P09216
Gene name |
Prkce (Pkce) |
Protein name |
Protein kinase C epsilon type |
Names |
nPKC-epsilon |
Species |
Rattus norvegicus (Rat) |
KEGG Pathway |
rno:29340 |
EC number |
2.7.11.13: Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
Protein Class |
|
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
549-572 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
412-732 (Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, Novel Protein Kinase C epsilon) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
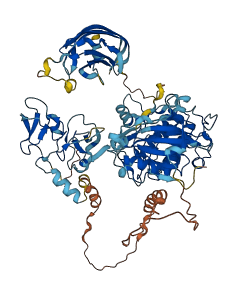
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

2 structures for P09216
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1GMI | X-ray | 170 A | A | 1-136 | PDB |
| AF-P09216-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for P09216
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for P09216 | |||||
No associated diseases with P09216
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.11.13 | Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
15 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cell periphery | The part of a cell encompassing the cell cortex, the plasma membrane, and any external encapsulating structures. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytoskeleton | A cellular structure that forms the internal framework of eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. The cytoskeleton includes intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, the microtrabecular lattice, and other structures characterized by a polymeric filamentous nature and long-range order within the cell. The various elements of the cytoskeleton not only serve in the maintenance of cellular shape but also have roles in other cellular functions, including cellular movement, cell division, endocytosis, and movement of organelles. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| endoplasmic reticulum | The irregular network of unit membranes, visible only by electron microscopy, that occurs in the cytoplasm of many eukaryotic cells. The membranes form a complex meshwork of tubular channels, which are often expanded into slitlike cavities called cisternae. The ER takes two forms, rough (or granular), with ribosomes adhering to the outer surface, and smooth (with no ribosomes attached). |
| glutamatergic synapse | A synapse that uses glutamate as a neurotransmitter. |
| Golgi membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding any of the compartments of the Golgi apparatus. |
| membrane | A lipid bilayer along with all the proteins and protein complexes embedded in it an attached to it. |
| mitochondrion | A semiautonomous, self replicating organelle that occurs in varying numbers, shapes, and sizes in the cytoplasm of virtually all eukaryotic cells. It is notably the site of tissue respiration. |
| neuromuscular junction | The junction between the axon of a motor neuron and a muscle fiber. In response to the arrival of action potentials, the presynaptic button releases molecules of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft. These diffuse across the cleft and transmit the signal to the postsynaptic membrane of the muscle fiber, leading to a change in post-synaptic potential. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| perinuclear region of cytoplasm | Cytoplasm situated near, or occurring around, the nucleus. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| presynaptic cytosol | The region of the cytosol consisting of all cytosol that is part of the presynapse. |
| T-tubule | Invagination of the plasma membrane of a muscle cell that extends inward from the cell surface around each myofibril. The ends of T-tubules make contact with the sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane. |
17 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| 14-3-3 protein binding | Binding to a 14-3-3 protein. A 14-3-3 protein is any of a large family of approximately 30kDa acidic proteins which exist primarily as homo- and heterodimers within all eukaryotic cells, and have been implicated in the modulation of distinct biological processes by binding to specific phosphorylated sites on diverse target proteins, thereby forcing conformational changes or influencing interactions between their targets and other molecules. Each 14-3-3 protein sequence can be roughly divided into three sections: a divergent amino terminus, the conserved core region and a divergent carboxy-terminus. The conserved middle core region of the 14-3-3s encodes an amphipathic groove that forms the main functional domain, a cradle for interacting with client proteins. |
| actin monomer binding | Binding to monomeric actin, also known as G-actin. |
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| calcium-dependent protein kinase C activity | Calcium-dependent catalysis of the reaction: ATP + a protein = ADP + a phosphoprotein. |
| calcium-independent protein kinase C activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + a protein = ADP + a phosphoprotein. This reaction requires diacylglycerol but not calcium. |
| enzyme activator activity | Binds to and increases the activity of an enzyme. |
| enzyme binding | Binding to an enzyme, a protein with catalytic activity. |
| ethanol binding | Binding to ethanol, CH(3)-CH(2)-OH. |
| metal ion binding | Binding to a metal ion. |
| protein kinase activity | Catalysis of the phosphorylation of an amino acid residue in a protein, usually according to the reaction: a protein + ATP = a phosphoprotein + ADP. |
| protein kinase binding | Binding to a protein kinase, any enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a protein substrate. |
| protein kinase C activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + a protein = ADP + a phosphoprotein. This reaction requires diacylglycerol. |
| protein serine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate. |
| protein serine/threonine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate, and ATP + protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate. |
| SH3 domain binding | Binding to a SH3 domain (Src homology 3) of a protein, small protein modules containing approximately 50 amino acid residues found in a great variety of intracellular or membrane-associated proteins. |
| signaling receptor activator activity | The function of interacting (directly or indirectly) with receptors such that the proportion of receptors in the active form is increased. |
| signaling receptor binding | Binding to one or more specific sites on a receptor molecule, a macromolecule that undergoes combination with a hormone, neurotransmitter, drug or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell function. |
