P12928
Gene name |
Pklr |
Protein name |
Pyruvate kinase PKLR |
Names |
EC 2.7.1.40 , L-PK , Pyruvate kinase isozymes L/R |
Species |
Rattus norvegicus (Rat) |
KEGG Pathway |
rno:24651 |
EC number |
2.7.1.40: Phosphotransferases with an alcohol group as acceptor |
Protein Class |
|
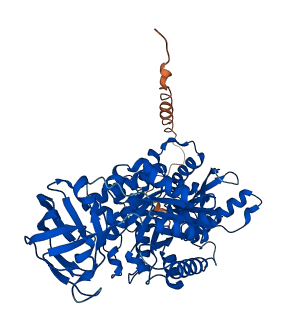
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
86-418 (Pyruvate kinase) |
Relief mechanism |
PTM, Partner binding |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
References
- Yeon JH et al. (2016) "Systems-wide Identification of cis-Regulatory Elements in Proteins", Cell systems, 2, 89-100
- Zhang Z et al. (2019) "PKM2, function and expression and regulation", Cell & bioscience, 9, 52
- Zahra K et al. (2020) "Pyruvate Kinase M2 and Cancer: The Role of PKM2 in Promoting Tumorigenesis", Frontiers in oncology, 10, 159
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

3 structures for P12928
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6ECH | X-ray | 219 A | A/B/C/D | 34-574 | PDB |
| 6ECK | X-ray | 236 A | A/B | 34-574 | PDB |
| AF-P12928-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
1 variants for P12928
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs198543461 | 486 | Q>R | No | EVA |
No associated diseases with P12928
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.1.40 | Phosphotransferases with an alcohol group as acceptor |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
3 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
6 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| kinase activity | Catalysis of the transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a substrate molecule. |
| magnesium ion binding | Binding to a magnesium (Mg) ion. |
| monosaccharide binding | Binding to a monosaccharide. Monosaccharides are the simplest carbohydrates; they are polyhydroxy aldehydes HnC(=O)H or polyhydroxy ketones HnC(=O)mH with three or more carbon atoms. They form the constitutional repeating units of oligo- and polysaccharides. |
| potassium ion binding | Binding to a potassium ion (K+). |
| pyruvate kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction |
12 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cellular response to epinephrine stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an epinephrine stimulus. Epinephrine is a catecholamine that has the formula C9H13NO3; it is secreted by the adrenal medulla to act as a hormone, and released by certain neurons to act as a neurotransmitter active in the central nervous system. |
| cellular response to insulin stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an insulin stimulus. Insulin is a polypeptide hormone produced by the islets of Langerhans of the pancreas in mammals, and by the homologous organs of other organisms. |
| glycolytic process | The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of a carbohydrate into pyruvate, with the concomitant production of a small amount of ATP and the reduction of NAD(P) to NAD(P)H. Glycolysis begins with the metabolism of a carbohydrate to generate products that can enter the pathway and ends with the production of pyruvate. Pyruvate may be converted to acetyl-coenzyme A, ethanol, lactate, or other small molecules. |
| phosphorylation | The process of introducing a phosphate group into a molecule, usually with the formation of a phosphoric ester, a phosphoric anhydride or a phosphoric amide. |
| pyruvate biosynthetic process | The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of pyruvate, 2-oxopropanoate. |
| response to ATP | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an ATP (adenosine 5'-triphosphate) stimulus. |
| response to cAMP | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a cAMP (cyclic AMP, adenosine 3',5'-cyclophosphate) stimulus. |
| response to glucose | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a glucose stimulus. |
| response to hypoxia | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating lowered oxygen tension. Hypoxia, defined as a decline in O2 levels below normoxic levels of 20.8 - 20.95%, results in metabolic adaptation at both the cellular and organismal level. |
| response to metal ion | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a metal ion stimulus. |
| response to nutrient | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a nutrient stimulus. |
| response to other organism | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus from another living organism. |
12 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P52489 | PYK2 | Pyruvate kinase 2 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) | SS |
| P00549 | CDC19 | Pyruvate kinase 1 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) | SS |
| P11979 | PKM | Pyruvate kinase PKM | Felis catus (Cat) (Felis silvestris catus) | SS |
| P00548 | PKM | Pyruvate kinase PKM | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q29536 | PKLR | Pyruvate kinase PKLR | Canis lupus familiaris (Dog) (Canis familiaris) | SS |
| O62619 | PyK | Pyruvate kinase | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| P14618 | PKM | Pyruvate kinase PKM | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P30613 | PKLR | Pyruvate kinase PKLR | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P52480 | Pkm | Pyruvate kinase PKM | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P53657 | Pklr | Pyruvate kinase PKLR | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P11980 | Pkm | Pyruvate kinase PKM | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q9LIK0 | PKP1 | Plastidial pyruvate kinase 1, chloroplastic | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MSVQENTLPQ | QLWPWIFRSQ | KDLAKSALSG | APGGPAGYLR | RASVAQLTQE | LGTAFFQQQQ |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| LPAAMADTFL | EHLCLLDIDS | QPVAARSTSI | IATIGPASRS | VDRLKEMIKA | GMNIARLNFS |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| HGSHEYHAES | IANIREATES | FATSPLSYRP | VAIALDTKGP | EIRTGVLQGG | PESEVEIVKG |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| SQVLVTVDPK | FQTRGDAKTV | WVDYHNITRV | VAVGGRIYID | DGLISLVVQK | IGPEGLVTEV |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| EHGGILGSRK | GVNLPNTEVD | LPGLSEQDLL | DLRFGVQHNV | DIIFASFVRK | ASDVLAVRDA |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| LGPEGQNIKI | ISKIENHEGV | KKFDEILEVS | DGIMVARGDL | GIEIPAEKVF | LAQKMMIGRC |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| NLAGKPVVCA | TQMLESMITK | ARPTRAETSD | VANAVLDGAD | CIMLSGETAK | GSFPVEAVMM |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| QHAIAREAEA | AVYHRQLFEE | LRRAAPLSRD | PTEVTAIGAV | EASFKCCAAA | IIVLTKTGRS |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| AQLLSQYRPR | AAVIAVTRSA | QAARQVHLSR | GVFPLLYREP | PEAIWADDVD | RRVQFGIESG |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | |||
| KLRGFLRVGD | LVIVVTGWRP | GSGYTNIMRV | LSVS |