P07948
Gene name |
LYN (JTK8) |
Protein name |
Tyrosine-protein kinase Lyn |
Names |
Lck/Yes-related novel protein tyrosine kinase, V-yes-1 Yamaguchi sarcoma viral related oncogene homolog, p53Lyn, p56Lyn |
Species |
Homo sapiens (Human) |
KEGG Pathway |
hsa:4067 |
EC number |
2.7.10.2: Protein-tyrosine kinases |
Protein Class |
|
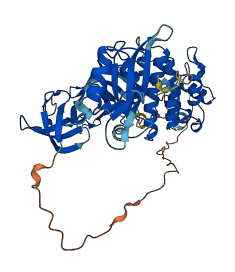
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
247-501 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Ligand binding |
Assay |
|
Target domain |
247-501 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Ligand binding, Partner binding, PTM |
Assay |
|
Target domain |
247-501 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
Target domain |
247-501 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
PTM |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
384-408 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
247-501 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
References
- Register AC et al. (2014) "SH2-catalytic domain linker heterogeneity influences allosteric coupling across the SFK family", Biochemistry, 53, 6910-23
- Boggon TJ et al. (2004) "Structure and regulation of Src family kinases", Oncogene, 23, 7918-27
- Wang Q et al. (2010) "Multicolor monitoring of dysregulated protein kinases in chronic myelogenous leukemia", ACS chemical biology, 5, 887-95
- Sotirellis N et al. (1995) "Autophosphorylation induces autoactivation and a decrease in the Src homology 2 domain accessibility of the Lyn protein kinase", The Journal of biological chemistry, 270, 29773-80
- Williams NK et al. (2009) "Crystal structures of the Lyn protein tyrosine kinase domain in its Apo- and inhibitor-bound state", The Journal of biological chemistry, 284, 284-291
- Saharinen P et al. (2003) "Autoinhibition of Jak2 tyrosine kinase is dependent on specific regions in its pseudokinase domain", Molecular biology of the cell, 14, 1448-59
- Brian BF 4th et al. (2022) "SH3-domain mutations selectively disrupt Csk homodimerization or PTPN22 binding", Scientific reports, 12, 5875
- Hantschel O et al. (2003) "A myristoyl/phosphotyrosine switch regulates c-Abl", Cell, 112, 845-57
- Walkenhorst J et al. (1996) "Analysis of human c-Abl tyrosine kinase activity and regulation in S. pombe", Oncogene, 12, 1513-20
- Pluk H et al. (2002) "Autoinhibition of c-Abl", Cell, 108, 247-59
- Woodring PJ et al. (2001) "Inhibition of c-Abl tyrosine kinase activity by filamentous actin", The Journal of biological chemistry, 276, 27104-10
- Prieto-Echagüe V et al. (2010) "Cancer-associated mutations activate the nonreceptor tyrosine kinase Ack1", The Journal of biological chemistry, 285, 10605-15
- Choi I et al. (2016) "LRRK2 Inhibits FAK Activity by Promoting FERM-mediated Autoinhibition of FAK and Recruiting the Tyrosine Phosphatase, SHP-2", Experimental neurobiology, 25, 269-276
- Lietha D et al. (2007) "Structural basis for the autoinhibition of focal adhesion kinase", Cell, 129, 1177-87
- Engen JR et al. (2008) "Structure and dynamic regulation of Src-family kinases", Cellular and molecular life sciences : CMLS, 65, 3058-73
- Alvarado JJ et al. (2010) "Crystal structure of the Src family kinase Hck SH3-SH2 linker regulatory region supports an SH3-dominant activation mechanism", The Journal of biological chemistry, 285, 35455-61
- Laham LE et al. (2000) "The activation loop in Lck regulates oncogenic potential by inhibiting basal kinase activity and restricting substrate specificity", Oncogene, 19, 3961-70
- Furlan G et al. (2014) "Phosphatase CD45 both positively and negatively regulates T cell receptor phosphorylation in reconstituted membrane protein clusters", The Journal of biological chemistry, 289, 28514-25
- Hong E et al. (2004) "Solution structure and backbone dynamics of the non-receptor protein-tyrosine kinase-6 Src homology 2 domain", The Journal of biological chemistry, 279, 29700-8
- Ko S et al. (2009) "Structural basis of the auto-inhibition mechanism of nonreceptor tyrosine kinase PTK6", Biochemical and biophysical research communications, 384, 236-42
- Qiu H et al. (2002) "Regulation of the nonreceptor tyrosine kinase Brk by autophosphorylation and by autoinhibition", The Journal of biological chemistry, 277, 34634-41
- Bond PJ et al. (2011) "Molecular mechanism of selective recruitment of Syk kinases by the membrane antigen-receptor complex", The Journal of biological chemistry, 286, 25872-81
- Brdicka T et al. (2005) "Intramolecular regulatory switch in ZAP-70: analogy with receptor tyrosine kinases", Molecular and cellular biology, 25, 4924-33
- Kulathu Y et al. (2009) "Autoinhibition and adapter function of Syk", Immunological reviews, 232, 286-99
- Ma W et al. (2009) "Mutation profile of JAK2 transcripts in patients with chronic myeloproliferative neoplasias", The Journal of molecular diagnostics : JMD, 11, 49-53
- Williams JC et al. (1997) "The 2.35 A crystal structure of the inactivated form of chicken Src: a dynamic molecule with multiple regulatory interactions", Journal of molecular biology, 274, 757-75
- Meng Y et al. (2014) "Locking the active conformation of c-Src kinase through the phosphorylation of the activation loop", Journal of molecular biology, 426, 423-35
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

210 variants for P07948
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
CA371277682 rs1203220814 |
4 | I>V | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1320979570 CA371277715 |
8 | G>E | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA4753887 rs765585716 |
10 | D>N | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA371277760 rs1473699462 |
12 | L>F | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA4753889 rs771793789 |
14 | D>G | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs771793789 CA371277797 |
14 | D>V | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs140614548 CA371277808 |
15 | D>H | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs140614548 CA4753891 |
15 | D>N | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA371277835 rs1366782003 |
16 | G>E | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs754484935 CA4753892 |
17 | V>I | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1170061438 CA371277858 |
18 | D>N | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs747832100 CA4753894 |
23 | P>A | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs769769478 CA4753895 |
25 | R>C | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1341743995 CA371277986 |
25 | R>H | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs113498934 CA177240298 |
27 | T>P | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs773082600 CA4753896 |
28 | E>G | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1285322860 CA371278012 |
29 | R>I | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA371278010 rs1285322860 |
29 | R>K | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs377153434 CA4753897 |
30 | T>A | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA4753898 rs770953840 |
30 | T>I | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA177240306 rs377153434 |
