P11233
Gene name |
RALA (RAL) |
Protein name |
Ras-related protein Ral-A |
Names |
|
Species |
Homo sapiens (Human) |
KEGG Pathway |
hsa:5898 |
EC number |
3.6.5.2: Acting on GTP; involved in cellular and subcellular movement |
Protein Class |
|
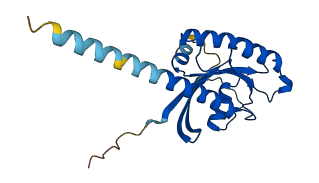
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

17 structures for P11233
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1UAD | X-ray | 210 A | A/B | 9-183 | PDB |
| 1ZC3 | X-ray | 200 A | A/C | 9-183 | PDB |
| 1ZC4 | X-ray | 250 A | A/C | 9-183 | PDB |
| 2A78 | X-ray | 181 A | A | 9-183 | PDB |
| 2A9K | X-ray | 173 A | A | 9-183 | PDB |
| 2BOV | X-ray | 266 A | A | 1-206 | PDB |
| 6P0I | X-ray | 118 A | B | 1-178 | PDB |
| 6P0J | X-ray | 131 A | B | 1-178 | PDB |
| 6P0K | X-ray | 149 A | B | 1-178 | PDB |
| 6P0L | X-ray | 130 A | B | 1-178 | PDB |
| 6P0M | X-ray | 150 A | B | 1-178 | PDB |
| 6P0N | X-ray | 163 A | B | 1-178 | PDB |
| 6P0O | X-ray | 154 A | B | 1-178 | PDB |
| 7NQC | NMR | - | B | 187-203 | PDB |
| 8FJH | X-ray | 154 A | B | 1-178 | PDB |
| 8FJI | X-ray | 148 A | B | 1-178 | PDB |
| AF-P11233-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
72 variants for P11233
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VAR_085759 | 25 | V>L | HINCONS; decreased GTPase activity; decreased RALA effector binding [UniProt] | Yes | UniProt |
|
VAR_085760 RCV000623667 RCV000656548 RCV001380398 CA367304555 rs1554297905 RCV001526588 |
25 | V>M | Intellectual disability Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. Inborn genetic diseases Hiatt-Neu-Cooper neurodevelopmental syndrome HINCONS; decreased GTPase activity; decreased RALA effector binding [ClinVar, NCI-TCGA, UniProt] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar UniProt Ensembl NCI-TCGA dbSNP |
| VAR_085761 | 128 | K>R | HINCONS [UniProt] | Yes | UniProt |
| VAR_085762 | 130 | D>G | HINCONS; decreased GTPase activity; decreased RALA effector binding [UniProt] | Yes | UniProt |
| VAR_085763 | 157 | S>A | HINCONS; decreased GTPase activity; increased RALA effector binding [UniProt] | Yes | UniProt |
| VAR_085764 | 158 | A>del | HINCONS; unknown pathological significance [UniProt] | Yes | UniProt |
| VAR_085765 | 176 | R>del | HINCONS; unknown pathological significance [UniProt] | Yes | UniProt |
|
CA4228188 rs148748965 |
2 | A>T | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA367304441 rs1583749635 |
8 | G>R | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA4228189 rs773729121 |
15 | H>Y | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs761038297 CA4228190 |
16 | K>R | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs199965004 CA4228191 |
19 | M>V | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs202208612 CA157680738 |
27 | K>R | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes |
|
|
CA4228194 rs765338145 |
37 | D>N | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
| TCGA novel | 43 | Y>H | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
|
rs779790125 CA4228221 |
57 | L>I | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
| TCGA novel | 61 | E>K | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
|
rs925401675 CA367305130 |
64 | I>M | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA157681135 rs868072378 |
65 | D>N | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
| TCGA novel | 69 | T>I | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
|
rs199637067 CA157681136 |
74 | D>G | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes |
|
|
CA367305211 rs1439954793 |
76 | A>T | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1174857880 CA367305247 COSM3832759 |
81 | N>S | Variant assessed as Somatic; 0.0 impact. breast [NCI-TCGA, Cosmic] | No |
ClinGen cosmic curated NCI-TCGA gnomAD |
|
rs1422580576 CA367305317 |
91 | C>F | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1422580576 CA367305319 |
91 | C>Y | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs746173249 CA4228228 |
98 | M>R | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA157681137 rs1053085090 |
101 | F>C | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1403612922 CA367305405 |
104 | T>A | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA367305409 rs1446667992 |
104 | T>I | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA4228229 rs770007567 |
105 | A>T | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA4228246 rs746261267 |
117 | D>N | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1467908386 CA367306136 |
118 | E>D | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs998666233 CA157681774 |
121 | P>A | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA367306173 rs998666233 |
121 | P>S | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
| TCGA novel | 123 | L>I | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
|
RCV001092565 rs1792929407 |
130 | D>E | No |
