59 | A>T | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs866133137 CA314453833 |
59 | A>V | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA314453842 rs1034743332 |
60 | E>D | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1186308773 CA408927385 |
61 | P>H | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA408927397 rs1417751781 |
62 | K>M | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1169430712 CA408927425 |
64 | F>L | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA314453860 rs956880395 |
68 | N>D | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA408927481 rs1432925945 |
69 | S>P | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA314453873 rs1009723505 |
74 | T>N | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA408927559 rs1406890537 |
75 | S>P | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA408927578 rs1417211462 |
76 | P>L | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs775787758 CA9847691 |
76 | P>S | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA408927608 rs1346600412 |
79 | A>T | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA9847693 rs764609637 |
79 | A>V | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1249784345 CA408927629 |
80 | G>D | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA408927639 rs1280055104 |
81 | P>Q | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA408927667 rs1487039786 |
84 | G>S | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA9847704 rs777586605 |
86 | V>E | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA9847703 rs755760984 |
86 | V>L | No |
ClinGen ExAC |
|
|
rs769864399 CA9847705 |
89 | F>S | No |
ClinGen ExAC |
|
|
CA408927938 rs1451326787 |
99 | T>K | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA408927976 rs1340628132 |
105 | F>L | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA9847712 rs747298865 |
110 | R>Q | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs772219397 CA9847711 |
110 | R>W | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA314455614 rs377182327 |
111 | L>F | No |
ClinGen ESP |
|
|
rs768964838 CA9847713 |
112 | Q>H | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1159660243 CA408928053 |
116 | N>S | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA9847715 rs762030353 |
117 | T>I | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA408928724 rs1446194954 |
124 | A>V | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs760138531 CA9847742 |
126 | S>L | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs760138531 CA408928737 |
126 | S>W | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs753372606 CA9847744 |
128 | S>C | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs750199560 CA9847747 |
131 | Q>E | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA314464150 rs374918628 |
132 | T>A | No |
ClinGen ESP TOPMed |
|
|
rs1241057049 CA408928774 |
132 | T>R | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1412626612 CA408928802 |
136 | P>R | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs755055234 CA9847751 |
141 | A>V | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs748389510 CA9847753 |
144 | D>N | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA9847754 rs770029502 |
147 | Q>* | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs746439256 CA9847776 |
151 | W>C | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs772598405 CA9847777 |
154 | G>S | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA9847778 rs776051245 |
156 | I>V | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs769358602 CA9847781 |
159 | R>W | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA408928990 rs1368749598 |
162 | E>Q | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA9847782 rs762684562 |
164 | L>V | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA314464519 rs969649905 |
165 | L>M | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA314464541 rs971949259 |
167 | N>H | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA408929029 rs1250584696 |
168 | A>G | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs572415651 CA314464549 |
168 | A>P | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA9847784 rs751370904 |
169 | E>G | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs759443292 CA408929044 |
170 | N>K | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA9847786 rs540682385 |
171 | P>L | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA408929062 rs1366542593 |
173 | G>V | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA408929068 rs1207997534 |
174 | T>S | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs6018260 VAR_051699 CA314464620 |
176 | L>F | No |
ClinGen UniProt Ensembl dbSNP |
|
|
CA9847791 rs143889833 |
177 | V>L | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA9847793 rs143889833 |
177 | V>L | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs143889833 CA9847792 |
177 | V>M | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA408929086 rs1416349077 |
178 | R>* | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs758848299 CA9847794 |
179 | E>D | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA408929118 rs1388458954 |
182 | T>I | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs146865960 CA9847795 |
183 | T>M | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA314466921 rs75363208 |
187 | Y>S | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs1158176653 CA408929204 |
194 | F>V | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA408929219 rs1198673480 |
195 | D>E | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA408929212 rs1198824064 |
195 | D>N | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1458527600 CA408929221 |
196 | N>D | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1458527600 CA408929220 |
196 | N>Y | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA9847835 rs755567292 |
197 | A>S | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs755567292 CA408929228 |
197 | A>T | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA9847836 rs781751002 |
197 | A>V | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1276049609 CA408929236 |
198 | K>R | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA408929243 rs753404366 |
199 | G>D | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs753404366 CA9847837 |
199 | G>V | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1048616788 CA314466972 |
200 | L>R | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs1331636640 CA408929261 |
202 | V>A | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA9847838 rs368312821 |
202 | V>L | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA408929258 rs368312821 |
202 | V>M | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA9847839 rs778554009 |
208 | R>C | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA314467002 rs867236697 |
208 | R>H | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA408929315 rs1289430309 |
210 | L>V | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA408929332 rs1450021163 |
212 | S>T | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA408929343 rs1478333895 |
214 | G>C | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1409547366 CA408929370 |
218 | T>P | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1409547366 CA408929372 |
218 | T>S | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA408929377 rs1601014278 |
219 | S>P | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA9847844 rs768609250 |
220 | R>C | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA408929388 rs1192783756 |
221 | T>A | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1192783756 CA408929387 |
221 | T>P | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs761890358 CA9847846 |
223 | F>L | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1409798282 CA408929418 |
225 | S>G | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA9847847 rs769916129 |
225 | S>I | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1229404250 CA408929428 |
