P08953
Gene name |
Tl |
Protein name |
Protein toll |
Names |
|
Species |
Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) |
KEGG Pathway |
dme:Dmel_CG5490 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
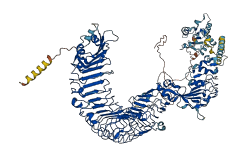
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

19 variants for P08953
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 98 | E>G | strain: MelZim6 [UniProt] | No | ||
| 218 | G>S | strain: MelZim7 [UniProt] | No | ||
| 245 | T>S | strain: MelZim3 [UniProt] | No | ||
| 390 | T>I | strain: MelZim3 and MelZim7 [UniProt] | No | ||
| 414 | G>A | strain: MelZim3 [UniProt] | No | ||
| 435 | V>L | strain: MelZim8 [UniProt] | No | ||
| 460 | M>T | strain: MelZim6 [UniProt] | No | ||
| 471 | Y>D | strain: MelZim1, MelZim4, MelZim5 and MelZim6 [UniProt] | No | ||
| 486 | I>R | strain: MelZim6 [UniProt] | No | ||
| 513 | G>R | strain: MelZim1, MelZim5 and MelZim6 [UniProt] | No | ||
| 538 | A>E | strain: MelZim1, MelZim5 and MelZim6 [UniProt] | No | ||
| 544 | H>Y | strain: MelZim1, MelZim5 and MelZim6 [UniProt] | No | ||
| 568 | T>M | strain: MelZim1, MelZim5 and MelZim6 [UniProt] | No | ||
| 592 | T>A | strain: MelZim6 [UniProt] | No | ||
| 603 | L>M | strain: MelZim1, MelZim5 and MelZim6 [UniProt] | No | ||
| 681 | L>V | strain: MelZim1, MelZim3, MelZim4, MelZim5, MelZim6 and MelZim7 [UniProt] | No | ||
| 714 | T>I | strain: MelZim5 and MelZim8 [UniProt] | No | ||
| 732 | T>S | strain: MelZim8 [UniProt] | No | ||
| 741 | M>I | strain: MelZim1 [UniProt] | No |
No associated diseases with P08953
20 regional properties for P08953
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Toll/interleukin-1 receptor homology (TIR) domain | 857 - 996 | IPR000157 |
| domain | Leucine-rich repeat N-terminal domain | 630 - 667 | IPR000372 |
| domain | Cysteine-rich flanking region, C-terminal | 561 - 619 | IPR000483-1 |
| domain | Cysteine-rich flanking region, C-terminal | 751 - 800 | IPR000483-2 |
| repeat | Leucine-rich repeat | 367 - 388 | IPR001611-1 |
| repeat | Leucine-rich repeat | 390 - 450 | IPR001611-2 |
| repeat | Leucine-rich repeat | 498 - 521 | IPR001611-3 |
| repeat | Leucine-rich repeat | 715 - 730 | IPR001611-4 |
| repeat | Leucine-rich repeat, typical subtype | 173 - 195 | IPR003591-1 |
| repeat | Leucine-rich repeat, typical subtype | 196 - 219 | IPR003591-2 |
| repeat | Leucine-rich repeat, typical subtype | 220 - 243 | IPR003591-3 |
| repeat | Leucine-rich repeat, typical subtype | 245 - 267 | IPR003591-4 |
| repeat | Leucine-rich repeat, typical subtype | 268 - 291 | IPR003591-5 |
| repeat | Leucine-rich repeat, typical subtype | 342 - 364 | IPR003591-6 |
| repeat | Leucine-rich repeat, typical subtype | 366 - 388 | IPR003591-7 |
| repeat | Leucine-rich repeat, typical subtype | 389 - 412 | IPR003591-8 |
| repeat | Leucine-rich repeat, typical subtype | 413 - 436 | IPR003591-9 |
| repeat | Leucine-rich repeat, typical subtype | 496 - 521 | IPR003591-10 |
| repeat | Leucine-rich repeat, typical subtype | 714 - 736 | IPR003591-11 |
| repeat | BspA type Leucine rich repeat region | 152 - 270 | IPR026906 |
Functions
6 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cell surface | The external part of the cell wall and/or plasma membrane. |
| cleavage furrow | The cleavage furrow is a plasma membrane invagination at the cell division site. The cleavage furrow begins as a shallow groove and eventually deepens to divide the cytoplasm. |
| early endosome | A membrane-bounded organelle that receives incoming material from primary endocytic vesicles that have been generated by clathrin-dependent and clathrin-independent endocytosis; vesicles fuse with the early endosome to deliver cargo for sorting into recycling or degradation pathways. |
| external side of plasma membrane | The leaflet of the plasma membrane that faces away from the cytoplasm and any proteins embedded or anchored in it or attached to its surface. |
| integral component of plasma membrane | The component of the plasma membrane consisting of the gene products and protein complexes having at least some part of their peptide sequence embedded in the hydrophobic region of the membrane. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
9 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytokine binding | Binding to a cytokine, any of a group of proteins that function to control the survival, growth and differentiation of tissues and cells, and which have autocrine and paracrine activity. |