ClinVar dbSNP |
|
| TCGA novel | 131 | L>S | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
|
CA367306325 rs1562625749 |
132 | E>D | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA157681776 rs755490850 COSM601112 |
134 | K>E | lung Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [Cosmic, NCI-TCGA] | No |
ClinGen cosmic curated Ensembl NCI-TCGA |
|
rs1268255721 CA367306384 |
136 | Q>H | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA367306389 rs1426487923 |
137 | V>I | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs144758382 CA4228248 |
139 | V>A | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs905148563 CA157681777 |
139 | V>I | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs905148563 CA367306413 |
139 | V>L | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs749579357 CA4228249 |
144 | N>I | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
| TCGA novel | 150 | N>S | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
|
rs1182241643 CA367306626 |
154 | V>L | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA367306697 rs1279842543 |
159 | K>T | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1341106770 CA367306723 |
161 | R>Q | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs777203688 CA157681778 |
162 | A>V | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs954149915 CA157681779 |
166 | K>R | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs778965935 CA4228273 |
167 | V>I | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs778965935 CA367307138 |
167 | V>L | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1276921611 CA367307160 |
170 | D>Y | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA367307180 rs1314503939 |
172 | M>I | Variant assessed as Somatic; 0.0 impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No |
ClinGen NCI-TCGA gnomAD |
|
COSM136597 RCV000613992 CA367307205 rs1204820978 |
176 | R>* | large_intestine Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. endometrium skin [Cosmic, NCI-TCGA] | No |
ClinGen cosmic curated ClinVar NCI-TCGA TOPMed dbSNP gnomAD |
|
CA367307204 rs1204820978 |
176 | R>G | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1237668380 CA367307207 |
176 | R>Q | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA367307209 rs1456452448 |
177 | A>T | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA4228275 rs772097468 |
177 | A>V | Variant assessed as Somatic; 0.0 impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No |
ClinGen ExAC NCI-TCGA gnomAD |
|
rs770974524 CA4228278 |
180 | M>I | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA4228277 rs747006447 |
180 | M>L | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
| TCGA novel | 183 | S>G | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
|
rs1029615410 CA157682751 |
183 | S>N | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
| TCGA novel | 186 | K>M | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
|
CA4228279 rs375520261 |
190 | K>N | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
| rs1169805854 | 190 | K>R | Variant assessed as Somatic; 0.0 impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
|
rs774954955 CA4228282 |
194 | S>G | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA157682753 rs1008860129 |
197 | K>Q | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
COSM1089525 CA367307366 rs1433814025 |
198 | R>I | Variant assessed as Somatic; 0.0 impact. endometrium [NCI-TCGA, Cosmic] | No |
ClinGen cosmic curated NCI-TCGA gnomAD |
|
CA367307368 rs1273472125 |
198 | R>S | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
| TCGA novel | 201 | E>K | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
1 associated diseases with P11233
[MIM: 619311]: Hiatt-Neu-Cooper neurodevelopmental syndrome (HINCONS)
An autosomal dominant neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by global developmental delay, delayed walking or inability to walk, impaired intellectual development, poor or absent speech, axial hypotonia, and facial dysmorphism. Additional variable features may include seizures, autistic or behavioral abnormalities, and brain abnormalities. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30500825, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30761613}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.
Without disease ID
- An autosomal dominant neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by global developmental delay, delayed walking or inability to walk, impaired intellectual development, poor or absent speech, axial hypotonia, and facial dysmorphism. Additional variable features may include seizures, autistic or behavioral abnormalities, and brain abnormalities. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30500825, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30761613}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.
