P08752
Gene name |
Gnai2 (Gnai-2) |
Protein name |
Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G |
Names |
i subunit alpha-2 , Adenylate cyclase-inhibiting G alpha protein |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:14678 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
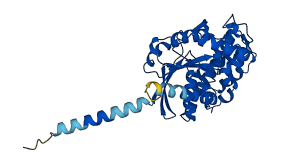
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
185-349 (Ras-like domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Ligand binding, Partner binding |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
References
- Yeon JH et al. (2016) "Systems-wide Identification of cis-Regulatory Elements in Proteins", Cell systems, 2, 89-100
- Goricanec D et al. (2016) "Conformational dynamics of a G-protein α subunit is tightly regulated by nucleotide binding", Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 113, E3629-38
- Coleman DE et al. (1999) "Structure of Gialpha1.GppNHp, autoinhibition in a galpha protein-substrate complex", The Journal of biological chemistry, 274, 16669-72
- Lutz S et al. (2007) "Structure of Galphaq-p63RhoGEF-RhoA complex reveals a pathway for the activation of RhoA by GPCRs", Science (New York, N.Y.), 318, 1923-7
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for P08752
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-P08752-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
13 variants for P08752
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs3400107051 | 173 | Q>* | No | EVA | |
| rs3389075600 | 173 | Q>R | No | EVA | |
| rs3389045809 | 174 | D>V | No | EVA | |
| rs3400743249 | 177 | R>W | No | EVA | |
| rs3389045881 | 194 | D>E | No | EVA | |
| rs3389075631 | 244 | M>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3389045892 | 244 | M>T | No | EVA | |
| rs3389045854 | 275 | F>L | No | EVA | |
| rs3389070969 | 296 | K>M | No | EVA | |
| rs3400626095 | 316 | D>A | No | EVA | |
| rs3389045863 | 328 | T>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3389079196 | 343 | V>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3389066691 | 346 | K>M | No | EVA |
No associated diseases with P08752
No regional properties for P08752
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| No domain, repeats, and functional sites for P08752 | |||
Functions
11 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cell body | The portion of a cell bearing surface projections such as axons, dendrites, cilia, or flagella that includes the nucleus, but excludes all cell projections. |
| centrosome | A structure comprised of a core structure (in most organisms, a pair of centrioles) and peripheral material from which a microtubule-based structure, such as a spindle apparatus, is organized. Centrosomes occur close to the nucleus during interphase in many eukaryotic cells, though in animal cells it changes continually during the cell-division cycle. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| dendrite | A neuron projection that has a short, tapering, morphology. Dendrites receive and integrate signals from other neurons or from sensory stimuli, and conduct nerve impulses towards the axon or the cell body. In most neurons, the impulse is conveyed from dendrites to axon via the cell body, but in some types of unipolar neuron, the impulse does not travel via the cell body. |
| heterotrimeric G-protein complex | Any of a family of heterotrimeric GTP-binding and hydrolyzing proteins; they belong to a superfamily of GTPases that includes monomeric proteins such as EF-Tu and RAS. Heterotrimeric G-proteins consist of three subunits; the alpha subunit contains the guanine nucleotide binding site and possesses GTPase activity; the beta and gamma subunits are tightly associated and function as a beta-gamma heterodimer; extrinsic plasma membrane proteins (cytoplasmic face) that function as a complex to transduce signals from G protein-coupled receptors to an effector protein. |
| midbody | A thin cytoplasmic bridge formed between daughter cells at the end of cytokinesis. The midbody forms where the contractile ring constricts, and may persist for some time before finally breaking to complete cytokinesis. |
| neuronal dense core vesicle | A dense core vesicle (granule) that is part of a neuron. These vesicles typically contain neuropeptides. They can be found in all parts of neurons, including the soma, dendrites, axonal swellings (varicosities) and synaptic terminals. |
| nucleoplasm | That part of the nuclear content other than the chromosomes or the nucleolus. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| synapse | The junction between an axon of one neuron and a dendrite of another neuron, a muscle fiber or a glial cell. As the axon approaches the synapse it enlarges into a specialized structure, the presynaptic terminal bouton, which contains mitochondria and synaptic vesicles. At the tip of the terminal bouton is the presynaptic membrane; facing it, and separated from it by a minute cleft (the synaptic cleft) is a specialized area of membrane on the receiving cell, known as the postsynaptic membrane. In response to the arrival of nerve impulses, the presynaptic terminal bouton secretes molecules of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft. These diffuse across the cleft and transmit the signal to the postsynaptic membrane. |
5 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| G protein-coupled receptor binding | Binding to a G protein-coupled receptor. |
| G-protein beta/gamma-subunit complex binding | Binding to a complex of G-protein beta/gamma subunits. |
| GTP binding | Binding to GTP, guanosine triphosphate. |
| GTPase activity | Catalysis of the reaction |
| metal ion binding | Binding to a metal ion. |