30 | T>S | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1277026515 CA371278019 |
31 | I>V | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA371278037 rs1210443703 |
33 | V>A | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1426951318 CA371278061 |
37 | T>A | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs868693193 CA177240321 |
41 | Q>E | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs745815088 CA4753922 |
45 | V>I | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1453595757 CA371278139 |
46 | P>L | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA371278144 rs145665634 |
47 | E>D | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA4753923 rs145665634 |
47 | E>D | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA177242072 rs904265167 |
47 | E>K | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA177242076 rs937513100 |
47 | E>V | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs776719521 CA4753924 |
48 | S>F | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA371278145 rs1379045539 |
48 | S>T | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
COSM1100619 rs1389792964 CA371278199 |
56 | F>L | endometrium [Cosmic] | No |
ClinGen cosmic curated gnomAD |
|
rs145218552 CA177242091 |
59 | K>E | No |
ClinGen ESP |
|
|
rs1563523229 CA371278225 |
59 | K>N | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA371278846 rs1288882059 |
60 | D>G | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs368390497 CA177242539 |
61 | P>A | No |
ClinGen ESP gnomAD |
|
|
CA371278874 rs1266934243 |
62 | E>G | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA4753948 rs773485609 |
62 | E>K | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA4753949 rs763145713 |
66 | D>V | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA4753950 rs771212623 |
68 | V>A | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA371278958 rs1249218775 |
68 | V>L | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs774711116 CA4753951 |
70 | A>T | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs898663743 CA177242551 |
71 | L>F | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs180953595 CA177242553 |
73 | P>A | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes |
|
|
CA4753953 rs768019017 |
75 | D>H | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1370509547 CA371279057 |
76 | G>S | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA371279068 rs1458760721 |
77 | I>V | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs144428385 CA177242559 |
78 | H>P | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs760301322 CA4753956 |
79 | P>L | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs760301322 CA371279105 |
79 | P>R | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1308646005 CA371279116 |
80 | D>Y | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA4753960 rs778579501 |
81 | D>G | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA371279165 rs1314809224 |
83 | S>C | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA371279251 rs1301994322 |
87 | G>R | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA371279280 rs1272028935 |
88 | E>D | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs921531136 CA177242581 |
88 | E>G | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA4753961 rs750197405 |
89 | K>E | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs149135061 CA177242585 |
90 | M>I | No |
ClinGen ESP |
|
|
CA371279299 rs1205433036 |
90 | M>V | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA4753990 rs775941123 |
96 | H>Q | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1277517826 CA371279681 |
98 | E>K | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA371279712 rs1220446165 |
99 | W>C | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1301290559 CA371279787 |
104 | S>F | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA371279792 rs1327891278 |
105 | L>V | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA4753991 rs747525732 |
106 | L>S | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA371279850 rs1585630872 |
109 | K>E | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA371279889 rs1219499238 |
111 | G>R | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs776030927 CA4753993 |
113 | I>T | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA177243620 rs969084724 |
114 | P>S | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs764645431 CA4753995 |
117 | Y>H | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA371280078 rs1430012311 |
122 | N>S | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1472321274 CA371280100 |
123 | T>I | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA4753996 rs556383645 |
125 | E>K | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ExAC |
|
|
CA4753997 rs576253860 |
126 | T>I | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA371280188 rs1401060789 |
128 | E>K | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA4754018 rs770520912 |
130 | F>L | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1163804753 CA371280328 |
132 | K>R | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA4754020 rs368483911 |
134 | I>V | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1479195262 CA371280406 |
138 | D>G | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs752739111 CA4754022 |
139 | A>T | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA371280448 rs1563525237 |
141 | R>M | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA177243665 rs760473420 |
145 | A>S | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs760473420 CA4754023 |
145 | A>T | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1292762388 CA371280556 |
149 | S>G | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA4754027 rs141769918 |
150 | A>S | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA4754026 rs141769918 |
150 | A>T | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA4754028 rs751804664 |
150 | A>V | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1438497156 CA371280600 |
152 | A>S | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA371280596 rs1438497156 |
152 | A>T | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA371280627 rs1481703596 |
154 | L>F | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA371280641 rs1235714245 |
155 | I>V | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1390701632 CA371280691 |
158 | S>T | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs529349503 CA177243684 |
162 | K>E | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA177243681 rs529349503 |
162 | K>Q | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA177244250 rs868430124 |
163 | G>E | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs749791683 CA4754054 |
165 | F>L | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1320519678 CA371281286 |
173 | D>N | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA177244282 rs963559943 |
175 | V>M | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA4754057 rs745525931 |
176 | H>P | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA4754058 rs138779681 |