1 regional properties for P11233
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Small GTP-binding protein domain | 16 - 168 | IPR005225 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 3.6.5.2 | Acting on GTP; involved in cellular and subcellular movement |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
8 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cell surface | The external part of the cell wall and/or plasma membrane. |
| cleavage furrow | The cleavage furrow is a plasma membrane invagination at the cell division site. The cleavage furrow begins as a shallow groove and eventually deepens to divide the cytoplasm. |
| cytoplasmic vesicle membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding a cytoplasmic vesicle. |
| extracellular exosome | A vesicle that is released into the extracellular region by fusion of the limiting endosomal membrane of a multivesicular body with the plasma membrane. Extracellular exosomes, also simply called exosomes, have a diameter of about 40-100 nm. |
| Flemming body | A cell part that is the central region of the midbody characterized by a gap in alpha-tubulin staining. It is a dense structure of antiparallel microtubules from the central spindle in the middle of the intercellular bridge. |
| focal adhesion | A cell-substrate junction that anchors the cell to the extracellular matrix and that forms a point of termination of actin filaments. In insects focal adhesion has also been referred to as hemi-adherens junction (HAJ). |
| mitochondrion | A semiautonomous, self replicating organelle that occurs in varying numbers, shapes, and sizes in the cytoplasm of virtually all eukaryotic cells. It is notably the site of tissue respiration. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
8 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATPase binding | Binding to an ATPase, any enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP. |
| Edg-2 lysophosphatidic acid receptor binding | Binding to an Edg-2 lysophosphatidic acid receptor. |
| G protein activity | A molecular function regulator that cycles between active GTP-bound and inactive GDP-bound states. In its active state, binds to a variety of effector proteins to regulate cellular processes. Intrinsic GTPase activity returns the G protein to its GDP-bound state. The return to the GDP-bound state can be accelerated by the action of a GTPase-activating protein (GAP). |
| GDP binding | Binding to GDP, guanosine 5'-diphosphate. |
| GTP binding | Binding to GTP, guanosine triphosphate. |
| GTPase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: GTP + H2O = GDP + H+ + phosphate. |
| myosin binding | Binding to a myosin; myosins are any of a superfamily of molecular motor proteins that bind to actin and use the energy of ATP hydrolysis to generate force and movement along actin filaments. |
| ubiquitin protein ligase binding | Binding to a ubiquitin protein ligase enzyme, any of the E3 proteins. |
15 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| actin cytoskeleton reorganization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in dynamic structural changes to the arrangement of constituent parts of cytoskeletal structures comprising actin filaments and their associated proteins. |
| cell cycle | The progression of biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur in a cell during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events. Canonically, the cell cycle comprises the replication and segregation of genetic material followed by the division of the cell, but in endocycles or syncytial cells nuclear replication or nuclear division may not be followed by cell division. |
| cell division | The process resulting in division and partitioning of components of a cell to form more cells; may or may not be accompanied by the physical separation of a cell into distinct, individually membrane-bounded daughter cells. |
| chemotaxis | The directed movement of a motile cell or organism, or the directed growth of a cell guided by a specific chemical concentration gradient. Movement may be towards a higher concentration (positive chemotaxis) or towards a lower concentration (negative chemotaxis). |
| establishment of protein localization to mitochondrion | The directed movement of a protein to the mitochondrion or a part of the mitochondrion. |
| exocytosis | A process of secretion by a cell that results in the release of intracellular molecules (e.g. hormones, matrix proteins) contained within a membrane-bounded vesicle. Exocytosis can occur either by full fusion, when the vesicle collapses into the plasma membrane, or by a kiss-and-run mechanism that involves the formation of a transient contact, a pore, between a granule (for exemple of chromaffin cells) and the plasma membrane. The latter process most of the time leads to only partial secretion of the granule content. Exocytosis begins with steps that prepare vesicles for fusion with the membrane (tethering and docking) and ends when molecules are secreted from the cell. |
| membrane raft localization | Any process in which membrane rafts are transported to, or maintained in, a specific location. Membrane rafts are small (10-200 nm), heterogeneous, highly dynamic, sterol- and sphingolipid-enriched membrane domains that compartmentalize cellular processes. |
| neural tube closure | The last step in the formation of the neural tube, where the paired neural folds are brought together and fuse at the dorsal midline. |
| positive regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway activity. |
