P0CW01
Gene name |
TSPY10 |
Protein name |
Testis-specific Y-encoded protein 10 |
Names |
|
Species |
Homo sapiens (Human) |
KEGG Pathway |
hsa:728137 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
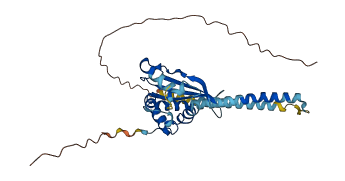
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for P0CW01
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-P0CW01-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
17 variants for P0CW01
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
rs1603145591 CA414974447 |
35 | K>N | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA414974989 rs1603145604 |
74 | V>G | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs1603145607 CA414975016 |
76 | V>G | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs1603145614 CA414975170 |
88 | E>G | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs1603145619 CA414975186 |
89 | E>G | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs1353461329 CA414975451 |
109 | L>P | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1556185323 CA414975744 |
131 | S>T | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA414975936 rs1401946011 |
144 | H>Q | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1556185358 CA414975964 |
147 | R>C | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA414976207 rs1278882587 |
164 | A>S | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA414976604 rs1603145682 |
190 | E>G | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA414977164 rs1225448270 |
228 | R>G | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1556185436 CA414977292 |
237 | W>* | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA414977427 rs1556185448 |
247 | R>C | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA414977745 rs1556185461 |
269 | S>F | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
| TCGA novel | 302 | G>E | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
|
rs746060619 CA10572532 |
304 | S>F | No |
ClinGen ExAC |
No associated diseases with P0CW01
No regional properties for P0CW01
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| No domain, repeats, and functional sites for P0CW01 | |||
3 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| chromatin | The ordered and organized complex of DNA, protein, and sometimes RNA, that forms the chromosome. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
2 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| chromatin binding | Binding to chromatin, the network of fibers of DNA, protein, and sometimes RNA, that make up the chromosomes of the eukaryotic nucleus during interphase. |
| histone binding | Binding to a histone, any of a group of water-soluble proteins found in association with the DNA of eukaryotic or archaeal chromosomes. They are involved in the condensation and coiling of chromosomes during cell division and have also been implicated in gene regulation and DNA replication. They may be chemically modified (methylated, acetlyated and others) to regulate gene transcription. |
4 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cell differentiation | The process in which relatively unspecialized cells, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cells, acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate and its subsequent development to the mature state. |
| gonadal mesoderm development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the gonadal mesoderm over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The gonadal mesoderm is the middle layer of the three primary germ layers of the embryo which will go on to form the gonads of the organism. |
| nucleosome assembly | The aggregation, arrangement and bonding together of a nucleosome, the beadlike structural units of eukaryotic chromatin composed of histones and DNA. |
| spermatogenesis | The developmental process by which male germ line stem cells self renew or give rise to successive cell types resulting in the development of a spermatozoa. |
15 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O19110 | TSPY1 | Testis-specific Y-encoded protein 1 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| Q99457 | NAP1L3 | Nucleosome assembly protein 1-like 3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P55209 | NAP1L1 | Nucleosome assembly protein 1-like 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q01534 | TSPY1 | Testis-specific Y-encoded protein 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P0CV99 | TSPY4 | Testis-specific Y-encoded protein 4 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P0CV98 | TSPY3 | Testis-specific Y-encoded protein 3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P0CW00 | TSPY8 | Testis-specific Y-encoded protein 8 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| A6NKD2 | TSPY2 | Testis-specific Y-encoded protein 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q8N831 | TSPYL6 | Testis-specific Y-encoded-like protein 6 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9H2G4 | TSPYL2 | Testis-specific Y-encoded-like protein 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P0DME0 | SETSIP | Protein SETSIP | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q01105 | SET | Protein SET | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q9H489 | TSPY26P | Putative testis-specific Y-encoded-like protein 3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9EQU5 | Set | Protein SET | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| Q9R1M3 | Tspy1 | Testis-specific Y-encoded protein 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MRPEGSLTYR | VPERLRQGFC | GVGRAAQALV | CASAKEGTAF | RMEAVQEGAA | GVESEQAALG |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| EEAVLLLDDI | MAEVEVVAEE | EGLVERREEA | QRAQQAVPGP | GPMTPESALE | ELLAVQVELE |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| PVNAQARKAF | SRQREKMERR | RKPHLDRRGA | VIQSVPGFWA | NVIANHPQMS | ALITDEDEDM |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| LSYMVSLEVE | EEKHPVHLCK | IMLFFRSNPY | FQNKVITKEY | LVNITEYRAS | HSTPIEWYPD |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| YEVEAYRRRH | HNSSLNFFNW | FSDHNFAGSN | KIAEILCKDL | WRNPLQYYKR | MKPPEEGTET |
| SGDSQLLS |