P12003
Gene name |
VCL (VINC1) |
Protein name |
Vinculin |
Names |
Metavinculin |
Species |
Gallus gallus (Chicken) |
KEGG Pathway |
gga:396422 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
VINCULIN (PTHR46180) |
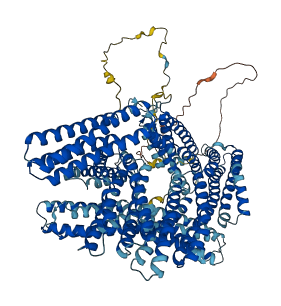
Descriptions
Vinculin is a highly conserved intracellular protein with a crucial role in the maintenance and regulation of cell adhesion and migration. N-terminal globular head (Vh) is composed of subdomains (D1-D4). The C-terminal tail (Vt) binds F-actin. A strap sequence (878-890) between Pro-rich region and Vt packs against the Vt and thereby masks the F-actin-binding domain in Vt.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
896-1066 (Vt domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Ligand binding |
Assay |
Mutagenesis experiment, Structural analysis |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure
Activated structure

16 structures for P12003
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1QKR | X-ray | 180 A | A/B | 879-1135 | PDB |
| 1ST6 | X-ray | 310 A | A | 1-1135 | PDB |
| 1T01 | X-ray | 206 A | A | 1-254 | PDB |
| 1U6H | X-ray | 238 A | A | 1-259 | PDB |
| 1XWJ | X-ray | 260 A | A | 2-259 | PDB |
| 1ZVZ | X-ray | 180 A | A | 2-259 | PDB |
| 1ZW2 | X-ray | 210 A | A | 2-259 | PDB |
| 1ZW3 | X-ray | 330 A | A | 2-259 | PDB |
| 2GDC | X-ray | 274 A | A | 1-266 | PDB |
| 3JBI | EM | 850 A | V | 879-1130 | PDB |
| 3ZDL | X-ray | 230 A | A | 1-259 | PDB |
| 4E17 | X-ray | 230 A | A | 1-259 | PDB |
| 4E18 | X-ray | 240 A | A | 1-259 | PDB |
| 6FQ4 | X-ray | 289 A | A | 1-259 | PDB |
| 6NR7 | X-ray | 300 A | A | 1-1135 | PDB |
| AF-P12003-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
20 variants for P12003
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs1059717185 | 3 | V>A | No | Ensembl | |
| rs739133759 | 39 | D>N | No | Ensembl | |
| rs317315561 | 318 | R>H | No | Ensembl | |
| rs738602965 | 402 | S>R | No | Ensembl | |
| rs731452740 | 540 | D>A | No | Ensembl | |
| rs741660021 | 551 | L>R | No | Ensembl | |
| rs741207127 | 602 | T>P | No | Ensembl | |
| rs733694874 | 604 | T>P | No | Ensembl | |
| rs316607838 | 612 | A>P | No | Ensembl | |
| rs741437392 | 682 | L>P | No | Ensembl | |
| rs733879540 | 683 | L>P | No | Ensembl | |
| rs741323329 | 848 | D>G | No | Ensembl | |
| rs735779422 | 920 | I>F | No | Ensembl | |
| rs739957860 | 928 | V>G | No | Ensembl | |
| rs738211400 | 933 | E>G | No | Ensembl | |
| rs736113463 | 934 | D>G | No | Ensembl | |
| rs315952633 | 942 | L>P | No | Ensembl | |
| rs739496308 | 951 | E>G | No | Ensembl | |
| rs740517948 | 1037 | V>G | No | Ensembl | |
| rs731575335 | 1098 | N>T | No | Ensembl |
No associated diseases with P12003
3 regional properties for P12003
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| conserved_site | Vinculin, conserved site | 162 - 182 | IPR000633-1 |
| conserved_site | Vinculin, conserved site | 277 - 287 | IPR000633-2 |
| conserved_site | Vinculin, conserved site | 497 - 507 | IPR000633-3 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | ||
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | PTHR46180 | VINCULIN |
| PANTHER Subfamily | PTHR46180:SF1 | VINCULIN |
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category |
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor pathway Vinculin Integrin signalling pathway Vinculin |
|
21 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| actin cytoskeleton | The part of the cytoskeleton (the internal framework of a cell) composed of actin and associated proteins. Includes actin cytoskeleton-associated complexes. |
| adherens junction | A cell-cell junction composed of the epithelial cadherin-catenin complex. The epithelial cadherins, or E-cadherins, of each interacting cell extend through the plasma membrane into the extracellular space and bind to each other. The E-cadherins bind to catenins on the cytoplasmic side of the membrane, where the E-cadherin-catenin complex binds to cytoskeletal components and regulatory and signaling molecules. |