179 | V>D | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC |
|
|
CA371281333 rs1390921575 |
180 | I>T | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA4754060 rs371276691 |
185 | I>T | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA371281429 rs1563526105 |
192 | G>D | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs980144064 CA177244316 |
193 | Y>C | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA371281494 rs1387153318 |
197 | P>L | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1210415750 CA371281504 |
198 | R>Q | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1261988146 CA371281531 |
200 | T>I | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1450616523 CA371281555 |
202 | P>A | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA371281560 rs1585632566 |
202 | P>L | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs761779641 CA4754063 |
203 | C>R | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA177244326 rs993632078 |
203 | C>Y | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs1378812030 CA371281580 |
204 | I>V | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA371281604 rs147376208 |
205 | S>R | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
COSM192595 CA4754066 rs759824481 |
206 | D>N | large_intestine [Cosmic] | No |
ClinGen cosmic curated ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
rs767680075 CA177244328 |
207 | M>L | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs767680075 CA4754067 |
207 | M>V | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA4754068 rs752931705 COSM454696 |
209 | K>N | breast [Cosmic] | No |
ClinGen cosmic curated ExAC gnomAD |
|
rs954830015 CA177244332 |
209 | K>R | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs954830015 CA371281659 |
209 | K>T | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA371281707 rs1392782066 |
212 | Q>R | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs748124598 CA4754082 |
215 | A>T | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA4754083 rs769802335 |
216 | D>G | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA177245419 rs562665552 |
225 | A>G | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs867077413 CA177245435 |
227 | I>V | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA371282244 rs1318070217 |
229 | P>H | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA177245450 rs968310586 |
229 | P>S | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs1311279576 CA371282322 |
232 | Q>R | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs983473142 CA177245492 |
234 | P>L | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA371282367 rs1563527049 |
234 | P>S | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs866107007 CA177245497 |
236 | D>N | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
COSM3779282 rs779606369 CA4754095 |
244 | R>Q | urinary_tract [Cosmic] | No |
ClinGen cosmic curated ExAC gnomAD |
|
rs1387477088 CA371282677 |
244 | R>W | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs908759570 CA371282709 |
245 | E>D | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA177245539 rs935530221 |
246 | S>A | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA177245544 rs542156034 |
247 | I>L | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs1333413333 CA371282828 |
251 | K>I | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs143856948 CA4754097 |
251 | K>Q | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1563527131 CA371282846 |
252 | R>M | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA371282890 rs376329765 |
255 | A>S | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs376329765 CA4754099 |
255 | A>T | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA371282927 rs1434756440 |
257 | Q>* | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1585648246 CA371284778 |
264 | G>V | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs1265583163 CA371284783 |
265 | Y>C | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA371284784 rs1265583163 |
265 | Y>F | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs45587541 CA177253045 |
267 | N>D | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs1208569792 CA371284806 |
268 | N>S | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1585648302 CA371284858 |
276 | T>P | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA4754125 rs201201305 |
279 | P>S | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA371284909 rs1369796828 |
284 | V>M | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA4754127 rs776908593 |
292 | N>D | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA371285047 rs1422982748 |
296 | T>A | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1585648386 CA371285068 |
298 | Q>K | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA371285112 rs531258350 |
300 | D>E | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes gnomAD |
|
|
CA4754130 rs551018256 |
301 | K>R | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
COSM75325 CA4754132 rs766955887 |
303 | V>L | ovary [Cosmic] | No |
ClinGen cosmic curated ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
CA4754133 rs373128303 |
304 | R>K | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1183826897 CA371285166 |
304 | R>S | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs55803865 CA177253120 |
306 | Y>* | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs745631117 CA177253121 |
307 | A>S | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs753621314 CA4754139 |
315 | I>V | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1216734638 CA371285365 |
320 | E>K | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1246400601 CA371285435 |
324 | K>R | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA4754159 rs764933395 |
333 | S>N | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1327427054 CA371286271 COSM1100635 |
334 | D>N | endometrium [Cosmic] | No |
ClinGen cosmic curated gnomAD |
|
CA4754160 rs750361940 |
334 | D>V | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs374928456 CA4754161 |
337 | G>R | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA177255312 rs374928456 |
337 | G>S | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1585651408 CA371286309 |
339 | V>G | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs748270691 CA4754163 |
341 | L>F | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
COSM1673919 rs1218543185 CA371288252 |
359 | E>K | large_intestine [Cosmic] | No |
ClinGen cosmic curated gnomAD |
|
CA4754186 rs201895605 |
360 | R>Q | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs144335088 CA4754185 |
360 | R>W | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA4754187 rs746274497 |
364 | I>V | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA177279491 rs969562107 |
373 | V>I | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA4754192 rs775942701 |
374 | L>P | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA4754195 rs772832021 |
377 | E>K | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA371288380 rs1319883203 |
379 | L>F | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1384729059 CA371288387 |
