P11346
Gene name |
Raf |
Protein name |
Raf homolog serine/threonine-protein kinase Raf |
Names |
D-Raf, dRAF-1, Protein pole-hole |
Species |
Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) |
KEGG Pathway |
dme:Dmel_CG2845 |
EC number |
2.7.11.1: Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
Protein Class |
|
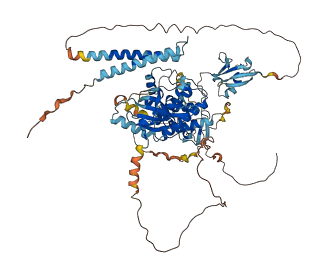
Descriptions
(Annotation based on sequence homology with P04049)
Raf proteins are Ras-regulated serine/threonine protein kinases that control the activation of the ERK/MARK cascade, and consists of three isoforms, A-Raf, B-Raf, and Raf-1 (C-Raf). When the catalytic domain of Raf-1 is expressed alone, it exhibits a constitutive activity. Raf-1 is regulated by an N-terminal autoinhibitory domain including Ras binding domain (RBD) and cysteine-rich domain (CRD). The autoinhibitory region blocks the catalytic kinase domain and the autoinhibition is interrupted by the interaction with active PAK1 or Src.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
565-590 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
429-690 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for P11346
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-P11346-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
4 variants for P11346
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 322 | P>L | strain: AA1 [UniProt] | No | ||
| 327 | S>T | strain: KLH4 and KLH6 [UniProt] | No | ||
| 360 | S>R | strain: Reids2 [UniProt] | No | ||
| 465 | A>T | strain: 5-17-88b#5 [UniProt] | No |
No associated diseases with P11346
6 regional properties for P11346
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Protein kinase domain | 429 - 690 | IPR000719 |
| domain | Serine-threonine/tyrosine-protein kinase, catalytic domain | 432 - 685 | IPR001245 |
| domain | Protein kinase C-like, phorbol ester/diacylglycerol-binding domain | 222 - 269 | IPR002219 |
| domain | Raf-like Ras-binding | 141 - 212 | IPR003116 |
| active_site | Serine/threonine-protein kinase, active site | 544 - 556 | IPR008271 |
| binding_site | Protein kinase, ATP binding site | 435 - 455 | IPR017441 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.11.1 | Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
3 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
6 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| kinase binding | Binding to a kinase, any enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group. |
| MAP kinase kinase kinase activity | Catalysis of the phosphorylation and activation of a MAP kinase kinase; each MAP kinase kinase can be phosphorylated by any of several MAP kinase kinase kinases. |
| metal ion binding | Binding to a metal ion. |
| protein serine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate. |
| protein serine/threonine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate, and ATP + protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate. |
37 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| border follicle cell migration | The directed movement of a border cell through the nurse cells to reach the oocyte. An example of this is found in Drosophila melanogaster. |
| cellular response to starvation | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of deprivation of nourishment. |
| compound eye photoreceptor development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a light-responsive receptor in the compound eye over time, from its formation to the mature structure. |
| dorsal appendage formation | Establishment of the dorsal filaments, elaborate specializations of the chorion that protrude from the anterior end of the egg and facilitate embryonic respiration. |
| dorsal/ventral axis specification, ovarian follicular epithelium | Polarization of the ovarian follicle cells along the dorsal/ventral axis. An example of this process is found in Drosophila melanogaster. |
| epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by binding of a ligand to the tyrosine kinase receptor EGFR (ERBB1) on the surface of a cell. The pathway ends with regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| epithelial cell migration, open tracheal system | The orderly movement of epithelial cells during development of an open tracheal system. An example of this is found in Drosophila melanogaster. |
| ERK1 and ERK2 cascade | An intracellular protein kinase cascade containing at least ERK1 or ERK2 (MAPKs), a MEK (a MAPKK) and a MAP3K. The cascade may involve 4 different kinases, as it can also contain an additional tier: the upstream MAP4K. The kinases in each tier phosphorylate and activate the kinase in the downstream tier to transmit a signal within a cell. |
| fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals generated as a consequence of a fibroblast growth factor receptor binding to one of its physiological ligands. |