22 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway | A G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway in which the signal is transmitted via the activation of adenylyl cyclase activity and a subsequent increase in the intracellular concentration of cyclic AMP (cAMP). |
| adenylate cyclase-inhibiting G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway | A G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway in which the signal is transmitted via the inhibition of adenylyl cyclase activity and a subsequent decrease in the intracellular concentration of cyclic AMP (cAMP). |
| cell cycle | The progression of biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur in a cell during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events. Canonically, the cell cycle comprises the replication and segregation of genetic material followed by the division of the cell, but in endocycles or syncytial cells nuclear replication or nuclear division may not be followed by cell division. |
| cell division | The process resulting in division and partitioning of components of a cell to form more cells; may or may not be accompanied by the physical separation of a cell into distinct, individually membrane-bounded daughter cells. |
| cell population proliferation | The multiplication or reproduction of cells, resulting in the expansion of a cell population. |
| G protein-coupled acetylcholine receptor signaling pathway | A G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway initiated by a ligand binding to an acetylcholine receptor on the surface of a target cell, and ends with regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| G protein-coupled adenosine receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals generated as a consequence of a receptor binding to extracellular adenosine and transmitting the signal to a heterotrimeric G-protein complex to initiate a change in cell activity. |
| G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by a ligand binding to its receptor, in which the activated receptor promotes the exchange of GDP for GTP on the alpha-subunit of an associated heterotrimeric G-protein complex. The GTP-bound activated alpha-G-protein then dissociates from the beta- and gamma-subunits to further transmit the signal within the cell. The pathway begins with receptor-ligand interaction, and ends with regulation of a downstream cellular process. The pathway can start from the plasma membrane, Golgi or nuclear membrane. |
| gamma-aminobutyric acid signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals generated by the binding of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA, 4-aminobutyrate), an amino acid which acts as a neurotransmitter in some organisms, to its receptor on the surface of a target cell. |
| negative regulation of adenylate cyclase-activating adrenergic receptor signaling pathway involved in heart process | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of an adenylate cyclase-activating adrenergic receptor signaling pathway involved in some heart process. |
| negative regulation of apoptotic signaling pathway | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of apoptotic signaling pathway. |
| negative regulation of calcium ion-dependent exocytosis | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of calcium ion-dependent exocytosis. |
| negative regulation of synaptic transmission | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of synaptic transmission, the process of communication from a neuron to a target (neuron, muscle, or secretory cell) across a synapse. |
| positive regulation of cell migration | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell migration. |
| positive regulation of cell population proliferation | Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of cell proliferation. |
| positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction mediated by the ERK1 and ERK2 cascade. |
| positive regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway | Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of insulin receptor signaling. |
| positive regulation of neural precursor cell proliferation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of neural precursor cell proliferation. |
| positive regulation of superoxide anion generation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of enzymatic generation of superoxide by a cell. |
| positive regulation of urine volume | Any process that increases the amount of urine excreted from the body over a unit of time. |
| positive regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell proliferation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation. |
| regulation of calcium ion transport | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the directed movement of calcium ions into, out of or within a cell, or between cells, by means of some agent such as a transporter or pore. |
59 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P63097 | GNAI1 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| P0C7Q4 | GNAT3 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| P04696 | GNAT2 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| P04695 | GNAT1 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| P08239 | GNAO1 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| P50146 | GNAI1 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P50147 | GNAI2 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P38400 | GNAI2 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(i) subunit alpha-2 | Canis lupus familiaris (Dog) (Canis familiaris) | PR |