227 | Q>K | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1466226424 CA408929454 |
230 | V>A | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA9847850 rs149158994 |
232 | Y>C | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs751989465 CA9847851 |
234 | S>A | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA9847852 rs759914792 |
234 | S>C | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA408929479 rs759914792 |
234 | S>Y | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1400593225 CA408929496 |
235 | K>R | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1401292418 CA408929504 |
236 | H>R | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
VAR_041830 CA9847877 rs34881773 |
237 | A>T | No |
ClinGen UniProt ExAC TOPMed dbSNP gnomAD |
|
|
CA408929513 rs1433113895 |
238 | D>N | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1365991950 CA408929543 |
242 | H>P | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA408929544 rs1365991950 |
242 | H>R | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA226019 rs367543241 RCV000084818 |
243 | R>C | No |
ClinGen ClinVar ExAC dbSNP gnomAD |
|
|
rs751268997 CA9847880 |
243 | R>H | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs754617799 CA408929562 |
245 | T>N | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs754617799 CA9847881 |
245 | T>S | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs370773419 CA9847882 |
246 | T>S | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA408929572 rs1191846929 |
247 | V>A | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA408929568 rs1464185975 |
247 | V>M | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs756112018 CA9847884 |
249 | P>A | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs901620408 CA314469072 |
250 | T>A | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs767829559 CA408929589 |
250 | T>K | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs767829559 CA9847885 |
250 | T>M | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA9847888 rs774569491 |
252 | K>N | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs551439047 CA9847889 |
253 | P>L | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs973446215 CA314469132 |
255 | T>A | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs147010442 CA314469141 |
256 | Q>H | No |
ClinGen ESP TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA408929637 rs1455889060 |
258 | L>Q | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1274262123 CA408929662 |
262 | A>T | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA408929680 rs1235463689 |
264 | E>A | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA9847893 rs764665699 |
266 | P>L | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs776941746 CA9847894 |
267 | R>Q | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1475233098 CA408929708 |
268 | E>D | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA408929714 rs1328205125 |
269 | S>L | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA9847897 rs533607141 |
271 | R>Q | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA9847896 rs148049198 |
271 | R>W | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA9847898 rs754650463 |
272 | L>P | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs752496798 CA9847900 |
273 | E>G | No |
ClinGen ExAC |
|
|
CA9847902 rs766744528 |
283 | E>K | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA408929867 rs1246093856 |
290 | N>S | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1207881818 CA408929876 |
291 | G>D | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1340705473 CA408929871 |
291 | G>S | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs111844926 CA9847923 |
292 | T>I | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs111844926 CA9847922 |
292 | T>N | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1233868589 CA408929879 |
292 | T>S | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA408929886 rs1397126729 |
293 | T>I | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA9847925 rs750534584 |
296 | A>S | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1168068913 CA408929906 |
297 | I>V | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1388365171 CA408929925 |
299 | T>I | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA314471643 rs956512588 |
300 | L>P | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA408929955 rs1172425959 |
304 | T>M | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs747257425 CA408930033 |
315 | Q>H | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA9847930 rs768889863 |
319 | K>R | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs996960011 CA314471703 |
327 | Q>H | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA408930129 rs1411658070 |
329 | Y>C | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1274322227 CA408930136 |
330 | A>D | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs867593338 CA314471741 |
340 | V>I | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA408930233 rs1601020505 |
344 | M>I | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs754968435 CA408930228 |
344 | M>L | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs754968435 CA314471770 |
344 | M>V | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs763438144 CA9847935 |
345 | S>N | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA408930330 rs1601022188 |
356 | E>V | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA408930337 rs1224513777 |
357 | T>I | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA408930338 rs1224513777 |
357 | T>R | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1289307625 CA408930349 |
359 | K>R | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA408930356 rs1601022219 |
360 | Y>S | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA314473172 rs984277412 |
362 | R>W | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs1160967723 CA408930377 |
364 | P>S | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA314473196 rs778642449 |
367 | V>M | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs763031752 CA9847966 |
369 | M>I | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1056974481 CA314473200 |
369 | M>L | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA408930419 rs1249301882 |
370 | A>V | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs751597996 CA9847968 |
372 | Q>* | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA314474211 rs994208712 |
374 | A>T | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA408930464 rs1181484011 |
375 | S>L | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1190315469 CA408930495 |
380 | V>M | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs754204413 CA9847992 |
382 | R>L | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA9847991 rs754204413 |
382 | R>Q | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs764262104 CA9847990 |
382 | R>W | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA9847994 rs751005087 |
386 | V>I | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1252138081 CA408930562 |
388 | R>W | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA314474330 rs867805553 |
391 | R>C | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA9847996 rs758795351 |
391 | R>H | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
RCV000087213 rs367543243 CA229127 |
400 | N>K | No |
ClinGen ClinVar Ensembl dbSNP |
|
|
CA314474356 rs77538537 |
400 | N>T | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA408930680 rs1601023806 |
401 | L>V | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA408930703 rs1339354176 |
403 | C>Y | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA314474359 rs186207963 |
407 | D>H | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes gnomAD |
|
|
CA408930740 rs186207963 |
407 | D>N | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes gnomAD |
|
|
CA408930931 rs1274078983 |
418 | E>K | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs142822674 CA9848001 |