380 | M>K | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1384729059 CA371288388 |
380 | M>R | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA371288403 rs1162202927 |
382 | K>Q | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1301313182 CA371288605 |
409 | W>R | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1347486935 COSM1457577 CA371288618 |
410 | T>M | large_intestine [Cosmic] | No |
ClinGen cosmic curated TOPMed gnomAD |
|
CA4754218 rs201276146 |
425 | D>G | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA177280203 rs544301081 |
437 | V>F | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs1169746771 CA371276218 |
447 | R>K | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA4754250 rs777296861 |
451 | D>E | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA4754248 rs373301912 |
451 | D>N | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA4754252 rs778487640 |
455 | A>S | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA4754254 rs771766572 |
462 | M>I | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1382985468 CA371276429 |
462 | M>R | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1169208278 CA371276453 |
464 | R>C | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1465409982 CA371276459 |
464 | R>H | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs377327132 CA4754255 |
465 | V>M | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA4754258 rs146791536 |
470 | D>G | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA177240423 rs763743402 |
474 | D>E | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA371276642 rs1245357591 |
476 | M>I | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs771043198 CA4754260 |
477 | K>E | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs150197767 CA4754262 |
478 | M>I | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA4754261 rs774443127 |
478 | M>T | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA4754263 rs767796440 |
481 | K>R | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1428596452 CA371276734 |
482 | E>G | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA4754267 rs754329278 |
492 | Y>C | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1382352431 CA371276882 |
494 | Q>E | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA4754270 rs527508795 |
496 | V>I | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA177240451 rs62515392 |
498 | D>N | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA371276970 rs1265332460 |
501 | Y>C | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1585690632 CA371277056 |
508 | Y>S | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs777742447 CA177240460 |
512 | P>T | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
1 associated diseases with P07948
Without disease ID
8 regional properties for P07948
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Protein kinase domain | 194 - 443 | IPR000719 |
| domain | SH2 domain | 79 - 170 | IPR000980 |
| domain | Serine-threonine/tyrosine-protein kinase, catalytic domain | 195 - 438 | IPR001245 |
| domain | SH3 domain | 7 - 69 | IPR001452 |
| active_site | Tyrosine-protein kinase, active site | 307 - 319 | IPR008266 |
| binding_site | Protein kinase, ATP binding site | 200 - 221 | IPR017441 |
| domain | Tyrosine-protein kinase, catalytic domain | 194 - 438 | IPR020635 |
| domain | CSK-like, SH2 domain | 77 - 174 | IPR035027 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.10.2 | Protein-tyrosine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
19 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| adherens junction | A cell-cell junction composed of the epithelial cadherin-catenin complex. The epithelial cadherins, or E-cadherins, of each interacting cell extend through the plasma membrane into the extracellular space and bind to each other. The E-cadherins bind to catenins on the cytoplasmic side of the membrane, where the E-cadherin-catenin complex binds to cytoskeletal components and regulatory and signaling molecules. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| endocytic vesicle membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding an endocytic vesicle. |
| extracellular exosome | A vesicle that is released into the extracellular region by fusion of the limiting endosomal membrane of a multivesicular body with the plasma membrane. Extracellular exosomes, also simply called exosomes, have a diameter of about 40-100 nm. |
| extrinsic component of cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane | The component of a plasma membrane consisting of gene products and protein complexes that are loosely bound to its cytoplasmic surface, but not integrated into the hydrophobic region. |
| glutamatergic synapse | A synapse that uses glutamate as a neurotransmitter. |
| Golgi apparatus | A membrane-bound cytoplasmic organelle of the endomembrane system that further processes the core oligosaccharides (e.g. N-glycans) added to proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum and packages them into membrane-bound vesicles. The Golgi apparatus operates at the intersection of the secretory, lysosomal, and endocytic pathways. |
| integrin alpha2-beta1 complex | An integrin complex that comprises one alpha2 subunit and one beta1 subunit. |
| intracellular membrane-bounded organelle | Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane. |
| lysosomal membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding the lysosome and separating its contents from the cell cytoplasm. |
| membrane raft | Any of the small (10-200 nm), heterogeneous, highly dynamic, sterol- and sphingolipid-enriched membrane domains that compartmentalize cellular processes. Small rafts can sometimes be stabilized to form larger platforms through protein-protein and protein-lipid interactions. |
| mitochondrial crista | Any of the inward folds of the mitochondrial inner membrane. Their number, extent, and shape differ in mitochondria from different tissues and organisms. They appear to be devices for increasing the surface area of the mitochondrial inner membrane, where the enzymes of electron transport and oxidative phosphorylation are found. Their shape can vary with the respiratory state of the mitochondria. |
| mitochondrial intermembrane space | The region between the inner and outer lipid bilayers of the mitochondrial envelope. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| perinuclear region of cytoplasm | Cytoplasm situated near, or occurring around, the nucleus. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| postsynaptic density | An electron dense network of proteins within and adjacent to the postsynaptic membrane of an asymmetric, neuron-neuron synapse. Its major components include neurotransmitter receptors and the proteins that spatially and functionally organize them such as anchoring and scaffolding molecules, signaling enzymes and cytoskeletal components. |
| postsynaptic specialization, intracellular component | A network of proteins adjacent to the postsynaptic membrane. Its major components include the proteins that spatially and functionally organize neurotransmitter receptors in the adjacent membrane, such as anchoring and scaffolding molecules, signaling enzymes and cytoskeletal components. |