| brush border | The dense covering of microvilli on the apical surface of an epithelial cell in tissues such as the intestine, kidney, and choroid plexus; the microvilli aid absorption by increasing the surface area of the cell. |
| cell-cell junction | A cell junction that forms a connection between two or more cells of an organism; excludes direct cytoplasmic intercellular bridges, such as ring canals in insects. |
| costamere | Regular periodic sub membranous arrays of vinculin in skeletal and cardiac muscle cells, these arrays link Z-discs to the sarcolemma and are associated with links to extracellular matrix. |
| fascia adherens | A cell-cell junction that contains the transmembrane protein N-cadherin, which interacts with identical molecules from neighbouring cells to form a tight mechanical intercellular link; forms a large portion of the intercalated disc, the structure at which myofibrils terminate in cardiomyocytes. |
| focal adhesion | A cell-substrate junction that anchors the cell to the extracellular matrix and that forms a point of termination of actin filaments. In insects focal adhesion has also been referred to as hemi-adherens junction (HAJ). |
| inner dense plaque of desmosome | The desmosomal part containing the C-termini of desmoplakins which interact with the keratin intermediate filaments, serving to tether the intermediate filaments to the plasma membrane. |
| mitochondrial inner membrane | The inner, i.e. lumen-facing, lipid bilayer of the mitochondrial envelope. It is highly folded to form cristae. |
| muscle tendon junction | A cell-substrate junction found at the terminal anchorage site of skeletal muscle cells to tendons. |
| neuromuscular junction | The junction between the axon of a motor neuron and a muscle fiber. In response to the arrival of action potentials, the presynaptic button releases molecules of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft. These diffuse across the cleft and transmit the signal to the postsynaptic membrane of the muscle fiber, leading to a change in post-synaptic potential. |
| outer dense plaque of desmosome | The desmosomal part containing plakoglobins, plakophilins, the N-termini of desmoplakins, as well as the cytoplasmic tails of the desmosomal cadherins, which together attach the plaque to the plasma membrane. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| podosome | An actin-rich adhesion structure characterized by formation upon cell substrate contact and localization at the substrate-attached part of the cell, contain an F-actin-rich core surrounded by a ring structure containing proteins such as vinculin and talin, and have a diameter of 0.5 mm. |
| protein-containing complex | A stable assembly of two or more macromolecules, i.e. proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates or lipids, in which at least one component is a protein and the constituent parts function together. |
| sarcolemma | The outer membrane of a muscle cell, consisting of the plasma membrane, a covering basement membrane (about 100 nm thick and sometimes common to more than one fiber), and the associated loose network of collagen fibers. |
| skeletal muscle myofibril | A myofibril of a skeletal muscle fiber. |
| stress fiber | A contractile actin filament bundle that consists of short actin filaments with alternating polarity, cross-linked by alpha-actinin and possibly other actin bundling proteins, and with myosin present in a periodic distribution along the fiber. |
| terminal web | An actin-rich cytoskeletal network located beneath the microvilli of the apical plasma membrane of polarized epithelial cells. In addition to actin filaments, the terminal web may contain actin-binding proteins, myosin motor proteins, and intermediate filaments. The terminal web can function as a contractile structure that influences the spatial distribution of microvilli as well as the development and morphogenesis of tissues containing polarized epithelial cells. |
| Z disc | Platelike region of a muscle sarcomere to which the plus ends of actin filaments are attached. |
| zonula adherens | A cell-cell adherens junction which forms a continuous belt near the apex of epithelial cells. |
