P11345
Gene name |
Raf1 (Raf) |
Protein name |
RAF proto-oncogene serine/threonine-protein kinase |
Names |
Proto-oncogene c-RAF, cRaf, Raf-1 |
Species |
Rattus norvegicus (Rat) |
KEGG Pathway |
rno:24703 |
EC number |
2.7.11.1: Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
Protein Class |
|
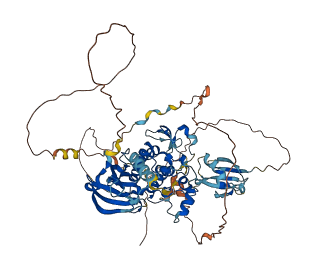
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
349-609 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
PTM |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
485-510 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
349-609 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
References
- Cutler RE Jr et al. (1998) "Autoregulation of the Raf-1 serine/threonine kinase", Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 95, 9214-9
- Tran NH et al. (2005) "B-Raf and Raf-1 are regulated by distinct autoregulatory mechanisms", The Journal of biological chemistry, 280, 16244-53
- Tran NH et al. (2003) "Phosphorylation of Raf-1 by p21-activated kinase 1 and Src regulates Raf-1 autoinhibition", The Journal of biological chemistry, 278, 11221-6
- Niault T et al. (2009) "From autoinhibition to inhibition in trans: the Raf-1 regulatory domain inhibits Rok-alpha kinase activity", The Journal of cell biology, 187, 335-42
- Zhang M et al. (2021) "B-Raf autoinhibition in the presence and absence of 14-3-3", Structure (London, England : 1993), 29, 768-777.e2
- Nussinov R et al. (2018) "Autoinhibition in Ras effectors Raf, PI3Kα, and RASSF5: a comprehensive review underscoring the challenges in pharmacological intervention", Biophysical reviews, 10, 1263-1282
- Hmitou I et al. (2007) "Differential regulation of B-raf isoforms by phosphorylation and autoinhibitory mechanisms", Molecular and cellular biology, 27, 31-43
- Hubbard SR (2004) "Oncogenic mutations in B-Raf: some losses yield gains", Cell, 116, 764-6
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

2 structures for P11345
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1RRB | NMR | - | A | 51-131 | PDB |
| AF-P11345-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for P11345
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for P11345 | |||||
No associated diseases with P11345
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.11.1 | Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
7 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| Golgi apparatus | A membrane-bound cytoplasmic organelle of the endomembrane system that further processes the core oligosaccharides (e.g. N-glycans) added to proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum and packages them into membrane-bound vesicles. The Golgi apparatus operates at the intersection of the secretory, lysosomal, and endocytic pathways. |
| mitochondrion | A semiautonomous, self replicating organelle that occurs in varying numbers, shapes, and sizes in the cytoplasm of virtually all eukaryotic cells. It is notably the site of tissue respiration. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| pseudopodium | A temporary protrusion or retractile process of a cell, associated with flowing movements of the protoplasm, and serving for locomotion and feeding. |
14 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| adenylate cyclase activator activity | Increases the activity of the enzyme that catalyzes the reaction: ATP = 3',5'-cyclic AMP + diphosphate. |
| adenylate cyclase binding | Binding to an adenylate cyclase. |
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| enzyme binding | Binding to an enzyme, a protein with catalytic activity. |
| identical protein binding | Binding to an identical protein or proteins. |
| MAP kinase kinase kinase activity | Catalysis of the phosphorylation and activation of a MAP kinase kinase; each MAP kinase kinase can be phosphorylated by any of several MAP kinase kinase kinases. |
| metal ion binding | Binding to a metal ion. |
| mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase binding | Binding to a mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase, a protein that can phosphorylate a MAP kinase. |
| protein kinase activity | Catalysis of the phosphorylation of an amino acid residue in a protein, usually according to the reaction: a protein + ATP = a phosphoprotein + ADP. |
| protein serine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate. |
| protein serine/threonine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate, and ATP + protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate. |
| protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + a protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate; ATP + a protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate; and ATP + a protein tyrosine = ADP + protein tyrosine phosphate. |
| protein-containing complex binding | Binding to a macromolecular complex. |
| small GTPase binding | Binding to a small monomeric GTPase. |
25 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| activation of adenylate cyclase activity | Any process that initiates the activity of the inactive enzyme adenylate cyclase. |
| cell differentiation | The process in which relatively unspecialized cells, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cells, acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate and its subsequent development to the mature state. |
| cellular glucose homeostasis | A cellular homeostatic process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady state of glucose within a cell or between a cell and its external environment. |
| death-inducing signaling complex assembly | A process of protein complex assembly in which the arrangement and bonding together of the set of components that form the protein complex is mediated by a death domain (DD) interaction, as part of the extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway. |
| face development | The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a face from an initial condition to its mature state. The face is the ventral division of the head. |
| heart development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the heart over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The heart is a hollow, muscular organ, which, by contracting rhythmically, keeps up the circulation of the blood. |
| insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus | The regulated release of proinsulin from secretory granules (B granules) in the B cells of the pancreas; accompanied by cleavage of proinsulin to form mature insulin, in response to a glucose stimulus. |
| intermediate filament cytoskeleton organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures comprising intermediate filaments and their associated proteins. |