43 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cell cycle | The progression of biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur in a cell during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events. Canonically, the cell cycle comprises the replication and segregation of genetic material followed by the division of the cell, but in endocycles or syncytial cells nuclear replication or nuclear division may not be followed by cell division. |
| cell division | The process resulting in division and partitioning of components of a cell to form more cells; may or may not be accompanied by the physical separation of a cell into distinct, individually membrane-bounded daughter cells. |
| cell-substrate adhesion | The attachment of a cell to the underlying substrate via adhesion molecules. |
| cellular response to ethanol | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an ethanol stimulus. |
| cellular response to hypoxia | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating lowered oxygen tension. Hypoxia, defined as a decline in O2 levels below normoxic levels of 20.8 - 20.95%, results in metabolic adaptation at both the cellular and organismal level. |
| cellular response to platelet-derived growth factor stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a platelet-derived growth factor stimulus. |
| cellular response to prostaglandin E stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a prostagladin E stimulus. |
| establishment of localization in cell | Any process, occuring in a cell, that localizes a substance or cellular component. This may occur via movement, tethering or selective degradation. |
| insulin secretion | The regulated release of proinsulin from secretory granules accompanied by cleavage of proinsulin to form mature insulin. In vertebrates, insulin is secreted from B granules in the B cells of the vertebrate pancreas and from insulin-producing cells in insects. |
| intracellular signal transduction | The process in which a signal is passed on to downstream components within the cell, which become activated themselves to further propagate the signal and finally trigger a change in the function or state of the cell. |
| lipopolysaccharide-mediated signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by the binding of a lipopolysaccharide (LPS) to a receptor on the surface of a target cell, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. Lipopolysaccharides are major components of the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria, making them prime targets for recognition by the immune system. |
| locomotory exploration behavior | The specific movement from place to place of an organism in response to a novel environment. |
| macrophage activation involved in immune response | A change in morphology and behavior of a macrophage resulting from exposure to a cytokine, chemokine, cellular ligand, or soluble factor, leading to the initiation or perpetuation of an immune response. |
| MAPK cascade | An intracellular protein kinase cascade containing at least a MAPK, a MAPKK and a MAP3K. The cascade can also contain an additional tiers: the upstream MAP4K. The kinases in each tier phosphorylate and activate the kinase in the downstream tier to transmit a signal within a cell. |
| mucus secretion | The regulated release of mucus by the mucosa. Mucus is a viscous slimy secretion consisting of mucins and various inorganic salts dissolved in water, with suspended epithelial cells and leukocytes. The mucosa, or mucous membrane, is the membrane covered with epithelium that lines the tubular organs of the body. Mucins are carbohydrate-rich glycoproteins that have a lubricating and protective function. |
| negative regulation of apoptotic process | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cell death by apoptotic process. |
| negative regulation of mitochondrial calcium ion concentration | Any process that decreases the concentration of calcium ions in mitochondria. |
| negative regulation of mitochondrial membrane potential | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of establishment or extent of a mitochondrial membrane potential, the electric potential existing across any mitochondrial membrane arising from charges in the membrane itself and from the charges present in the media on either side of the membrane. |
| negative regulation of protein ubiquitination | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the addition of ubiquitin groups to a protein. |
| negative regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the release into the cytosolic compartment of calcium ions sequestered in the endoplasmic reticulum or mitochondria. |
| peptidyl-serine phosphorylation | The phosphorylation of peptidyl-serine to form peptidyl-O-phospho-L-serine. |
| positive regulation of actin filament polymerization | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of actin polymerization. |
| positive regulation of cell-substrate adhesion | Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell-substrate adhesion. Cell-substrate adhesion is the attachment of a cell to the underlying substrate via adhesion molecules. |
| positive regulation of cellular glucuronidation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cellular glucuronidation. |
| positive regulation of cytokinesis | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the division of the cytoplasm of a cell, and its separation into two daughter cells. |
| positive regulation of epithelial cell migration | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of epithelial cell migration. |
| positive regulation of fibroblast migration | Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of fibroblast cell migration. Fibroblast cell migration is accomplished by extension and retraction of a pseudopodium. |
| positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling. |
| positive regulation of insulin secretion | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the regulated release of insulin. |
| positive regulation of lipid catabolic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of lipids. |
| positive regulation of MAPK cascade | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction mediated by the MAPK cascade. |
| positive regulation of mucus secretion | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the regulated release of mucus from a cell or a tissue. |
| positive regulation of synaptic transmission, GABAergic | Any process that activates, maintains or increases the frequency, rate or extent of GABAergic synaptic transmission, the process of communication from a neuron to another neuron across a synapse using the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). |
| positive regulation of wound healing | Any process that increases the rate, frequency, or extent of the series of events that restore integrity to a damaged tissue, following an injury. |
| protein phosphorylation | The process of introducing a phosphate group on to a protein. |
| regulation of insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the regulated release of insulin that contributes to the response of a cell to glucose. |