| gastrulation | A complex and coordinated series of cellular movements that occurs at the end of cleavage during embryonic development of most animals. The details of gastrulation vary from species to species, but usually result in the formation of the three primary germ layers, ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm. |
| hemocyte differentiation | The process in which a relatively unspecialized cell acquires the characteristics of a mature hemocyte. Hemocytes are blood cells associated with a hemocoel (the cavity containing most of the major organs of the arthropod body) which are involved in defense and clotting of hemolymph, but not involved in transport of oxygen. |
| imaginal disc-derived wing morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structures of the imaginal disc-derived wing are generated and organized. The wing is an appendage modified for flying. |
| imaginal disc-derived wing vein specification | The regionalization process in which the area of a imaginal disc-derived wing that will form a wing vein is specified. |
| instar larval development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the larva over time, from its formation to the mature structure. This begins with the newly hatched first-instar larva, through its maturation to the end of the last larval stage. An example of this process is found in Drosophila melanogaster. |
| lamellocyte differentiation | The process in which a relatively unspecialized hemocyte precursor cell acquires the specialized features of a lamellocyte. Lamellocytes are a hemocyte lineage that exists only in larvae, but are seldom observed in healthy animals. Lamellocytes differentiate massively in the lymph glands after parasitization and are large flat cells devoted to encapsulation of invaders too large to be phagocytosed by plasmatocytes. |
| MAPK cascade | An intracellular protein kinase cascade containing at least a MAPK, a MAPKK and a MAP3K. The cascade can also contain an additional tiers: the upstream MAP4K. The kinases in each tier phosphorylate and activate the kinase in the downstream tier to transmit a signal within a cell. |
| metamorphosis | A biological process in which an animal physically develops after birth or hatching, involving a conspicuous and relatively abrupt change in the animal's form or structure. Examples include the change from tadpole to frog, and the change from larva to adult. An example of this is found in Drosophila melanogaster. |
| negative regulation of apoptotic signaling pathway | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of apoptotic signaling pathway. |
| negative regulation of macroautophagy | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of macroautophagy. |
| photoreceptor cell development | Development of a photoreceptor, a cell that responds to incident electromagnetic radiation, particularly visible light. |
| photoreceptor cell differentiation | The specialization of organization of a photoreceptor, a cell that responds to incident electromagnetic radiation, particularly visible light. An example of this process is found in Drosophila melanogaster. |
| positive regulation of cell population proliferation | Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of cell proliferation. |
| positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction mediated by the ERK1 and ERK2 cascade. |
| positive regulation of photoreceptor cell differentiation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of photoreceptor cell differentiation. An example of this process is found in Drosophila melanogaster. |
| protein autophosphorylation | The phosphorylation by a protein of one or more of its own amino acid residues (cis-autophosphorylation), or residues on an identical protein (trans-autophosphorylation). |
| R7 cell fate commitment | The process in which the R7 photoreceptor commits to its cell fate. The R7 receptor contributes the central part of the rhabdomere in the apical parts of the ommatidium. |
| Ras protein signal transduction | The series of molecular signals within the cell that are mediated by a member of the Ras superfamily of proteins switching to a GTP-bound active state. |
| regulation of cellular pH | Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal equilibrium of hydrogen ions (protons) within a cell or between a cell and its external environment. |
| regulation of multicellular organism growth | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of growth of the body of an organism so that it reaches its usual body size. |
| sevenless signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by an extracellular ligand binding to sevenless (sev; a receptor tyrosine kinase) on the surface of a target cell, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| spermatogenesis | The developmental process by which male germ line stem cells self renew or give rise to successive cell types resulting in the development of a spermatozoa. |