| cytokine receptor activity | Combining with a cytokine and transmitting the signal from one side of the membrane to the other to initiate a change in cell activity. |
| identical protein binding | Binding to an identical protein or proteins. |
| NAD(P)+ nucleosidase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: NAD(P)+ + H2O = ADP-ribose(P) + nicotinamide. |
| NAD+ nucleotidase, cyclic ADP-ribose generating | Catalysis of the reaction: NAD+ + H2O = nicotinamide + ADP-ribose that proceeds in a stepwise fashion by ADP-ribosyl cyclase activity followed by cyclic ADP-ribose hydrolase activity. |
| signaling receptor activity | Receiving a signal and transmitting it in the cell to initiate a change in cell activity. A signal is a physical entity or change in state that is used to transfer information in order to trigger a response. |
| TIR domain binding | Binding to a Toll-Interleukin receptor (TIR) domain of a protein. The TIR domain is an intracellular 200 residue domain that is found in the Toll protein, the interleukin-1 receptor (IL-1R), and MyD88; it contains three highly-conserved regions, and mediates protein-protein interactions between the Toll-like receptors (TLRs) and signal-transduction components. |
| transmembrane signaling receptor activity | Combining with an extracellular or intracellular signal and transmitting the signal from one side of the membrane to the other to initiate a change in cell activity or state as part of signal transduction. |
| virion binding | Binding to a virion, either by binding to components of the capsid or the viral envelope. |
24 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| antifungal innate immune response | An defense response against a fungus mediated through an innate immune response. An innate immune response is mediated by germline encoded components that directly recognize components of potential pathogens. |
| cell adhesion | The attachment of a cell, either to another cell or to an underlying substrate such as the extracellular matrix, via cell adhesion molecules. |
| cell competition in a multicellular organism | Competitive interactions within multicellular organisms between cell populations that differ in growth rates, leading to the elimination of the slowest-growing cells. |
| defense response to Gram-positive bacterium | Reactions triggered in response to the presence of a Gram-positive bacterium that act to protect the cell or organism. |
| defense response to oomycetes | Reactions triggered in response to the presence of oomycetes that act to protect the cell or organism. |
| detection of virus | The series of events in which a stimulus from a virus is received and converted into a molecular signal. |
| dorsal/ventral axis specification | The establishment, maintenance and elaboration of the dorsal/ventral axis. The dorsal/ventral axis is defined by a line that runs orthogonal to both the anterior/posterior and left/right axes. The dorsal end is defined by the upper or back side of an organism. The ventral end is defined by the lower or front side of an organism. |
| heart development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the heart over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The heart is a hollow, muscular organ, which, by contracting rhythmically, keeps up the circulation of the blood. |
| innate immune response | Innate immune responses are defense responses mediated by germline encoded components that directly recognize components of potential pathogens. |
| larval somatic muscle development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the larval somatic muscle over time, from its formation to the mature structure. |
| negative regulation of cell growth | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate, extent or direction of cell growth. |
| negative regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of insulin receptor signaling. |
| negative regulation of multicellular organism growth | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of growth of an organism to reach its usual body size. |
| positive regulation of antifungal peptide production | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of antifungal peptide production. |
| positive regulation of antimicrobial peptide production | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of antimicrobial peptide production. |
| positive regulation of hemocyte proliferation | Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of hemocyte proliferation. Hemocytes are blood cells associated with a hemocoel (the cavity containing most of the major organs of the arthropod body) that are involved in defense and clotting of hemolymph, but not involved in transport of oxygen. An example of this process is found in Drosophila melanogaster. |
| positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription from an RNA polymerase II promoter. |
| regulation of embryonic pattern specification | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of embryonic pattern specification. |
| response to tumor cell | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus from a tumor cell. |
| response to wounding | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating damage to the organism. |
| synapse assembly | The aggregation, arrangement and bonding together of a set of components to form a synapse. This process ends when the synapse is mature (functional). |
| synaptic target inhibition | The process in which a neuronal cell in a multicellular organism recognizes chemorepellent signals that inhibit its growth toward the source. |
| Toll signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by an extracellular ligand binding to the receptor Toll on the surface of a target cell, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| toll-like receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by a ligand binding to a toll-like receptor on the surface of a target cell. Toll-like receptors directly bind pattern motifs from a variety of microbial sources to initiate an innate immune response. |
9 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q5I2M7 | TLR9 | Toll-like receptor 9 | Felis catus (Cat) (Felis silvestris catus) | SS |
| Q5I2M8 | TLR9 | Toll-like receptor 9 | Canis lupus familiaris (Dog) (Canis familiaris) | SS |
| Q2EEY0 | TLR9 | Toll-like receptor 9 | Equus caballus (Horse) | SS |
| Q9NR96 | TLR9 | Toll-like receptor 9 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q9NYK1 | TLR7 | Toll-like receptor 7 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P58681 | Tlr7 | Toll-like receptor 7 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q9EQU3 | Tlr9 | Toll-like receptor 9 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q5I2M3 | TLR9 | Toll-like receptor 9 | Sus scrofa (Pig) | SS |
| A5H2Z9 | Tlr7 | Toll-like receptor 7 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MSRLKAASEL | ALLVIILQLL | QWPGSEASFG | RDACSEMSID | GLCQCAPIMS | EYEIICPANA |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| ENPTFRLTIQ | PKDYVQIMCN | LTDTTDYQQL | PKKLRIGEVD | RVQMRRCMLP | GHTPIASILD |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| YLGIVSPTTL | IFESDNLGMN | ITRQHLDRLH | GLKRFRFTTR | RLTHIPANLL | TDMRNLSHLE |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| LRANIEEMPS | HLFDDLENLE | SIEFGSNKLR | QMPRGIFGKM | PKLKQLNLWS | NQLHNLTKHD |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| FEGATSVLGI | DIHDNGIEQL | PHDVFAHLTN | VTDINLSANL | FRSLPQGLFD | HNKHLNEVRL |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| MNNRVPLATL | PSRLFANQPE | LQILRLRAEL | QSLPGDLFEH | STQITNISLG | DNLLKTLPAT |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| LLEHQVNLLS | LDLSNNRLTH | LPDSLFAHTT | NLTDLRLEDN | LLTGISGDIF | SNLGNLVTLV |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| MSRNRLRTID | SRAFVSTNGL | RHLHLDHNDI | DLQQPLLDIM | LQTQINSPFG | YMHGLLTLNL |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| RNNSIIFVYN | DWKNTMLQLR | ELDLSYNNIS | SLGYEDLAFL | SQNRLHVNMT | HNKIRRIALP |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| EDVHLGEGYN | NNLVHVDLND | NPLVCDCTIL | WFIQLVRGVH | KPQYSRQFKL | RTDRLVCSQP |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| NVLEGTPVRQ | IEPQTLICPL | DFSDDPRERK | CPRGCNCHVR | TYDKALVINC | HSGNLTHVPR |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| LPNLHKNMQL | MELHLENNTL | LRLPSANTPG | YESVTSLHLA | GNNLTSIDVD | QLPTNLTHLD |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| ISWNHLQMLN | ATVLGFLNRT | MKWRSVKLSG | NPWMCDCTAK | PLLLFTQDNF | ERIGDRNEMM |
| 790 | 800 | 810 | 820 | 830 | 840 |
| CVNAEMPTRM | VELSTNDICP | AEKGVFIALA | VVIALTGLLA | GFTAALYYKF | QTEIKIWLYA |
| 850 | 860 | 870 | 880 | 890 | 900 |
| HNLLLWFVTE | EDLDKDKKFD | AFISYSHKDQ | SFIEDYLVPQ | LEHGPQKFQL | CVHERDWLVG |
| 910 | 920 | 930 | 940 | 950 | 960 |
| GHIPENIMRS | VADSRRTIIV | LSQNFIKSEW | ARLEFRAAHR | SALNEGRSRI | IVIIYSDIGD |
| 970 | 980 | 990 | 1000 | 1010 | 1020 |
| VEKLDEELKA | YLKMNTYLKW | GDPWFWDKLR | FALPHRRPVG | NIGNGALIKT | ALKGSTDDKL |
| 1030 | 1040 | 1050 | 1060 | 1070 | 1080 |
| ELIKPSPVTP | PLTTPPAEAT | KNPLVAQLNG | VTPHQAIMIA | NGKNGLTNLY | TPNGKSHGNG |
| 1090 | |||||
| HINGAFIINT | NAKQSDV |