P0AFF6
Gene name |
nusA (b3169, JW3138) |
Protein name |
Transcription termination/antitermination protein NusA |
Names |
N utilization substance protein A, Transcription termination/antitermination L factor |
Species |
Escherichia coli (strain K12) |
KEGG Pathway |
ecj:JW3138, eco:b3169, |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
TRANSCRIPTION TERMINATION FACTOR NUSA (PTHR22648) |
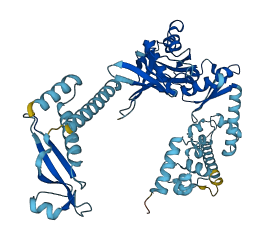
Descriptions
Elongating Escherichia coli RNAP is modulated by NusA protein. The C-terminal domain (CTD) of the RNAP α subunit (αCTD) interacts with the acidic CTD 2 (AR2) of NusA, releasing the autoinhibitory blockade of the NusA S1-KH1-KH2 motif and allowing NusA to bind nascent nut spacer RNA. In free NusA, the AR2 domain within NusA intramolecularly interacts with the KH1 domain of SKK motif, preventing RNA binding by NusA-SKK and rendering NusA autoinhibited. This autoinhibition can be relieved by the alpha-CTD of RNAP as NusA-SKK and CTD share binding sites on NusA-AR2.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
200-270 (KH1 domain of SKK) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
Deletion assay, Structural analysis |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
References
- Dudenhoeffer BR et al. (2019) "SuhB is an integral part of the ribosomal antitermination complex and interacts with NusA", Nucleic acids research, 47, 6504-6518
- Schweimer K et al. (2011) "NusA interaction with the α subunit of E. coli RNA polymerase is via the UP element site and releases autoinhibition", Structure (London, England : 1993), 19, 945-54
- Eisenmann A et al. (2005) "The E. coli NusA carboxy-terminal domains are structurally similar and show specific RNAP- and lambdaN interaction", Protein science : a publication of the Protein Society, 14, 2018-29
- Yeon JH et al. (2016) "Systems-wide Identification of cis-Regulatory Elements in Proteins", Cell systems, 2, 89-100
Autoinhibited structure
Activated structure

37 structures for P0AFF6
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1U9L | X-ray | 190 A | A/B | 352-421 | PDB |
| 1WCL | NMR | - | A | 351-426 | PDB |
| 1WCN | NMR | - | A | 426-495 | PDB |
| 2JZB | NMR | - | B | 424-495 | PDB |
| 2KWP | NMR | - | A | 1-125 | PDB |
| 5LM7 | X-ray | 335 A | A/C | 1-426 | PDB |
| 5LM9 | X-ray | 214 A | A | 101-426 | PDB |
| 5MS0 | EM | 980 A | M | 1-495 | PDB |
| 6FLQ | EM | 410 A | F | 1-495 | PDB |
| 6GOV | EM | 370 A | A | 1-495 | PDB |
| 6IB8 | X-ray | 165 A | C | 427-495 | PDB |
| 6TQN | EM | 380 A | A | 1-495 | PDB |
| 6TQO | EM | 400 A | A | 1-495 | PDB |
| 6X6T | EM | 320 A | AG | 1-495 | PDB |
| 6X7F | EM | 350 A | AG | 1-495 | PDB |
| 6X7K | EM | 310 A | AG | 1-495 | PDB |
| 6X9Q | EM | 480 A | AG | 1-495 | PDB |
| 6XAS | EM | 380 A | G | 1-495 | PDB |
| 6XAV | EM | 770 A | G | 1-495 | PDB |
| 6XDQ | EM | 370 A | AG | 1-495 | PDB |
| 6Z9P | EM | 390 A | A | 1-495 | PDB |
| 6Z9Q | EM | 570 A | A | 1-495 | PDB |
| 6Z9R | EM | 410 A | A | 1-495 | PDB |
| 6Z9S | EM | 440 A | A | 1-495 | PDB |
| 6Z9T | EM | 410 A | A | 1-495 | PDB |
| 7ADB | EM | 440 A | A | 1-495 | PDB |
| 7ADC | EM | 400 A | A | 1-495 | PDB |
| 7ADD | EM | 430 A | A | 1-495 | PDB |
| 7ADE | EM | 420 A | A | 1-495 | PDB |
| 7PY3 | EM | 380 A | F | 1-495 | PDB |
| 7PY5 | EM | 390 A | F | 1-495 | PDB |
| 7PY6 | EM | 410 A | F | 1-495 | PDB |
| 7PY7 | EM | 410 A | F | 1-495 | PDB |
| 7PYJ | EM | 420 A | F | 1-495 | PDB |
| 7PYK | EM | 410 A | F | 1-495 | PDB |
| 7UBN | EM | 336 A | N | 1-495 | PDB |
| AF-P0AFF6-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for P0AFF6
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for P0AFF6 | |||||
No associated diseases with P0AFF6
No regional properties for P0AFF6
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| No domain, repeats, and functional sites for P0AFF6 | |||
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | ||
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | PTHR22648 | TRANSCRIPTION TERMINATION FACTOR NUSA |