420 | T>M | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA9848004 rs759567556 |
422 | R>Q | No |
ClinGen ExAC |
|
|
rs1459444714 CA408930991 |
422 | R>W | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1208655105 CA408931111 |
424 | G>D | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1294447485 CA408931143 |
426 | K>R | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA408931272 rs1490969287 |
432 | T>M | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA408931299 rs1200637641 |
434 | P>A | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA408931307 rs1251506584 |
435 | E>K | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1417607384 CA408931337 |
436 | A>T | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA9848021 rs745612156 |
439 | Y>C | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA314474661 rs202242810 |
441 | R>C | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs772053084 CA9848022 |
441 | R>H | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA408931544 rs1406655378 |
446 | S>L | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA314474695 rs1056084684 |
448 | V>L | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA408931560 rs1056084684 |
448 | V>M | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA9848027 rs765324314 |
453 | I>V | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1171125750 CA408931708 |
460 | T>K | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs752182272 CA9848031 |
463 | R>Q | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
RCV000084824 rs367543247 CA226031 |
463 | R>W | No |
ClinGen ClinVar Ensembl dbSNP |
|
|
CA408931752 rs1251532695 |
465 | P>S | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA314475088 rs997451700 |
468 | G>V | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs1221989600 CA408931923 |
472 | R>C | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA9848048 rs774838914 |
472 | R>H | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA314475149 rs950614364 |
476 | D>E | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA408931962 rs1484879243 |
476 | D>N | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA408931994 rs1420046989 |
478 | V>M | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1173914321 CA408932021 |
480 | R>Q | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1479989919 CA408932019 |
480 | R>W | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA9848051 rs753395244 |
483 | R>Q | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs768098520 CA9848050 |
483 | R>W | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1317072077 CA408932078 |
485 | P>L | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA408932084 rs1342906456 |
486 | C>Y | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs756665933 CA9848052 |
487 | P>L | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs750108303 CA9848054 |
488 | P>L | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA9848055 rs758015155 |
489 | E>Q | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs367543248 CA226033 RCV000084825 |
492 | E>K | No |
ClinGen ClinVar ExAC TOPMed dbSNP gnomAD |
|
|
CA9848058 rs780921646 |
493 | S>F | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs780921646 CA408932160 |
493 | S>Y | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1197051295 CA408932185 |
496 | D>N | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA9848060 rs769834016 |
497 | L>F | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA408932197 rs769834016 |
497 | L>V | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA408932207 rs1344423676 |
498 | M>L | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA408932219 rs1303357004 |
499 | C>R | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA408932276 rs1405253806 |
503 | R>Q | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs564099857 CA9848062 |
503 | R>W | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs771233913 CA9848063 |
505 | E>D | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1159129326 CA408932306 |
506 | P>S | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA408932340 rs1305388441 |
509 | R>W | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA408932348 rs1346524802 |
510 | P>A | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA408932349 rs1346524802 |
510 | P>S | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA9848066 rs768153592 |
517 | A>G | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1358694181 CA408932512 |
524 | T>M | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA9848070 rs749923525 |
526 | T>A | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1180746688 CA408932536 |
526 | T>I | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA408932550 rs1470934154 |
527 | E>D | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1177310598 CA408932554 |
528 | P>S | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA9848072 rs562042369 |
529 | Q>L | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs754707860 CA408932619 |
533 | G>R | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs754707860 CA9848074 |
533 | G>R | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
2 associated diseases with P12931
[MIM: 616937]: Thrombocytopenia 6 (THC6)
A form of thrombocytopenia, a hematologic disorder defined by a decrease in the number of platelets in circulating blood, resulting in the potential for increased bleeding and decreased ability for clotting. THC6 is an autosomal dominant form. Affected individuals may also have bone abnormalities and an increased risk for myelofibrosis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26936507}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.
Without disease ID
- A form of thrombocytopenia, a hematologic disorder defined by a decrease in the number of platelets in circulating blood, resulting in the potential for increased bleeding and decreased ability for clotting. THC6 is an autosomal dominant form. Affected individuals may also have bone abnormalities and an increased risk for myelofibrosis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26936507}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.
7 regional properties for P12931
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Protein kinase domain | 270 - 523 | IPR000719 |
| domain | SH2 domain | 149 - 248 | IPR000980 |
| domain | Serine-threonine/tyrosine-protein kinase, catalytic domain | 271 - 518 | IPR001245 |
| domain | SH3 domain | 84 - 145 | IPR001452 |
| active_site | Tyrosine-protein kinase, active site | 385 - 397 | IPR008266 |
| binding_site | Protein kinase, ATP binding site | 276 - 298 | IPR017441 |
| domain | Tyrosine-protein kinase, catalytic domain | 270 - 519 | IPR020635 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.10.2 | Protein-tyrosine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
22 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| actin filament | A filamentous structure formed of a two-stranded helical polymer of the protein actin and associated proteins. Actin filaments are a major component of the contractile apparatus of skeletal muscle and the microfilaments of the cytoskeleton of eukaryotic cells. The filaments, comprising polymerized globular actin molecules, appear as flexible structures with a diameter of 5-9 nm. They are organized into a variety of linear bundles, two-dimensional networks, and three dimensional gels. In the cytoskeleton they are most highly concentrated in the cortex of the cell just beneath the plasma membrane. |
| caveola | A membrane raft that forms small pit, depression, or invagination that communicates with the outside of a cell and extends inward, indenting the cytoplasm and the cell membrane. Examples include flask-shaped invaginations of the plasma membrane in adipocytes associated with caveolin proteins, and minute pits or incuppings of the cell membrane formed during pinocytosis. Caveolae may be pinched off to form free vesicles within the cytoplasm. |