| terminal branching, open tracheal system | Formation of terminal branches in the open tracheal system. These are long cytoplasmic extensions that form fine tubules that transport oxygen directly to the tissues. An example of the process is found in Drosophila melanogaster. |
| terminal region determination | Specification of the terminal regions (the two non-segmented ends) of the embryo by the gap genes; exemplified in insects by the actions of huckebein and tailless gene products. |
| torso signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by an extracellular ligand binding to torso (a receptor tyrosine kinase) on the surface of a target cell, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by a ligand binding to a vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) on the surface of the target cell, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| wing and notum subfield formation | The regionalization process that subdivides the wing imaginal disc into the wing and notum (body wall) subfields, thus determining whether cells ultimately differentiate wing or notum-specific structures. |
| wing disc morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structures derived from the wing disc are generated and organized. This includes the transformation of a wing imaginal disc from a monolayered epithelium in the larvae of holometabolous insects into recognizable adult structures including the wing hinge, wing blade and pleura. |
18 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A7E3S4 | RAF1 | RAF proto-oncogene serine/threonine-protein kinase | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| P05625 | RAF1 | RAF proto-oncogene serine/threonine-protein kinase | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | PR |
| Q04982 | BRAF | Serine/threonine-protein kinase B-raf | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q95UN8 | slpr | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | EV |
| P15056 | BRAF | Serine/threonine-protein kinase B-raf | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P04049 | RAF1 | RAF proto-oncogene serine/threonine-protein kinase | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P10398 | ARAF | Serine/threonine-protein kinase A-Raf | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q8NB16 | MLKL | Mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P04627 | Araf | Serine/threonine-protein kinase A-Raf | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q99N57 | Raf1 | RAF proto-oncogene serine/threonine-protein kinase | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q9D2Y4 | Mlkl | Mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P28028 | Braf | Serine/threonine-protein kinase B-raf | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| O19004 | ARAF | Serine/threonine-protein kinase A-Raf | Sus scrofa (Pig) | PR |
| P11345 | Raf1 | RAF proto-oncogene serine/threonine-protein kinase | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P14056 | Araf | Serine/threonine-protein kinase A-Raf | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q07292 | lin-45 | Raf homolog serine/threonine-protein kinase | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| Q9FPR3 | EDR1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase EDR1 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q05609 | CTR1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase CTR1 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MSSESSTEGD | SDLYDPLAEE | LHNVQLVKHV | TRENIDALNA | KFANLQEPPA | MYLIEYQELT |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| SKLHELEAKE | QELMERLNSQ | DQQEDSSLVE | RFKEQPHYQN | QTQILQQQRQ | LARVHHGNDL |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| TDSLGSQPGS | QCGTLTRQPK | ILLRAHLPNQ | QRTSVEVISG | VRLCDALMKA | LKLRQLTPDM |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| CEVSTTHSGR | HIIPWHTDIG | TLHVEEIFVR | LLDKFPIRTH | IKHQIIRKTF | FSLVFCEGCR |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| RLLFTGFYCS | QCNFRFHQRC | ANRVPMLCQP | FPMDSYYQLL | LAENPDNGVG | FPGRGTAVRF |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| NMSSRSRSRR | CSSSGSSSSS | KPPSSSSGNH | RQGRPPRISQ | DDRSNSAPNV | CINNIRSVTS |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| EVQRSLIMQA | RPPLPHPCTD | HSNSTQASPT | STLKHNRPRA | RSADESNKNL | LLRDAKSSEE |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| NWNILAEEIL | IGPRIGSGSF | GTVYRAHWHG | PVAVKTLNVK | TPSPAQLQAF | KNEVAMLKKT |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| RHCNILLFMG | CVSKPSLAIV | TQWCEGSSLY | KHVHVSETKF | KLNTLIDIGR | QVAQGMDYLH |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| AKNIIHRDLK | SNNIFLHEDL | SVKIGDFGLA | TAKTRWSGEK | QANQPTGSIL | WMAPEVIRMQ |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| ELNPYSFQSD | VYAFGIVMYE | LLAECLPYGH | ISNKDQILFM | VGRGLLRPDM | SQVRSDAPQA |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| LKRLAEDCIK | YTPKDRPLFR | PLLNMLENML | RTLPKIHRSA | SEPNLTQSQL | QNDEFLYLPS |
| 730 | |||||
| PKTPVNFNNF | QFFGSAGNI |