18 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| enzyme binding | Binding to an enzyme, a protein with catalytic activity. |
| ephrin receptor binding | Binding to an ephrin receptor. |
| gamma-tubulin binding | Binding to the microtubule constituent protein gamma-tubulin. |
| glycosphingolipid binding | Binding to glycosphingolipid, a compound with residues of sphingoid and at least one monosaccharide. |
| integrin binding | Binding to an integrin. |
| kinase activity | Catalysis of the transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a substrate molecule. |
| non-membrane spanning protein tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + protein L-tyrosine = ADP + protein L-tyrosine phosphate by a non-membrane spanning protein. |
| phosphoprotein binding | Binding to a phosphorylated protein. |
| phosphorylation-dependent protein binding | Binding to a protein upon phosphorylation of the target protein. |
| platelet-derived growth factor receptor binding | Binding to a platelet-derived growth factor receptor. |
| protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + a protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate; ATP + a protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate; and ATP + a protein tyrosine = ADP + protein tyrosine phosphate. |
| protein tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + a protein tyrosine = ADP + protein tyrosine phosphate. |
| scaffold protein binding | Binding to a scaffold protein. Scaffold proteins are crucial regulators of many key signaling pathways. Although not strictly defined in function, they are known to interact and/or bind with multiple members of a signaling pathway, tethering them into complexes. |
| SH3 domain binding | Binding to a SH3 domain (Src homology 3) of a protein, small protein modules containing approximately 50 amino acid residues found in a great variety of intracellular or membrane-associated proteins. |
| signaling receptor binding | Binding to one or more specific sites on a receptor molecule, a macromolecule that undergoes combination with a hormone, neurotransmitter, drug or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell function. |
| transmembrane transporter binding | Binding to a transmembrane transporter, a protein or protein complex that enables the transfer of a substance, usually a specific substance or a group of related substances, from one side of a membrane to the other. |
| ubiquitin protein ligase binding | Binding to a ubiquitin protein ligase enzyme, any of the E3 proteins. |
81 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| adaptive immune response | An immune response mediated by cells expressing specific receptors for antigen produced through a somatic diversification process, and allowing for an enhanced secondary response to subsequent exposures to the same antigen (immunological memory). |
| B cell homeostasis | The process of regulating the proliferation and elimination of B cells such that the total number of B cells within a whole or part of an organism is stable over time in the absence of an outside stimulus. |
| B cell receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by the cross-linking of an antigen receptor on a B cell. |
| cell differentiation | The process in which relatively unspecialized cells, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cells, acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate and its subsequent development to the mature state. |
| cellular response to DNA damage stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating damage to its DNA from environmental insults or errors during metabolism. |
| cellular response to extracellular stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an extracellular stimulus. |
| cellular response to heat | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a heat stimulus, a temperature stimulus above the optimal temperature for that organism. |
| cellular response to retinoic acid | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a retinoic acid stimulus. |
| dendritic cell differentiation | The process in which a precursor cell type acquires the specialized features of a dendritic cell. A dendritic cell is a leukocyte of dendritic lineage specialized in the uptake, processing, and transport of antigens to lymph nodes for the purpose of stimulating an immune response via T cell activation. |
| ephrin receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by ephrin binding to its receptor, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| erythrocyte differentiation | The process in which a myeloid precursor cell acquires specializes features of an erythrocyte. |
| Fc receptor mediated inhibitory signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals generated as a consequence of the binding of the Fc portion of an immunoglobulin by an Fc receptor capable of inhibiting an immune effector process contributing to an immune response. The Fc portion of an immunoglobulin is its C-terminal constant region. |
| Fc receptor mediated stimulatory signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals generated as a consequence of a the binding of the Fc portion of an immunoglobulin by an Fc receptor capable of activating or perpetuating an immune response. The Fc portion of an immunoglobulin is its C-terminal constant region. |
| Fc-epsilon receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by the binding of the Fc portion of immunoglobulin E (IgE) to an Fc-epsilon receptor on the surface of a target cell, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. The Fc portion of an immunoglobulin is its C-terminal constant region. |
| Fc-gamma receptor signaling pathway involved in phagocytosis | An Fc-gamma receptor signaling pathway that contributes to the endocytic engulfment of external particulate material by phagocytes. |
| growth hormone receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT | The process in which STAT proteins (Signal Transducers and Activators of Transcription) are activated by members of the JAK (janus activated kinase) family of tyrosine kinases, following the binding of physiological ligands to the growth hormone receptor. Once activated, STATs dimerize and translocate to the nucleus and modulate the expression of target genes. |
| histamine secretion by mast cell | The regulated release of histamine by a mast cell or group of mast cells. |
| immune response-regulating cell surface receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by an extracellular ligand binding to a receptor on the surface of the target cell capable of activating, perpetuating, or inhibiting an immune response. |
| innate immune response | Innate immune responses are defense responses mediated by germline encoded components that directly recognize components of potential pathogens. |