| P16378 | Galphao | G protein alpha o subunit | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| P25157 | cta | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit alpha homolog | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| P20353 | Galphai | G protein alpha i subunit | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| P11488 | GNAT1 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P19087 | GNAT2 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P09471 | GNAO1 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q03113 | GNA12 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit alpha-12 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P63096 | GNAI1 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P08754 | GNAI3 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| A8MTJ3 | GNAT3 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q14344 | GNA13 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit alpha-13 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P19086 | GNAZ | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P04899 | GNAI2 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| B2RSH2 | Gnai1 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| O70443 | Gnaz | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P20612 | Gnat1 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P27600 | Gna12 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit alpha-12 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P27601 | Gna13 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit alpha-13 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P50149 | Gnat2 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q3V3I2 | Gnat3 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q9DC51 | Gnai3 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P21279 | Gnaq | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(q) subunit alpha | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P30678 | Gna15 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit alpha-15 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P18872 | Gnao1 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P93564 | GPA1 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-1 subunit | Solanum tuberosum (Potato) | SS |
| Q63210 | Gna12 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit alpha-12 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P19627 | Gnaz | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P29348 | Gnat3 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P59215 | Gnao1 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P08753 | Gnai3 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q6Q7Y5 | Gna13 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit alpha-13 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P04897 | Gnai2 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q0DJ33 | GPA1 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-1 subunit | Oryza sativa subsp. japonica (Rice) | SS |
| O76584 | gpa-11 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-11 subunit | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| P51875 | goa-1 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| Q18434 | odr-3 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-17 subunit | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| Q9BIG4 | gpa-10 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-10 subunit | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| P28052 | gpa-3 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-3 subunit | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| Q9XTB2 | gpa-13 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-13 subunit | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| Q93743 | gpa-6 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-6 subunit | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| Q20907 | gpa-8 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-8 subunit | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| P91907 | gpa-15 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-15 subunit | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| Q21917 | gpa-7 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-7 subunit | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| Q9BIG5 | gpa-4 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-4 subunit | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| P28051 | gpa-1 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-1 subunit | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| Q9N2V6 | gpa-16 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-16 subunit | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| P49084 | GPA1 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-1 subunit | Glycine max (Soybean) (Glycine hispida) | SS |
| P93163 | GPA2 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-2 subunit | Glycine max (Soybean) (Glycine hispida) | SS |
| O80462 | XLG1 | Extra-large guanine nucleotide-binding protein 1 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| P18064 | GPA1 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-1 subunit | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| P26981 | GPA1 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-1 subunit | Solanum lycopersicum (Tomato) (Lycopersicon esculentum) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MGCTVSAEDK | AAAERSKMID | KNLREDGEKA | AREVKLLLLG | AGESGKSTIV | KQMKIIHEDG |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| YSEEECRQYR | AVVYSNTIQS | IMAIVKAMGN | LQIDFADPQR | ADDARQLFAL | SCAAEEQGML |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| PEDLSGVIRR | LWADHGVQAC | FGRSREYQLN | DSAAYYLNDL | ERIAQSDYIP | TQQDVLRTRV |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| KTTGIVETHF | TFKDLHFKMF | DVGGQRSERK | KWIHCFEGVT | AIIFCVALSA | YDLVLAEDEE |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| MNRMHESMKL | FDSICNNKWF | TDTSIILFLN | KKDLFEEKIT | QSSLTICFPE | YTGANKYDEA |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | |
| ASYIQSKFED | LNKRKDTKEI | YTHFTCATDT | KNVQFVFDAV | TDVIIKNNLK | DCGLF |