| cell junction | A cellular component that forms a specialized region of connection between two or more cells, or between a cell and the extracellular matrix, or between two membrane-bound components of a cell, such as flagella. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| extracellular exosome | A vesicle that is released into the extracellular region by fusion of the limiting endosomal membrane of a multivesicular body with the plasma membrane. Extracellular exosomes, also simply called exosomes, have a diameter of about 40-100 nm. |
| extrinsic component of cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane | The component of a plasma membrane consisting of gene products and protein complexes that are loosely bound to its cytoplasmic surface, but not integrated into the hydrophobic region. |
| focal adhesion | A cell-substrate junction that anchors the cell to the extracellular matrix and that forms a point of termination of actin filaments. In insects focal adhesion has also been referred to as hemi-adherens junction (HAJ). |
| glutamatergic synapse | A synapse that uses glutamate as a neurotransmitter. |
| late endosome | A prelysosomal endocytic organelle differentiated from early endosomes by lower lumenal pH and different protein composition. Late endosomes are more spherical than early endosomes and are mostly juxtanuclear, being concentrated near the microtubule organizing center. |
| lysosome | A small lytic vacuole that has cell cycle-independent morphology found in most animal cells and that contains a variety of hydrolases, most of which have their maximal activities in the pH range 5-6. The contained enzymes display latency if properly isolated. About 40 different lysosomal hydrolases are known and lysosomes have a great variety of morphologies and functions. |
| membrane raft | Any of the small (10-200 nm), heterogeneous, highly dynamic, sterol- and sphingolipid-enriched membrane domains that compartmentalize cellular processes. Small rafts can sometimes be stabilized to form larger platforms through protein-protein and protein-lipid interactions. |
| mitochondrial inner membrane | The inner, i.e. lumen-facing, lipid bilayer of the mitochondrial envelope. It is highly folded to form cristae. |
| mitochondrion | A semiautonomous, self replicating organelle that occurs in varying numbers, shapes, and sizes in the cytoplasm of virtually all eukaryotic cells. It is notably the site of tissue respiration. |
| neuron projection | A prolongation or process extending from a nerve cell, e.g. an axon or dendrite. |
| nucleoplasm | That part of the nuclear content other than the chromosomes or the nucleolus. |
| perinuclear region of cytoplasm | Cytoplasm situated near, or occurring around, the nucleus. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| podosome | An actin-rich adhesion structure characterized by formation upon cell substrate contact and localization at the substrate-attached part of the cell, contain an F-actin-rich core surrounded by a ring structure containing proteins such as vinculin and talin, and have a diameter of 0.5 mm. |
| postsynaptic density | An electron dense network of proteins within and adjacent to the postsynaptic membrane of an asymmetric, neuron-neuron synapse. Its major components include neurotransmitter receptors and the proteins that spatially and functionally organize them such as anchoring and scaffolding molecules, signaling enzymes and cytoskeletal components. |
| postsynaptic specialization, intracellular component | A network of proteins adjacent to the postsynaptic membrane. Its major components include the proteins that spatially and functionally organize neurotransmitter receptors in the adjacent membrane, such as anchoring and scaffolding molecules, signaling enzymes and cytoskeletal components. |
| ruffle membrane | The portion of the plasma membrane surrounding a ruffle. |
26 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| ATPase binding | Binding to an ATPase, any enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP. |
| BMP receptor binding | Binding to a BMP receptor. |
| cadherin binding | Binding to cadherin, a type I membrane protein involved in cell adhesion. |
| connexin binding | Binding to a connexin, any of a group of related proteins that assemble to form gap junctions. |
| enzyme binding | Binding to an enzyme, a protein with catalytic activity. |
| ephrin receptor binding | Binding to an ephrin receptor. |
| estrogen receptor binding | Binding to a nuclear estrogen receptor. |
| growth factor receptor binding | Binding to a growth factor receptor. |
| heme binding | Binding to a heme, a compound composed of iron complexed in a porphyrin (tetrapyrrole) ring. |
| insulin receptor binding | Binding to an insulin receptor. |
| integrin binding | Binding to an integrin. |
| kinase binding | Binding to a kinase, any enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group. |
| non-membrane spanning protein tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + protein L-tyrosine = ADP + protein L-tyrosine phosphate by a non-membrane spanning protein. |
| phospholipase activator activity | Increases the activity of a phospholipase, an enzyme that catalyzes of the hydrolysis of a glycerophospholipid. |
| phospholipase binding | Binding to a phospholipase. |
| phosphoprotein binding | Binding to a phosphorylated protein. |
| protein C-terminus binding | Binding to a protein C-terminus, the end of a peptide chain at which the 1-carboxyl function of a constituent amino acid is not attached in peptide linkage to another amino-acid residue. |
| protein kinase activity | Catalysis of the phosphorylation of an amino acid residue in a protein, usually according to the reaction: a protein + ATP = a phosphoprotein + ADP. |
| protein kinase C binding | Binding to protein kinase C. |
| protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + a protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate; ATP + a protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate; and ATP + a protein tyrosine = ADP + protein tyrosine phosphate. |
| protein tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + a protein tyrosine = ADP + protein tyrosine phosphate. |
| scaffold protein binding | Binding to a scaffold protein. Scaffold proteins are crucial regulators of many key signaling pathways. Although not strictly defined in function, they are known to interact and/or bind with multiple members of a signaling pathway, tethering them into complexes. |
| SH2 domain binding | Binding to a SH2 domain (Src homology 2) of a protein, a protein domain of about 100 amino-acid residues and belonging to the alpha + beta domain class. |
| signaling receptor binding | Binding to one or more specific sites on a receptor molecule, a macromolecule that undergoes combination with a hormone, neurotransmitter, drug or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell function. |
| transmembrane transporter binding | Binding to a transmembrane transporter, a protein or protein complex that enables the transfer of a substance, usually a specific substance or a group of related substances, from one side of a membrane to the other. |
116 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| activation of protein kinase B activity | Any process that initiates the activity of the inactive enzyme protein kinase B. |
| adherens junction organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of an adherens junction. An adherens junction is a cell-cell junction composed of the epithelial cadherin-catenin complex at which the cytoplasmic face of the plasma membrane is attached to actin filaments. |
| angiotensin-activated signaling pathway involved in heart process | An angiotensin receptor signaling pathway which contributes to a circulatory system process carried out by the heart. |