| intracellular signal transduction | The process in which a signal is passed on to downstream components within the cell, which become activated themselves to further propagate the signal and finally trigger a change in the function or state of the cell. |
| leukocyte migration | The movement of a leukocyte within or between different tissues and organs of the body. |
| lipopolysaccharide-mediated signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by the binding of a lipopolysaccharide (LPS) to a receptor on the surface of a target cell, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. Lipopolysaccharides are major components of the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria, making them prime targets for recognition by the immune system. |
| negative regulation of B cell proliferation | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the rate or extent of B cell proliferation. |
| negative regulation of cell population proliferation | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the rate or extent of cell proliferation. |
| negative regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction mediated by the ERK1 and ERK2 cascade. |
| negative regulation of immune response | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus. |
| negative regulation of inflammatory response to antigenic stimulus | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate, or extent of an inflammatory response to an antigenic stimulus. |
| negative regulation of intracellular signal transduction | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of intracellular signal transduction. |
| negative regulation of MAP kinase activity | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of MAP kinase activity. |
| negative regulation of mast cell proliferation | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the rate or extent of mast cell proliferation. |
| negative regulation of myeloid leukocyte differentiation | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate, or extent of myeloid leukocyte differentiation. |
| negative regulation of protein phosphorylation | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the rate of addition of phosphate groups to amino acids within a protein. |
| negative regulation of toll-like receptor 2 signaling pathway | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate, or extent of toll-like receptor 2 signaling pathway. |
| negative regulation of toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate, or extent of toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway. |
| neuron projection development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron projection over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A neuron projection is any process extending from a neural cell, such as axons or dendrites (collectively called neurites). |
| oligodendrocyte development | The process aimed at the progression of an oligodendrocyte over time, from initial commitment of the cell to a specific fate, to the fully functional differentiated cell. An oligodendrocyte is a type of glial cell involved in myelinating the axons in the central nervous system. |
| peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation | The phosphorylation of peptidyl-tyrosine to form peptidyl-O4'-phospho-L-tyrosine. |
| platelet degranulation | The regulated exocytosis of secretory granules containing preformed mediators such as histamine and serotonin by a platelet. |
| positive regulation of aspartic-type endopeptidase activity involved in amyloid precursor protein catabolic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of aspartic-type endopeptidase activity involved in amyloid precursor protein catabolic process. |
| positive regulation of cell migration | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell migration. |
| positive regulation of cell population proliferation | Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of cell proliferation. |
| positive regulation of cellular component movement | OBSOLETE. Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the movement of a cellular component. |
| positive regulation of dendritic cell apoptotic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of dendritic cell apoptotic process. |
| positive regulation of Fc receptor mediated stimulatory signaling pathway | Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of the Fc receptor mediated stimulatory signaling pathway. |
| positive regulation of glial cell proliferation | Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of glial cell proliferation. |
| positive regulation of mast cell proliferation | Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of mast cell proliferation. |
| positive regulation of neuron projection development | Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of neuron projection development. Neuron projection development is the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron projection over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A neuron projection is any process extending from a neural cell, such as axons or dendrites (collectively called neurites). |
| positive regulation of oligodendrocyte progenitor proliferation | Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of oligodendrocyte progenitor proliferation. |
| positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity. |
| positive regulation of protein phosphorylation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of addition of phosphate groups to amino acids within a protein. |
| positive regulation of stress-activated protein kinase signaling cascade | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of signaling via the stress-activated protein kinase signaling cascade. |
| positive regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the introduction of a phosphate group to a tyrosine residue of a STAT (Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription) protein. |
| protein autophosphorylation | The phosphorylation by a protein of one or more of its own amino acid residues (cis-autophosphorylation), or residues on an identical protein (trans-autophosphorylation). |
| protein phosphorylation | The process of introducing a phosphate group on to a protein. |
| regulation of B cell apoptotic process | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of B cell apoptotic process. |
| regulation of B cell receptor signaling pathway | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of signaling pathways initiated by the cross-linking of an antigen receptor on a B cell. |
| regulation of cell adhesion mediated by integrin | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of cell adhesion mediated by integrin. |
| regulation of cytokine production | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of production of a cytokine. |
| regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction mediated by the ERK1 and ERK2 cascade. |
| regulation of erythrocyte differentiation | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of erythrocyte differentiation. |
| regulation of mast cell activation | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of mast cell activation. |
