P0AFW0
Gene name |
rfaH (hlyT, sfrB, b3842, JW3818) |
Protein name |
Transcription antitermination protein RfaH |
Names |
|
Species |
Escherichia coli (strain K12) |
KEGG Pathway |
ecj:JW3818,eco:b3842 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
RHO-INTERACTING TRANSCRIPTION TERMINATION FACTOR NUSG (PTHR30265) |
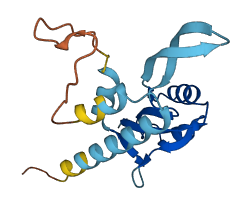
Descriptions
Transcription antitermination protein RfaH is an operon-specific paralog of NusG and consists of an NGN domain that is connected to a KOW domain via a flexible 15 amino acid linker. In free RfaH, KOW domain folds as an α-helical hairpin that interacts with the NGN domain, which masks the binding site for RNA polymerase (RNAP) at the interface on the NGN domain (autoinhibited state). Upon recruitment to a transcription elongation complex pausing at an operon polarity suppressor (ops) site, RfaH is activated by dissociating and refolding the liberated KOW domain into β-barrel state, which enhances distal genes transcription elongation in a specialized subset of operons that encode extracytoplasmic components, and serves as recruitment platform for ribosomes to activate activation. Upon release from RNAP, RfaH is transformed back into its autoinhibited state.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
1-100 (NGN-like domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Partner binding |
Assay |
Structural analysis, Deletion assay |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
No variants for P0AFW0
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for P0AFW0 | |||||
No associated diseases with P0AFW0
No regional properties for P0AFW0
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| No domain, repeats, and functional sites for P0AFW0 | |||
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | ||
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | PTHR30265 | RHO-INTERACTING TRANSCRIPTION TERMINATION FACTOR NUSG |
| PANTHER Subfamily | PTHR30265:SF7 | TRANSCRIPTION ANTITERMINATION PROTEIN RFAH |
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
1 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
5 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| bacterial-type RNA polymerase core enzyme binding | Binding to a bacterial-type RNA polymerase core enzyme, typically consisting of two alpha, one beta, one beta prime, and one omega subunit. |
| DNA binding | Any molecular function by which a gene product interacts selectively and non-covalently with DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). |
| regulatory RNA binding | Binding to a small regulatory RNA, a short RNA (usually 50-200 nt long) that is either independently transcribed or processed from a longer RNA by an RNAse enzyme. |
| transcription antitermination factor activity, DNA binding | Binds to DNA, typically within region of the promoter and transcribed region, to promote readthrough of a transcription termination site and thus extending the length of the RNA transcript produced. Examples of antitermination factors which bind DNA include the lambda Q protein. |
| translation activator activity | Any of a group of soluble proteins functioning in the activation of ribosome-mediated translation of mRNA into a polypeptide. |
4 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| DNA-templated transcription elongation | The extension of an RNA molecule after transcription initiation and promoter clearance at a DNA-dependent RNA polymerase promoter by the addition of ribonucleotides catalyzed by an RNA polymerase. |
| positive regulation of translation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of proteins by the translation of mRNA or circRNA. |
| transcription antitermination | A positive regulation of gene expression mechanism that allows RNA polymerase to continue transcription beyond a termination site, thus allowing expression of downstream genes under specific conditions. |
| transcription elongation-coupled chromatin remodeling | A chromatin remodeling process that reestablishes the chromatin structure following the passage of RNA polymerase II during transcription elongation, thus preventing cryptic transcription initiation. |
No homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No homologous proteins | ||||
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MQSWYLLYCK | RGQLQRAQEH | LERQAVNCLA | PMITLEKIVR | GKRTAVSEPL | FPNYLFVEFD |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| PEVIHTTTIN | ATRGVSHFVR | FGASPAIVPS | AVIHQLSVYK | PKDIVDPATP | YPGDKVIITE |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | ||
| GAFEGFQAIF | TEPDGEARSM | LLLNLINKEI | KHSVKNTEFR | KL |