| PANTHER Subfamily | PTHR22648:SF0 | TRANSCRIPTION TERMINATION_ANTITERMINATION PROTEIN NUSA |
| PANTHER Protein Class |
RNA processing factor
RNA metabolism protein |
|
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
2 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| transcription elongation factor complex | Any protein complex that interacts with RNA polymerase II to increase (positive transcription elongation factor) or reduce (negative transcription elongation factor) the rate of transcription elongation. |
5 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| bacterial-type RNA polymerase core enzyme binding | Binding to a bacterial-type RNA polymerase core enzyme, typically consisting of two alpha, one beta, one beta prime, and one omega subunit. |
| DNA-binding transcription factor activity | A transcription regulator activity that modulates transcription of gene sets via selective and non-covalent binding to a specific double-stranded genomic DNA sequence (sometimes referred to as a motif) within a cis-regulatory region. Regulatory regions include promoters (proximal and distal) and enhancers. Genes are transcriptional units, and include bacterial operons. |
| nucleotide binding | Binding to a nucleotide, any compound consisting of a nucleoside that is esterified with (ortho)phosphate or an oligophosphate at any hydroxyl group on the ribose or deoxyribose. |
| protein domain specific binding | Binding to a specific domain of a protein. |
| RNA binding | Binding to an RNA molecule or a portion thereof. |
5 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| DNA-templated transcription termination | The completion of transcription |
| protein complex oligomerization | The process of creating protein oligomers, compounds composed of a small number, usually between three and ten, of component monomers; protein oligomers may be composed of different or identical monomers. Oligomers may be formed by the polymerization of a number of monomers or the depolymerization of a large protein polymer. |
| regulation of DNA-templated transcription elongation | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of transcription elongation, the extension of an RNA molecule after transcription initiation and promoter clearance by the addition of ribonucleotides catalyzed by a DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. |
| ribosome biogenesis | A cellular process that results in the biosynthesis of constituent macromolecules, assembly, and arrangement of constituent parts of ribosome subunits; includes transport to the sites of protein synthesis. |
| transcription antitermination | A positive regulation of gene expression mechanism that allows RNA polymerase to continue transcription beyond a termination site, thus allowing expression of downstream genes under specific conditions. |
No homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No homologous proteins | ||||
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MNKEILAVVE | AVSNEKALPR | EKIFEALESA | LATATKKKYE | QEIDVRVQID | RKSGDFDTFR |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| RWLVVDEVTQ | PTKEITLEAA | RYEDESLNLG | DYVEDQIESV | TFDRITTQTA | KQVIVQKVRE |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| AERAMVVDQF | REHEGEIITG | VVKKVNRDNI | SLDLGNNAEA | VILREDMLPR | ENFRPGDRVR |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| GVLYSVRPEA | RGAQLFVTRS | KPEMLIELFR | IEVPEIGEEV | IEIKAAARDP | GSRAKIAVKT |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| NDKRIDPVGA | CVGMRGARVQ | AVSTELGGER | IDIVLWDDNP | AQFVINAMAP | ADVASIVVDE |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| DKHTMDIAVE | AGNLAQAIGR | NGQNVRLASQ | LSGWELNVMT | VDDLQAKHQA | EAHAAIDTFT |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| KYLDIDEDFA | TVLVEEGFST | LEELAYVPMK | ELLEIEGLDE | PTVEALRERA | KNALATIAQA |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| QEESLGDNKP | ADDLLNLEGV | DRDLAFKLAA | RGVCTLEDLA | EQGIDDLADI | EGLTDEKAGA |
| 490 | |||||
| LIMAARNICW | FGDEA |