| regulation of mast cell degranulation | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of mast cell degranulation. |
| regulation of monocyte chemotaxis | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of monocyte chemotaxis. |
| regulation of platelet aggregation | Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of platelet aggregation. Platelet aggregation is the adhesion of one platelet to one or more other platelets via adhesion molecules. |
| regulation of protein phosphorylation | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of addition of phosphate groups into an amino acid in a protein. |
| regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the release into the cytosolic compartment of calcium ions sequestered in the endoplasmic reticulum or mitochondria. |
| response to amino acid | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an amino acid stimulus. An amino acid is a carboxylic acids containing one or more amino groups. |
| response to axon injury | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an axon injury stimulus. |
| response to carbohydrate | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a carbohydrate stimulus. |
| response to hormone | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a hormone stimulus. |
| response to insulin | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an insulin stimulus. Insulin is a polypeptide hormone produced by the islets of Langerhans of the pancreas in mammals, and by the homologous organs of other organisms. |
| response to organic cyclic compound | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an organic cyclic compound stimulus. |
| response to sterol depletion | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating deprivation of sterols. Sterols are a group of steroids characterized by the presence of one or more hydroxyl groups and a hydrocarbon side-chain in the molecule. |
| response to toxic substance | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a toxic stimulus. |
| response to xenobiotic stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus from a xenobiotic, a compound foreign to the organim exposed to it. It may be synthesized by another organism (like ampicilin) or it can be a synthetic chemical. |
| signal transduction | The cellular process in which a signal is conveyed to trigger a change in the activity or state of a cell. Signal transduction begins with reception of a signal (e.g. a ligand binding to a receptor or receptor activation by a stimulus such as light), or for signal transduction in the absence of ligand, signal-withdrawal or the activity of a constitutively active receptor. Signal transduction ends with regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. regulation of transcription or regulation of a metabolic process. Signal transduction covers signaling from receptors located on the surface of the cell and signaling via molecules located within the cell. For signaling between cells, signal transduction is restricted to events at and within the receiving cell. |
| stimulatory C-type lectin receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by the binding of C-type lectin to its receptor on the surface of a target cell, and resulting in cellular activation. |
| T cell costimulation | The process of providing, via surface-bound receptor-ligand pairs, a second, antigen-independent, signal in addition to that provided by the T cell receptor to augment T cell activation. |
| tolerance induction to self antigen | Tolerance induction directed at self antigens. |
| toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by a ligand binding to toll-like receptor 4. |
| transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by an extracellular ligand binding to a receptor on the surface of the target cell where the receptor possesses tyrosine kinase activity, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
90 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A0JNB0 | FYN | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| Q0VBZ0 | CSK | Tyrosine-protein kinase CSK | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| Q3ZC95 | BTK | Tyrosine-protein kinase | Bos taurus (Bovine) | EV SS |
| P42683 | LCK | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase LCK | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P41239 | CSK | Tyrosine-protein kinase CSK | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P00523 | SRC | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | EV |
| Q02977 | YRK | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Yrk | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q8JH64 | BTK | Tyrosine-protein kinase BTK | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P09324 | YES1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase Yes | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q05876 | FYN | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q75R65 | JAK2 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK2 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q24592 | hop | Tyrosine-protein kinase hopscotch | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | PR |
| P08630 | Btk | Tyrosine-protein kinase Btk | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| Q9V9J3 | Src42A | Tyrosine-protein kinase Src42A | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| P00528 | Src64B | Tyrosine-protein kinase Src64B | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| P23458 | JAK1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| O60674 | JAK2 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P52333 | JAK3 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P29597 | TYK2 | Non-receptor tyrosine-protein kinase TYK2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P43405 | SYK | Tyrosine-protein kinase SYK | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P43403 | ZAP70 | Tyrosine-protein kinase ZAP-70 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q13882 | PTK6 | Protein-tyrosine kinase 6 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P09769 | FGR | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fgr | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P06241 | FYN | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P12931 | SRC | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P06239 | LCK | Tyrosine-protein kinase Lck | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P51451 | BLK | Tyrosine-protein kinase Blk | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P08631 | HCK | Tyrosine-protein kinase HCK | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P07947 | YES1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase Yes | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P42685 | FRK | Tyrosine-protein kinase FRK | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q08881 | ITK | Tyrosine-protein kinase ITK/TSK | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q06187 | BTK | Tyrosine-protein kinase BTK | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P51813 | BMX | Cytoplasmic