12 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| actin filament binding | Binding to an actin filament, also known as F-actin, a helical filamentous polymer of globular G-actin subunits. |
| alpha-actinin binding | Binding to alpha-actinin, one of a family of proteins that cross-link F-actin as antiparallel homodimers. Alpha-actinin has a molecular mass of 93-103 KDa; at the N-terminus there are two calponin homology domains, at the C-terminus there are two EF-hands. These two domains are connected by the rod domain. This domain is formed by triple-helical spectrin repeats. |
| alpha-catenin binding | Binding to catenin complex alpha subunit. |
| beta-catenin binding | Binding to a catenin beta subunit. |
| cadherin binding | Binding to cadherin, a type I membrane protein involved in cell adhesion. |
| dystroglycan binding | Binding to dystroglycan, a glycoprotein found in non-muscle tissues as well as in muscle tissues, often in association with dystrophin. The native dystroglycan cleaved into two non-covalently associated subunits, alpha (N-terminal) and beta (C-terminal). |
| muscle alpha-actinin binding | Binding to muscle isoforms of actinin. Muscle alpha-actinin isoforms are found in skeletal and cardiac muscle and are localized to the Z-disc. |
| protein homodimerization activity | Binding to an identical protein to form a homodimer. |
| scaffold protein binding | Binding to a scaffold protein. Scaffold proteins are crucial regulators of many key signaling pathways. Although not strictly defined in function, they are known to interact and/or bind with multiple members of a signaling pathway, tethering them into complexes. |
| structural molecule activity | The action of a molecule that contributes to the structural integrity of a complex or its assembly within or outside a cell. |
| ubiquitin protein ligase binding | Binding to a ubiquitin protein ligase enzyme, any of the E3 proteins. |
| vinculin binding | Binding to vinculin, a protein found in muscle, fibroblasts, and epithelial cells that binds actin and appears to mediate attachment of actin filaments to integral proteins of the plasma membrane. |
11 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| adherens junction assembly | The aggregation, arrangement and bonding together of a set of components to form an adherens junction. An adherens junction is a cell-cell junction composed of the epithelial cadherin-catenin complex at which the cytoplasmic face of the plasma membrane is attached to actin filaments. |
| apical junction assembly | The formation of an apical junction, a functional unit located near the cell apex at the points of contact between epithelial cells composed of the tight junction, the zonula adherens junction and the desmosomes, by the aggregation, arrangement and bonding together of its constituents. |
| axon extension | Long distance growth of a single axon process involved in cellular development. |
| epithelial cell-cell adhesion | The attachment of an epithelial cell to another epithelial cell via adhesion molecules. |
| lamellipodium assembly | Formation of a lamellipodium, a thin sheetlike extension of the surface of a migrating cell. |
| morphogenesis of an epithelium | The process in which the anatomical structures of epithelia are generated and organized. An epithelium consists of closely packed cells arranged in one or more layers, that covers the outer surfaces of the body or lines any internal cavity or tube. |
| protein localization to cell surface | A process in which a protein is transported to, or maintained in, a location within the external part of the cell wall and/or plasma membrane. |
| regulation of cell migration | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell migration. |
| regulation of establishment of endothelial barrier | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of establishment of endothelial barrier. |
| regulation of focal adhesion assembly | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of focal adhesion formation, the establishment and maturation of focal adhesions. |