| bone resorption | The process in which specialized cells known as osteoclasts degrade the organic and inorganic portions of bone, and endocytose and transport the degradation products. |
| branching involved in mammary gland duct morphogenesis | The process in which the branching structure of the mammary gland duct is generated and organized. The mammary gland is a large compound sebaceous gland that in female mammals is modified to secrete milk. |
| cell adhesion | The attachment of a cell, either to another cell or to an underlying substrate such as the extracellular matrix, via cell adhesion molecules. |
| cell cycle | The progression of biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur in a cell during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events. Canonically, the cell cycle comprises the replication and segregation of genetic material followed by the division of the cell, but in endocycles or syncytial cells nuclear replication or nuclear division may not be followed by cell division. |
| cell differentiation | The process in which relatively unspecialized cells, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cells, acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate and its subsequent development to the mature state. |
| cell population proliferation | The multiplication or reproduction of cells, resulting in the expansion of a cell population. |
| cell-cell adhesion | The attachment of one cell to another cell via adhesion molecules. |
| cellular response to fatty acid | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a fatty acid stimulus. |
| cellular response to fluid shear stress | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a fluid shear stress stimulus. Fluid shear stress is the force acting on an object in a system where the fluid is moving across a solid surface. |
| cellular response to hydrogen peroxide | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) stimulus. |
| cellular response to hypoxia | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating lowered oxygen tension. Hypoxia, defined as a decline in O2 levels below normoxic levels of 20.8 - 20.95%, results in metabolic adaptation at both the cellular and organismal level. |
| cellular response to insulin stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an insulin stimulus. Insulin is a polypeptide hormone produced by the islets of Langerhans of the pancreas in mammals, and by the homologous organs of other organisms. |
| cellular response to lipopolysaccharide | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a lipopolysaccharide stimulus; lipopolysaccharide is a major component of the cell wall of gram-negative bacteria. |
| cellular response to peptide hormone stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a peptide hormone stimulus. A peptide hormone is any of a class of peptides that are secreted into the blood stream and have endocrine functions in living animals. |
| cellular response to platelet-derived growth factor stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a platelet-derived growth factor stimulus. |
| cellular response to progesterone stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a progesterone stimulus. |
| entry of bacterium into host cell | The process in which a bacterium enters a host cell. The host is defined as the larger of the organisms involved in a symbiotic interaction. |
| ephrin receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by ephrin binding to its receptor, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by binding of a ligand to the tyrosine kinase receptor EGFR (ERBB1) on the surface of a cell. The pathway ends with regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| ERBB2 signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by binding of a ligand to the tyrosine kinase receptor ERBB2 on the surface of a cell. The pathway ends with regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. ERBB2 receptors are themselves unable to bind to ligands, but act as a signal-amplifying tyrosine kinase within a heterodimeric pair. |
| Fc-gamma receptor signaling pathway involved in phagocytosis | An Fc-gamma receptor signaling pathway that contributes to the endocytic engulfment of external particulate material by phagocytes. |
| focal adhesion assembly | The aggregation and bonding together of a set of components to form a focal adhesion, a complex of intracellular signaling and structural proteins that provides a structural link between the internal actin cytoskeleton and the ECM, and also function as a locus of signal transduction activity. |
| forebrain development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the forebrain over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The forebrain is the anterior of the three primary divisions of the developing chordate brain or the corresponding part of the adult brain (in vertebrates, includes especially the cerebral hemispheres, the thalamus, and the hypothalamus and especially in higher vertebrates is the main control center for sensory and associative information processing, visceral functions, and voluntary motor functions). |
| innate immune response | Innate immune responses are defense responses mediated by germline encoded components that directly recognize components of potential pathogens. |
| integrin-mediated signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by an extracellular ligand binding to an integrin on the surface of a target cell, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| interleukin-6-mediated signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by interleukin-6 binding to a receptor on the surface of a target cell, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| intestinal epithelial cell development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a columnar/cuboidal epithelial cell of the intestine over time, from its formation to the mature structure. |
| intracellular signal transduction | The process in which a signal is passed on to downstream components within the cell, which become activated themselves to further propagate the signal and finally trigger a change in the function or state of the cell. |
| leukocyte migration | The movement of a leukocyte within or between different tissues and organs of the body. |
| macroautophagy | The major inducible pathway for the general turnover of cytoplasmic constituents in eukaryotic cells, it is also responsible for the degradation of active cytoplasmic enzymes and organelles during nutrient starvation. Macroautophagy involves the formation of double-membrane-bounded autophagosomes which enclose the cytoplasmic constituent targeted for degradation in a membrane-bounded structure. Autophagosomes then fuse with a lysosome (or vacuole) releasing single-membrane-bounded autophagic bodies that are then degraded within the lysosome (or vacuole). Some types of macroautophagy, e.g. pexophagy, mitophagy, involve selective targeting of the targets to be degraded. |
| negative regulation of anoikis | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of anoikis. |
| negative regulation of apoptotic process | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cell death by apoptotic process. |
| negative regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in the apoptotic process. |
| negative regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway. |
| negative regulation of focal adhesion assembly | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of focal adhesion assembly, the establishment and maturation of focal adhesions. |
| negative regulation of inflammatory response to antigenic stimulus | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate, or extent of an inflammatory response to an antigenic stimulus. |
| negative regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway. |
| negative regulation of mitochondrial depolarization | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the change in the membrane potential of the mitochondria from negative to positive. |