tyrosine-protein kinase BMX | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P42680 | TEC | Tyrosine-protein kinase Tec | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P42679 | MATK | Megakaryocyte-associated tyrosine-protein kinase | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P41240 | CSK | Tyrosine-protein kinase CSK | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q14289 | PTK2B | Protein-tyrosine kinase 2-beta | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q05397 | PTK2 | Focal adhesion kinase 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q13470 | TNK1 | Non-receptor tyrosine-protein kinase TNK1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q07912 | TNK2 | Activated CDC42 kinase 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P16591 | FER | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fer | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q6J9G0 | STYK1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase STYK1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P42684 | ABL2 | Tyrosine-protein kinase ABL2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P00519 | ABL1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase ABL1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q9R117 | Tyk2 | Non-receptor tyrosine-protein kinase TYK2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P08103 | Hck | Tyrosine-protein kinase HCK | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P16277 | Blk | Tyrosine-protein kinase Blk | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q62270 | Srms | Tyrosine-protein kinase Srms | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q64434 | Ptk6 | Protein-tyrosine kinase 6 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P05480 | Src | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| P14234 | Fgr | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fgr | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P35991 | Btk | Tyrosine-protein kinase BTK | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| P41241 | Csk | Tyrosine-protein kinase CSK | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| Q62137 | Jak3 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q62120 | Jak2 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| P06240 | Lck | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase LCK | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P24604 | Tec | Tyrosine-protein kinase Tec | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q04736 | Yes1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase Yes | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P39688 | Fyn | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P52332 | Jak1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q03526 | Itk | Tyrosine-protein kinase ITK/TSK | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P41242 | Matk | Megakaryocyte-associated tyrosine-protein kinase | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q922K9 | Frk | Tyrosine-protein kinase FRK | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P25911 | Lyn | Tyrosine-protein kinase Lyn | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| A1Y2K1 | FYN | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn | Sus scrofa (Pig) | SS |
| O19064 | JAK2 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK2 | Sus scrofa (Pig) | SS |
| Q62662 | Frk | Tyrosine-protein kinase FRK | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q62844 | Fyn | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P50545 | Hck | Tyrosine-protein kinase HCK | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q9WUD9 | Src | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q01621 | Lck | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase LCK | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q6P6U0 | Fgr | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fgr | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q62689 | Jak2 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK2 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q63272 | Jak3 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK3 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P32577 | Csk | Tyrosine-protein kinase CSK | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P41243 | Matk | Megakaryocyte-associated tyrosine-protein kinase | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| F1LM93 | Yes1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase Yes | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q07014 | Lyn | Tyrosine-protein kinase Lyn | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| G5ECJ6 | csk-1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase csk-1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| O45539 | src-2 | Tyrosine protein-kinase src-2 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| G5EE56 | src-1 | Tyrosine protein-kinase src-1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| F4JTP5 | STY46 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase STY46 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| O22558 | STY8 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase STY8 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q2MHE4 | HT1 | Serine/threonine/tyrosine-protein kinase HT1 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q8RWL6 | STY17 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase STY17 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| A1A5H8 | yes1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase yes | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| F1RDG9 | fynb | Tyrosine-protein kinase fynb | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| O12990 | jak1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK1 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | PR |
| Q1JPZ3 | src | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q6EWH2 | fyna | Tyrosine-protein kinase fyna | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MGCIKSKGKD | SLSDDGVDLK | TQPVRNTERT | IYVRDPTSNK | QQRPVPESQL | LPGQRFQTKD |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| PEEQGDIVVA | LYPYDGIHPD | DLSFKKGEKM | KVLEEHGEWW | KAKSLLTKKE | GFIPSNYVAK |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| LNTLETEEWF | FKDITRKDAE | RQLLAPGNSA | GAFLIRESET | LKGSFSLSVR | DFDPVHGDVI |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| KHYKIRSLDN | GGYYISPRIT | FPCISDMIKH | YQKQADGLCR | RLEKACISPK | PQKPWDKDAW |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| EIPRESIKLV | KRLGAGQFGE | VWMGYYNNST | KVAVKTLKPG | TMSVQAFLEE | ANLMKTLQHD |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| KLVRLYAVVT | REEPIYIITE | YMAKGSLLDF | LKSDEGGKVL | LPKLIDFSAQ | IAEGMAYIER |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| KNYIHRDLRA | ANVLVSESLM | CKIADFGLAR | VIEDNEYTAR | EGAKFPIKWT | APEAINFGCF |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| TIKSDVWSFG | ILLYEIVTYG | KIPYPGRTNA | DVMTALSQGY | RMPRVENCPD | ELYDIMKMCW |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | |||
| KEKAEERPTF | DYLQSVLDDF | YTATEGQYQQ | QP |