| regulation of protein localization to adherens junction | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of protein localization to adherens junction. An adherens junction is a cell-cell junction composed of the epithelial cadherin-catenin complex at which the cytoplasmic face of the plasma membrane is attached to actin filaments. |
16 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q3MHM6 | CTNNA1 | Catenin alpha-1 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| P30997 | CTNNA2 | Catenin alpha-2 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P35220 | alpha-Cat | Catenin alpha | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| P35221 | CTNNA1 | Catenin alpha-1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P26232 | CTNNA2 | Catenin alpha-2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q9UI47 | CTNNA3 | Catenin alpha-3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P18206 | VCL | Vinculin | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P26231 | Ctnna1 | Catenin alpha-1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| Q65CL1 | Ctnna3 | Catenin alpha-3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| Q61301 | Ctnna2 | Catenin alpha-2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| Q64727 | Vcl | Vinculin | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P26234 | VCL | Vinculin | Sus scrofa (Pig) | SS |
| P85972 | Vcl | Vinculin | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P90947 | hmp-1 | Alpha-catenin-like protein hmp-1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| A4IGI7 | ctnna2 | Catenin alpha-2 | Xenopus tropicalis (Western clawed frog) (Silurana tropicalis) | SS |
| B7ZC77 | Ctnna2 | Catenin alpha-2 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MPVFHTRTIE | SILEPVAQQI | SHLVIMHEEG | EVDGKAIPDL | TAPVSAVQAA | VSNLVRVGKE |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| TVQTTEDQIL | KRDMPPAFIK | VENACTKLVR | AAQMLQADPY | SVPARDYLID | GSRGILSGTS |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| DLLLTFDEAE | VRKIIRVCKG | ILEYLTVAEV | VETMEDLVTY | TKNLGPGMTK | MAKMIDERQQ |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| ELTHQEHRVM | LVNSMNTVKE | LLPVLISAMK | IFVTTKNTKS | QGIEEALKNR | NFTVEKMSAE |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| INEIIRVLQL | TSWDEDAWAS | KDTEAMKRAL | ALIDSKMNQA | KGWLRDPNAP | PGDAGEQAIR |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| QILDEAGKAG | ELCAGKERRE | ILGTCKTLGQ | MTDQLADLRA | RGQGATPMAM | QKAQQVSQGL |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| DLLTAKVENA | ARKLEAMTNS | KQAIAKKIDA | AQNWLADPNG | GSEGEEHIRG | IMSEARKVAE |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| LCEEPKERDD | ILRSLGEISA | LTAKLSDLRR | HGKGDSPEAR | ALAKQIATSL | QNLQSKTNRA |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| VANTRPVKAA | VHLEGKIEQA | QRWIDNPTVD | DRGVGQAAIR | GLVAEGRRLA | NVMMGPYRQD |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| LLAKCDRVDQ | LAAQLADLAA | RGEGESPQAR | AIAAQLQDSL | KDLKARMQEA | MTQEVSDVFS |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| DTTTPIKLLA | VAATAPSDTP | NREEVFEERA | ANFENHAARL | GATAEKAAAV | GTANKTTVEG |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| IQATVKSARE | LTPQVVSAAR | ILLRNPGNQA | AYEHFETMKN | QWIDNVEKMT | GLVDEAIDTK |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| SLLDASEEAI | KKDLDKCKVA | MANMQPQMLV | AGATSIARRA | NRILLVAKRE | VENSEDPKFR |
| 790 | 800 | 810 | 820 | 830 | 840 |
| EAVKAASDEL | SKTISPMVMD | AKAVAGNISD | PGLQKSFLDS | GYRILGAVAK | VREAFQPQEP |
| 850 | 860 | 870 | 880 | 890 | 900 |
| DFPPPPPDLE | HLHLTDELAP | PKPPLPEGEV | PPPRPPPPEE | KDEEFPEQKA | GEAINQPMMM |
| 910 | 920 | 930 | 940 | 950 | 960 |
| AARQLHDEAR | KWSSKPVTVI | NEAAEAGVDI | DEEDDADVEF | SLPSDIEDDY | EPELLLMPTN |
| 970 | 980 | 990 | 1000 | 1010 | 1020 |
| QPVNQPILAA | AQSLHREATK | WSSKGNDIIA | AAKRMALLMA | EMSRLVRGGS | GNKRALIQCA |
| 1030 | 1040 | 1050 | 1060 | 1070 | 1080 |
| KDIAKASDEV | TRLAKEVAKQ | CTDKRIRTNL | LQVCERIPTI | STQLKILSTV | KATMLGRTNI |
| 1090 | 1100 | 1110 | 1120 | 1130 | |
| SDEESEQATE | MLVHNAQNLM | QSVKETVREA | EAASIKIRTD | AGFTLRWVRK | TPWYQ |