| negative regulation of protein-containing complex assembly | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of protein complex assembly. |
| negative regulation of telomerase activity | Any process that stops or reduces the activity of the enzyme telomerase, which catalyzes of the reaction: deoxynucleoside triphosphate + DNA(n) = diphosphate + DNA(n+1). |
| negative regulation of telomere maintenance via telomerase | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the addition of telomeric repeats by telomerase. |
| negative regulation of transcription, DNA-templated | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cellular DNA-templated transcription. |
| neurotrophin TRK receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by neurotrophin binding to its receptor on the surface of a target cell where the receptor possesses tyrosine kinase activity, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| odontogenesis | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a tooth or teeth over time, from formation to the mature structure(s). A tooth is any hard bony, calcareous, or chitinous organ found in the mouth or pharynx of an animal and used in procuring or masticating food. |
| oogenesis | The complete process of formation and maturation of an ovum or female gamete from a primordial female germ cell. Examples of this process are found in Mus musculus and Drosophila melanogaster. |
| osteoclast development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a osteoclast from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate. An osteoclast is a specialized phagocytic cell associated with the absorption and removal of the mineralized matrix of bone tissue. |
| peptidyl-serine phosphorylation | The phosphorylation of peptidyl-serine to form peptidyl-O-phospho-L-serine. |
| peptidyl-tyrosine autophosphorylation | The phosphorylation by a protein of one or more of its own tyrosine amino acid residues, or a tyrosine residue on an identical protein. |
| peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation | The phosphorylation of peptidyl-tyrosine to form peptidyl-O4'-phospho-L-tyrosine. |
| platelet activation | A series of progressive, overlapping events triggered by exposure of the platelets to subendothelial tissue. These events include shape change, adhesiveness, aggregation, and release reactions. When carried through to completion, these events lead to the formation of a stable hemostatic plug. |
| positive regulation of apoptotic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell death by apoptotic process. |
| positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway | Any process that increases the rate, frequency, or extent of the Wnt signaling pathway through beta-catenin, the series of molecular signals initiated by binding of a Wnt protein to a frizzled family receptor on the surface of the target cell, followed by propagation of the signal via beta-catenin, and ending with a change in transcription of target genes. |
| positive regulation of cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of CDK activity. |
| positive regulation of cytokine production | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of production of a cytokine. |
| positive regulation of dephosphorylation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of removal of phosphate groups from a molecule. |
| positive regulation of DNA biosynthetic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of DNA biosynthetic process. |
| positive regulation of epithelial cell migration | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of epithelial cell migration. |
| positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction mediated by the ERK1 and ERK2 cascade. |
| positive regulation of glucose metabolic process | Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of glucose metabolism. Glucose metabolic processes are the chemical reactions and pathways involving glucose, the aldohexose gluco-hexose. |
| positive regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway | Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of insulin receptor signaling. |
| positive regulation of integrin activation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of integrin activation. |
| positive regulation of lamellipodium morphogenesis | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of lamellipodium morphogenesis. |
| positive regulation of MAP kinase activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of MAP kinase activity. |
| positive regulation of non-membrane spanning protein tyrosine kinase activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of non-membrane spanning protein tyrosine kinase activity. |
| positive regulation of Notch signaling pathway | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the Notch signaling pathway. |
| positive regulation of ovarian follicle development | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of ovarian follicle development. |
| positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the phosphorylation of peptidyl-tyrosine. |
| positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity. |
| positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction mediated by the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase cascade. |
| positive regulation of platelet-derived growth factor receptor-beta signaling pathway | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of platelet-derived growth factor receptor-beta signaling pathway. |
| positive regulation of podosome assembly | Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of podosome assembly. |
| positive regulation of protein autophosphorylation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the phosphorylation by a protein of one or more of its own residues. |
| positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of protein kinase B signaling, a series of reactions mediated by the intracellular serine/threonine kinase protein kinase B. |
| positive regulation of protein localization to nucleus | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of protein localization to nucleus. |
| positive regulation of protein processing | Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of protein maturation by peptide bond cleavage. |
| positive regulation of protein serine/threonine kinase activity | Any process that increases the rate, frequency, or extent of protein serine/threonine kinase activity. |
| positive regulation of protein transport | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the directed movement of a protein into, out of or within a cell, or between cells, by means of some agent such as a transporter or pore. |
| positive regulation of small GTPase mediated signal transduction | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of small GTPase mediated signal transduction. |
| positive regulation of smooth muscle cell migration | Any process that activates, maintains or increases the frequency, rate or extent of smooth muscle cell migration. |
| positive regulation of transcription, DNA-templated | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cellular DNA-templated transcription. |
| primary ovarian follicle growth | Increase in size of primary follicles including oocyte growth and granulosa and/or theca cell proliferation until more than one layer of granulosa cells is present (preantral follicle). |
| progesterone receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by progesterone binding to its receptor in the cytoplasm. |
| protein autophosphorylation | The phosphorylation by a protein of one or more of its own amino acid residues (cis-autophosphorylation), or residues on an identical protein (trans-autophosphorylation). |
| protein destabilization | Any process that decreases the stability of a protein, making it more vulnerable to degradative processes or aggregation. |