| intracellular signal transduction | The process in which a signal is passed on to downstream components within the cell, which become activated themselves to further propagate the signal and finally trigger a change in the function or state of the cell. |
| MAPK cascade | An intracellular protein kinase cascade containing at least a MAPK, a MAPKK and a MAP3K. The cascade can also contain an additional tiers: the upstream MAP4K. The kinases in each tier phosphorylate and activate the kinase in the downstream tier to transmit a signal within a cell. |
| negative regulation of apoptotic process | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cell death by apoptotic process. |
| negative regulation of cell population proliferation | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the rate or extent of cell proliferation. |
| negative regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway via death domain receptors | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway via death domain receptors. |
| negative regulation of protein-containing complex assembly | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of protein complex assembly. |
| neurotrophin TRK receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by neurotrophin binding to its receptor on the surface of a target cell where the receptor possesses tyrosine kinase activity, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| positive regulation of MAPK cascade | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction mediated by the MAPK cascade. |
| positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the phosphorylation of peptidyl-serine. |
| positive regulation of protein phosphorylation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of addition of phosphate groups to amino acids within a protein. |
| positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription from an RNA polymerase II promoter. |
| protein phosphorylation | The process of introducing a phosphate group on to a protein. |
| response to hypoxia | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating lowered oxygen tension. Hypoxia, defined as a decline in O2 levels below normoxic levels of 20.8 - 20.95%, results in metabolic adaptation at both the cellular and organismal level. |
| response to muscle stretch | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a myofibril being extended beyond its slack length. |
| somatic stem cell population maintenance | Any process by which an organism retains a population of somatic stem cells, undifferentiated cells in the embryo or adult which can undergo unlimited division and give rise to cell types of the body other than those of the germ-line. |
| thymus development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the thymus over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The thymus is a symmetric bi-lobed organ involved primarily in the differentiation of immature to mature T cells, with unique vascular, nervous, epithelial, and lymphoid cell components. |
| thyroid gland development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the thyroid gland over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The thyroid gland is an endoderm-derived gland that produces thyroid hormone. |
18 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A7E3S4 | RAF1 | RAF proto-oncogene serine/threonine-protein kinase | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| Q04982 | BRAF | Serine/threonine-protein kinase B-raf | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P05625 | RAF1 | RAF proto-oncogene serine/threonine-protein kinase | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | PR |
| P11346 | Raf | Raf homolog serine/threonine-protein kinase Raf | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | PR |
| P15056 | BRAF | Serine/threonine-protein kinase B-raf | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P10398 | ARAF | Serine/threonine-protein kinase A-Raf | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P04049 | RAF1 | RAF proto-oncogene serine/threonine-protein kinase | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P04627 | Araf | Serine/threonine-protein kinase A-Raf | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P28028 | Braf | Serine/threonine-protein kinase B-raf | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q99N57 | Raf1 | RAF proto-oncogene serine/threonine-protein kinase | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| O19004 | ARAF | Serine/threonine-protein kinase A-Raf | Sus scrofa (Pig) | PR |
| P14056 | Araf | Serine/threonine-protein kinase A-Raf | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q66HA1 | Map3k11 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 11 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| D3ZG83 | Map3k10 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 10 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q07292 | lin-45 | Raf homolog serine/threonine-protein kinase | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| Q9FPR3 | EDR1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase EDR1 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q2MHE4 | HT1 | Serine/threonine/tyrosine-protein kinase HT1 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q05609 | CTR1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase CTR1 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MEHIQGAWKT | ISNGFGLKDA | VFDGSSCISP | TIVQQFGYQR | RASDDGKLTD | SSKTSNTIRV |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| FLPNKQRTVV | NVRNGMSLHD | CLMKALKVRG | LQPECCAVFR | LLQEHKGKKA | RLDWNTDAAS |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| LIGEELQVDF | LDHVPLTTHN | FARKTFLKLA | FCDICQKFLL | NGFRCQTCGY | KFHEHCSTKV |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| PTMCVDWSNI | RQLLLFPNST | ASDSGVPAPP | SFTMRRMRES | VSRMPASSQH | RYSTPHAFTF |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| NTSSPSSEGS | LSQRQRSTST | PNVHMVSTTL | PVDSRMIEDA | IRSHSESASP | SALSSSPNNL |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| SPTGWSQPKT | PVPAQRERAP | GSGTQEKNKI | RPRGQRDSSY | YWEIEASEVM | LSTRIGSGSF |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| GTVYKGKWHG | DVAVKILKVV | DPTPEQLQAF | RNEVAVLRKT | RHVNILLFMG | YMTKDNLAIV |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| TQWCEGSSLY | KHLHVQETKF | QMFQLIDIAR | QTAQGMDYLH | AKNIIHRDMK | SNNIFLHEGL |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| TVKIGDFGLA | TVKSRWSGSQ | QVEQPTGSVL | WMAPEVIRMQ | DNNPFSFQSD | VYSYGIVLYE |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| LMTGELPYSH | INNRDQIIFM | VGRGYASPDL | SRLYKNCPKA | MKRLVADCVK | KVKEERPLFP |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | ||
| QILSSIELLQ | HSLPKINRSA | SEPSLHRAAH | TEDINACTLT | TSPRLPVF |