| regulation of lipid metabolic process | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving lipids. |
| regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the phosphorylation of peptidyl-tyrosine. |
| regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the release into the cytosolic compartment of calcium ions sequestered in the endoplasmic reticulum or mitochondria. |
| regulation of synaptic vesicle exocytosis | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of synaptic vesicle exocytosis. |
| response to morphine | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a morphine stimulus. Morphine is an opioid alkaloid, isolated from opium, with a complex ring structure. |
| synaptic transmission, GABAergic | The vesicular release of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). from a presynapse, across a chemical synapse, the subsequent activation of GABA receptors at the postsynapse of a target cell (neuron, muscle, or secretory cell) and the effects of this activation on the postsynaptic membrane potential and ionic composition of the postsynaptic cytosol. This process encompasses both spontaneous and evoked release of neurotransmitter and all parts of synaptic vesicle exocytosis. Evoked transmission starts with the arrival of an action potential at the presynapse. |
| TRAM-dependent toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by a ligand binding to a toll-like receptor 4 where the TRAM adaptor mediates transduction of the signal. Toll-like 4 receptors are pattern recognition receptors that bind bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) to initiate an innate immune response. |
34 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P24583 | PKC1 | Protein kinase C-like 1 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) | SS |
| A1A4I4 | PKN1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase N1 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| A1Z7T0 | Pkn | Serine/threonine-protein kinase N | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| P83099 | Pkcdelta | Putative protein kinase C delta type homolog | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | PR |
| Q04759 | PRKCQ | Protein kinase C theta type | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q6P5Z2 | PKN3 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase N3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q96LW2 | RSKR | Ribosomal protein S6 kinase-related protein | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P24723 | PRKCH | Protein kinase C eta type | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q16512 | PKN1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase N1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q16513 | PKN2 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase N2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q05655 | PRKCD | Protein kinase C delta type | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q02156 | PRKCE | Protein kinase C epsilon type | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P70268 | Pkn1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase N1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P23298 | Prkch | Protein kinase C eta type | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q02111 | Prkcq | Protein kinase C theta type | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q8BWW9 | Pkn2 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase N2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q8K045 | Pkn3 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase N3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P28867 | Prkcd | Protein kinase C delta type | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P16054 | Prkce | Protein kinase C epsilon type | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| O08874 | Pkn2 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase N2 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P09215 | Prkcd | Protein kinase C delta type | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q63433 | Pkn1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase N1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q64617 | Prkch | Protein kinase C eta type | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| O55173 | Pdpk1 | 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P09217 | Prkcz | Protein kinase C zeta type | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| F1M7Y5 | Prkci | Protein kinase C iota type | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P05696 | Prkca | Protein kinase C alpha type | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P63319 | Prkcg | Protein kinase C gamma type | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P47197 | Akt2 | RAC-beta serine/threonine-protein kinase | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P47196 | Akt1 | RAC-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q63484 | Akt3 | RAC-gamma serine/threonine-protein kinase | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P68403 | Prkcb | Protein kinase C beta type | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P34722 | tpa-1 | Protein kinase C-like 1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| A7MBL8 | pkn2 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase N2 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MVVFNGLLKI | KICEAVSLKP | TAWSLRHAVG | PRPQTFLLDP | YIALNVDDSR | IGQTATKQKT |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| NSPAWHDEFV | TDVCNGRKIE | LAVFHDAPIG | YDDFVANCTI | QFEELLQNGS | RHFEDWIDLE |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| PEGKVYVIID | LSGSSGEAPK | DNEERVFRER | MRPRKRQGAV | RRRVHQVNGH | KFMATYLRQP |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| TYCSHCRDFI | WGVIGKQGYQ | CQVCTCVVHK | RCHELIITKC | AGLKKQETPD | EVGSQRFSVN |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| MPHKFGIHNY | KVPTFCDHCG | SLLWGLLRQG | LQCKVCKMNV | HRRCETNVAP | NCGVDARGIA |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| KVLADLGVTP | DKITNSGQRR | KKLAAGAESP | QPASGNSPSE | DDRSKSAPTS | PCDQELKELE |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| NNIRKALSFD | NRGEEHRASS | STDGQLASPG | ENGEVRQGQA | KRLGLDEFNF | IKVLGKGSFG |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| KVMLAELKGK | DEVYAVKVLK | KDVILQDDDV | DCTMTEKRIL | ALARKHPYLT | QLYCCFQTKD |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| RLFFVMEYVN | GGDLMFQIQR | SRKFDEPRSG | FYAAEVTSAL | MFLHQHGVIY | RDLKLDNILL |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| DAEGHSKLAD | FGMCKEGILN | GVTTTTFCGT | PDYIAPEILQ | ELEYGPSVDW | WALGVLMYEM |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| MAGQPPFEAD | NEDDLFESIL | HDDVLYPVWL | SKEAVSILKA | FMTKNPHKRL | GCVAAQNGED |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| AIKQHPFFKE | IDWVLLEQKK | MKPPFKPRIK | TKRDVNNFDQ | DFTREEPILT | LVDEAIVKQI |
| 730 | |||||
| NQEEFKGFSY | FGEDLMP |