| regulation of bone resorption | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of bone tissue loss (resorption). |
| regulation of caveolin-mediated endocytosis | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of caveolin-mediated endocytosis. |
| regulation of cell projection assembly | Any process that modulates the rate, frequency, or extent of cell projection assembly. |
| regulation of cell-cell adhesion | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of attachment of a cell to another cell. |
| regulation of early endosome to late endosome transport | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of early endosome to late endosome transport. |
| regulation of epithelial cell migration | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of epithelial cell migration. |
| regulation of intracellular estrogen receptor signaling pathway | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the activity of an intracellular estrogen receptor signaling pathway. |
| regulation of postsynaptic neurotransmitter receptor activity | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of neurotransmitter receptor activity involved in synaptic transmission. Modulation may be via an effect on ligand affinity, or effector funtion such as ion selectivity or pore opening/closing in ionotropic receptors. |
| regulation of protein binding | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of protein binding. |
| regulation of vascular permeability | Any process that modulates the extent to which blood vessels can be pervaded by fluid. |
| response to acidic pH | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a pH stimulus with pH < 7. pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution. |
| response to electrical stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an electrical stimulus. |
| response to interleukin-1 | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an interleukin-1 stimulus. |
| response to mechanical stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a mechanical stimulus. |
| response to mineralocorticoid | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a mineralocorticoid stimulus. Mineralocorticoids are hormonal C21 corticosteroids synthesized from cholesterol and characterized by their similarity to aldosterone. Mineralocorticoids act primarily on water and electrolyte balance. |
| response to nutrient levels | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus reflecting the presence, absence, or concentration of nutrients. |
| response to virus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus from a virus. |
| response to xenobiotic stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus from a xenobiotic, a compound foreign to the organim exposed to it. It may be synthesized by another organism (like ampicilin) or it can be a synthetic chemical. |
| signal complex assembly | The aggregation, arrangement and bonding together of a set of components to form a complex capable of relaying a signal within a cell. |
| signal transduction | The cellular process in which a signal is conveyed to trigger a change in the activity or state of a cell. Signal transduction begins with reception of a signal (e.g. a ligand binding to a receptor or receptor activation by a stimulus such as light), or for signal transduction in the absence of ligand, signal-withdrawal or the activity of a constitutively active receptor. Signal transduction ends with regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. regulation of transcription or regulation of a metabolic process. Signal transduction covers signaling from receptors located on the surface of the cell and signaling via molecules located within the cell. For signaling between cells, signal transduction is restricted to events at and within the receiving cell. |
| stimulatory C-type lectin receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by the binding of C-type lectin to its receptor on the surface of a target cell, and resulting in cellular activation. |
| stress fiber assembly | The aggregation, arrangement and bonding together of a set of components to form a stress fiber. A stress fiber is a contractile actin filament bundle that consists of short actin filaments with alternating polarity. |
| substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading | The morphogenetic process that results in flattening of a cell as a consequence of its adhesion to a substrate. |
| T cell costimulation | The process of providing, via surface-bound receptor-ligand pairs, a second, antigen-independent, signal in addition to that provided by the T cell receptor to augment T cell activation. |
| transcytosis | The directed movement of endocytosed material through the cell and its exocytosis from the plasma membrane at the opposite side. |
| transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by an extracellular ligand binding to a transforming growth factor beta receptor on the surface of a target cell, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by an extracellular ligand binding to a receptor on the surface of the target cell where the receptor possesses tyrosine kinase activity, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| uterus development | The reproductive developmental process whose specific outcome is the progression of the uterus over time, from its formation to the mature structure. |
| vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by a ligand binding to a vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) on the surface of the target cell, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
90 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A0JNB0 | FYN | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| Q0VBZ0 | CSK | Tyrosine-protein kinase CSK | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| Q3ZC95 | BTK | Tyrosine-protein kinase | Bos taurus (Bovine) | EV SS |
| P42683 | LCK | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase LCK | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P41239 | CSK | Tyrosine-protein kinase CSK | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q02977 | YRK | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Yrk | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q8JH64 | BTK | Tyrosine-protein kinase BTK | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P09324 | YES1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase Yes | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q05876 | FYN | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q75R65 | JAK2 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK2 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P00523 | SRC | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | EV |
| Q24592 | hop | Tyrosine-protein kinase hopscotch | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | PR |