| positive regulation of filopodium assembly | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the assembly of a filopodium, a thin, stiff protrusion extended by the leading edge of a motile cell such as a crawling fibroblast or amoeba, or an axonal growth cone. |
| positive regulation of mitochondrial fission | Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of mitochondrial fission. Mitochondrial fission is the division of a mitochondrion within a cell to form two or more separate mitochondrial compartments. |
| Ras protein signal transduction | The series of molecular signals within the cell that are mediated by a member of the Ras superfamily of proteins switching to a GTP-bound active state. |
| receptor internalization | A receptor-mediated endocytosis process that results in the movement of receptors from the plasma membrane to the inside of the cell. The process begins when cell surface receptors are monoubiquitinated following ligand-induced activation. Receptors are subsequently taken up into endocytic vesicles from where they are either targeted to the lysosome or vacuole for degradation or recycled back to the plasma membrane. |
| regulation of exocytosis | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of exocytosis. |
| signal transduction | The cellular process in which a signal is conveyed to trigger a change in the activity or state of a cell. Signal transduction begins with reception of a signal (e.g. a ligand binding to a receptor or receptor activation by a stimulus such as light), or for signal transduction in the absence of ligand, signal-withdrawal or the activity of a constitutively active receptor. Signal transduction ends with regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. regulation of transcription or regulation of a metabolic process. Signal transduction covers signaling from receptors located on the surface of the cell and signaling via molecules located within the cell. For signaling between cells, signal transduction is restricted to events at and within the receiving cell. |
34 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P08642 | HRAS | GTPase HRas | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q6T310 | RASL11A | Ras-like protein family member 11A | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q8IYK8 | REM2 | GTP-binding protein REM 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P55040 | GEM | GTP-binding protein GEM | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q6IQ22 | RAB12 | Ras-related protein Rab-12 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9BU20 | CPLANE2 | Ciliogenesis and planar polarity effector 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q96HU8 | DIRAS2 | GTP-binding protein Di-Ras2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P62070 | RRAS2 | Ras-related protein R-Ras2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P11234 | RALB | Ras-related protein Ral-B | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q99578 | RIT2 | GTP-binding protein Rit2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P01116 | KRAS | GTPase KRas | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P01112 | HRAS | GTPase HRas | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q9JIW9 | Ralb | Ras-related protein Ral-B | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q61411 | Hras | GTPase HRas | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P32883 | Kras | GTPase KRas | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| O08989 | Mras | Ras-related protein M-Ras | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q5PR73 | Diras2 | GTP-binding protein Di-Ras2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q91Z61 | Diras1 | GTP-binding protein Di-Ras1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P62071 | Rras2 | Ras-related protein R-Ras2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P35283 | Rab12 | Ras-related protein Rab-12 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q08AT1 | Rasl12 | Ras-like protein family member 12 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| A2A825 | Cplane2 | Ciliogenesis and planar polarity effector 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P55041 | Gem | GTP-binding protein GEM | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P70425 | Rit2 | GTP-binding protein Rit2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q8VEL9 | Rem2 | GTP-binding protein REM 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P36860 | Ralb | Ras-related protein Ral-B | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P08644 | Kras | GTPase KRas | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q9WTY2 | Rem2 | GTP-binding protein REM 2 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P20171 | Hras | GTPase HRas | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q5BJQ5 | Rit2 | GTP-binding protein Rit2 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P97538 | Mras | Ras-related protein M-Ras | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| B7ZTR0 | cplane2 | Ciliogenesis and planar polarity effector 2 | Xenopus tropicalis (Western clawed frog) (Silurana tropicalis) | PR |
| P79737 | nras | GTPase NRas | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| A1DZY4 | zgc:110179 | Ras-like protein family member 11A-like | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MAANKPKGQN | SLALHKVIMV | GSGGVGKSAL | TLQFMYDEFV | EDYEPTKADS | YRKKVVLDGE |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| EVQIDILDTA | GQEDYAAIRD | NYFRSGEGFL | CVFSITEMES | FAATADFREQ | ILRVKEDENV |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| PFLLVGNKSD | LEDKRQVSVE | EAKNRAEQWN | VNYVETSAKT | RANVDKVFFD | LMREIRARKM |
| 190 | 200 | ||||
| EDSKEKNGKK | KRKSLAKRIR | ERCCIL |