P07560
Gene name |
SEC4 (SRO6, YFL005W) |
Protein name |
Ras-related protein SEC4 |
Names |
Suppressor of RHO3 protein 6 |
Species |
Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) |
KEGG Pathway |
sce:YFL005W |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
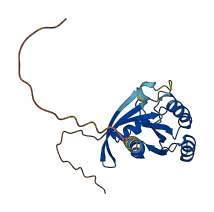
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

8 structures for P07560
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1G16 | X-ray | 180 A | A/B/C/D | 18-187 | PDB |
| 1G17 | X-ray | 200 A | A/B | 18-187 | PDB |
| 2EQB | X-ray | 270 A | A | 19-187 | PDB |
| 2OCY | X-ray | 330 A | C | 18-187 | PDB |
| 3CPH | X-ray | 290 A | A | 1-213 | PDB |
| 4Z8Y | X-ray | 190 A | A/B | 19-187 | PDB |
| 4ZDW | X-ray | 290 A | A | 19-187 | PDB |
| AF-P07560-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
2 variants for P07560
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s06-130732 | 135 | S>N | No | SGRP | |
| s06-130962 | 212 | S>P | No | SGRP |
No associated diseases with P07560
1 regional properties for P07560
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Small GTP-binding protein domain | 19 - 173 | IPR005225 |
Functions
12 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cellular bud neck | The constriction between the mother cell and daughter cell (bud) in an organism that reproduces by budding. |
| endoplasmic reticulum | The irregular network of unit membranes, visible only by electron microscopy, that occurs in the cytoplasm of many eukaryotic cells. The membranes form a complex meshwork of tubular channels, which are often expanded into slitlike cavities called cisternae. The ER takes two forms, rough (or granular), with ribosomes adhering to the outer surface, and smooth (with no ribosomes attached). |
| endosome | A vacuole to which materials ingested by endocytosis are delivered. |
| incipient cellular bud site | The portion of the budding yeast plasma membrane where a daughter cell will emerge. The yeast marks this spot with bud-site selection proteins before bud emergence occurs. Actin is polarized to this spot just prior to and during bud emergence. |
| intracellular membrane-bounded organelle | Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane. |
| mating projection tip | The apex of the mating projection in unicellular fungi exposed to mating pheromone; site of polarized growth. |
| mitochondrial outer membrane | The outer, i.e. cytoplasm-facing, lipid bilayer of the mitochondrial envelope. |
| mitochondrion | A semiautonomous, self replicating organelle that occurs in varying numbers, shapes, and sizes in the cytoplasm of virtually all eukaryotic cells. It is notably the site of tissue respiration. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| transport vesicle | Any of the vesicles of the constitutive secretory pathway, which carry cargo from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi, between Golgi cisternae, from the Golgi to the ER (retrograde transport) or to destinations within or outside the cell. |
| transport vesicle membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding a transport vesicle. |
| vesicle | Any small, fluid-filled, spherical organelle enclosed by membrane. |
2 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| GTP binding | Binding to GTP, guanosine triphosphate. |
| GTPase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: GTP + H2O = GDP + H+ + phosphate. |
10 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ascospore-type prospore assembly | During ascospore formation, the process in which each haploid nucleus becomes encapsulated by a double membrane. |
| autophagy | The cellular catabolic process in which cells digest parts of their own cytoplasm; allows for both recycling of macromolecular constituents under conditions of cellular stress and remodeling the intracellular structure for cell differentiation. |
| exocytosis | A process of secretion by a cell that results in the release of intracellular molecules (e.g. hormones, matrix proteins) contained within a membrane-bounded vesicle. Exocytosis can occur either by full fusion, when the vesicle collapses into the plasma membrane, or by a kiss-and-run mechanism that involves the formation of a transient contact, a pore, between a granule (for exemple of chromaffin cells) and the plasma membrane. The latter process most of the time leads to only partial secretion of the granule content. Exocytosis begins with steps that prepare vesicles for fusion with the membrane (tethering and docking) and ends when molecules are secreted from the cell. |
| Golgi to plasma membrane transport | The directed movement of substances from the Golgi to the plasma membrane in transport vesicles that move from the trans-Golgi network to the plasma membrane, where they fuse and release their contents by exocytosis. |
| membrane addition at site of cytokinesis | Any process involved in the net addition of membrane at the site of cytokinesis; includes vesicle recruitment and fusion, local lipid synthesis and insertion. |
| protein localization to plasma membrane | A process in which a protein is transported to, or maintained in, a specific location in the plasma membrane. |
| protein secretion | The controlled release of proteins from a cell. |
| regulation of exocytosis | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of exocytosis. |
| vesicle docking involved in exocytosis | The initial attachment of a vesicle membrane to a target membrane, mediated by proteins protruding from the membrane of the vesicle and the target membrane, that contributes to exocytosis. |
| vesicle fusion | Fusion of the membrane of a transport vesicle with its target membrane. |
23 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A4FV54 | RAB8A | Ras-related protein Rab-8A | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| Q5F470 | RAB8A | Ras-related protein Rab-8A | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | PR |
| P51152 | RAB12 | Ras-related protein Rab-12 | Canis lupus familiaris (Dog) (Canis familiaris) | PR |
| P61007 | RAB8A | Ras-related protein Rab-8A | Canis lupus familiaris (Dog) (Canis familiaris) | PR |
| Q8WXH6 | RAB40A | Ras-related protein Rab-40A | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P0C0E4 | RAB40AL | Ras-related protein Rab-40A-like | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q12829 | RAB40B | Ras-related protein Rab-40B | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q96S21 | RAB40C | Ras-related protein Rab-40C | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q6IQ22 | RAB12 | Ras-related protein Rab-12 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q92930 | RAB8B | Ras-related protein Rab-8B | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P61006 | RAB8A | Ras-related protein Rab-8A | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q8VHQ4 | Rab40c | Ras-related protein Rab-40C | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P35283 | Rab12 | Ras-related protein Rab-12 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9DD03 | Rab13 | Ras-related protein Rab-13 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P61028 | Rab8b | Ras-related protein Rab-8B | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P55258 | Rab8a | Ras-related protein Rab-8A | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q8VHP8 | Rab40b | Ras-related protein Rab-40B | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P35284 | Rab12 | Ras-related protein Rab-12 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P70550 | Rab8b | Ras-related protein Rab-8B | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P35280 | Rab8a | Ras-related protein Rab-8A | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| O24466 | RABE1A | Ras-related protein RABE1a | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9SF91 | RABE1E | Ras-related protein RABE1e | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9LZD4 | RABE1D | Ras-related protein RABE1d | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MSGLRTVSAS | SGNGKSYDSI | MKILLIGDSG | VGKSCLLVRF | VEDKFNPSFI | TTIGIDFKIK |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| TVDINGKKVK | LQLWDTAGQE | RFRTITTAYY | RGAMGIILVY | DVTDERTFTN | IKQWFKTVNE |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| HANDEAQLLL | VGNKSDMETR | VVTADQGEAL | AKELGIPFIE | SSAKNDDNVN | EIFFTLAKLI |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | |||
| QEKIDSNKLV | GVGNGKEGNI | SINSGSGNSS | KSNCC |