| P08630 | Btk | Tyrosine-protein kinase Btk | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| Q9V9J3 | Src42A | Tyrosine-protein kinase Src42A | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| P00528 | Src64B | Tyrosine-protein kinase Src64B | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| P23458 | JAK1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| O60674 | JAK2 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P52333 | JAK3 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P29597 | TYK2 | Non-receptor tyrosine-protein kinase TYK2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P43405 | SYK | Tyrosine-protein kinase SYK | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P43403 | ZAP70 | Tyrosine-protein kinase ZAP-70 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q13882 | PTK6 | Protein-tyrosine kinase 6 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P09769 | FGR | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fgr | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P07948 | LYN | Tyrosine-protein kinase Lyn | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P06241 | FYN | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P06239 | LCK | Tyrosine-protein kinase Lck | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P51451 | BLK | Tyrosine-protein kinase Blk | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P08631 | HCK | Tyrosine-protein kinase HCK | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P07947 | YES1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase Yes | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P42685 | FRK | Tyrosine-protein kinase FRK | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q08881 | ITK | Tyrosine-protein kinase ITK/TSK | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q06187 | BTK | Tyrosine-protein kinase BTK | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P51813 | BMX | Cytoplasmic tyrosine-protein kinase BMX | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P42680 | TEC | Tyrosine-protein kinase Tec | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P42679 | MATK | Megakaryocyte-associated tyrosine-protein kinase | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P41240 | CSK | Tyrosine-protein kinase CSK | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q14289 | PTK2B | Protein-tyrosine kinase 2-beta | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q05397 | PTK2 | Focal adhesion kinase 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q13470 | TNK1 | Non-receptor tyrosine-protein kinase TNK1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q07912 | TNK2 | Activated CDC42 kinase 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P16591 | FER | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fer | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q6J9G0 | STYK1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase STYK1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P42684 | ABL2 | Tyrosine-protein kinase ABL2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P00519 | ABL1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase ABL1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q9R117 | Tyk2 | Non-receptor tyrosine-protein kinase TYK2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P08103 | Hck | Tyrosine-protein kinase HCK | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P16277 | Blk | Tyrosine-protein kinase Blk | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q62270 | Srms | Tyrosine-protein kinase Srms | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q64434 | Ptk6 | Protein-tyrosine kinase 6 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P14234 | Fgr | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fgr | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P35991 | Btk | Tyrosine-protein kinase BTK | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| P41241 | Csk | Tyrosine-protein kinase CSK | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| P25911 | Lyn | Tyrosine-protein kinase Lyn | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| Q62137 | Jak3 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q62120 | Jak2 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| P06240 | Lck | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase LCK | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P24604 | Tec | Tyrosine-protein kinase Tec | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q04736 | Yes1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase Yes | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P39688 | Fyn | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P52332 | Jak1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q03526 | Itk | Tyrosine-protein kinase ITK/TSK | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P41242 | Matk | Megakaryocyte-associated tyrosine-protein kinase | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q922K9 | Frk | Tyrosine-protein kinase FRK | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P05480 | Src | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| A1Y2K1 | FYN | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn | Sus scrofa (Pig) | SS |
| O19064 | JAK2 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK2 | Sus scrofa (Pig) | SS |
| Q62662 | Frk | Tyrosine-protein kinase FRK | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q62844 | Fyn | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q07014 | Lyn | Tyrosine-protein kinase Lyn | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P50545 | Hck | Tyrosine-protein kinase HCK | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q01621 | Lck | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase LCK | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q6P6U0 | Fgr | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fgr | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q62689 | Jak2 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK2 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q63272 | Jak3 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK3 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P32577 | Csk | Tyrosine-protein kinase CSK | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P41243 | Matk | Megakaryocyte-associated tyrosine-protein kinase | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| F1LM93 | Yes1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase Yes | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q9WUD9 | Src | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| G5ECJ6 | csk-1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase csk-1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| O45539 | src-2 | Tyrosine protein-kinase src-2 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| G5EE56 | src-1 | Tyrosine protein-kinase src-1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| F4JTP5 | STY46 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase STY46 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| O22558 | STY8 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase STY8 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q2MHE4 | HT1 | Serine/threonine/tyrosine-protein kinase HT1 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q8RWL6 | STY17 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase STY17 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| A1A5H8 | yes1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase yes | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| F1RDG9 | fynb | Tyrosine-protein kinase fynb | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| O12990 | jak1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK1 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | PR |
| Q6EWH2 | fyna | Tyrosine-protein kinase fyna | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q1JPZ3 | src | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MGSNKSKPKD | ASQRRRSLEP | AENVHGAGGG | AFPASQTPSK | PASADGHRGP | SAAFAPAAAE |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| PKLFGGFNSS | DTVTSPQRAG | PLAGGVTTFV | ALYDYESRTE | TDLSFKKGER | LQIVNNTEGD |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| WWLAHSLSTG | QTGYIPSNYV | APSDSIQAEE | WYFGKITRRE | SERLLLNAEN | PRGTFLVRES |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| ETTKGAYCLS | VSDFDNAKGL | NVKHYKIRKL | DSGGFYITSR | TQFNSLQQLV | AYYSKHADGL |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| CHRLTTVCPT | SKPQTQGLAK | DAWEIPRESL | RLEVKLGQGC | FGEVWMGTWN | GTTRVAIKTL |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| KPGTMSPEAF | LQEAQVMKKL | RHEKLVQLYA | VVSEEPIYIV | TEYMSKGSLL | DFLKGETGKY |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| LRLPQLVDMA | AQIASGMAYV | ERMNYVHRDL | RAANILVGEN | LVCKVADFGL | ARLIEDNEYT |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| ARQGAKFPIK | WTAPEAALYG | RFTIKSDVWS | FGILLTELTT | KGRVPYPGMV | NREVLDQVER |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | |
| GYRMPCPPEC | PESLHDLMCQ | CWRKEPEERP | TFEYLQAFLE | DYFTSTEPQY | QPGENL |