P06241
Gene name |
FYN |
Protein name |
Tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn |
Names |
Proto-oncogene Syn, Proto-oncogene c-Fyn, Src-like kinase, SLK, p59-Fyn |
Species |
Homo sapiens (Human) |
KEGG Pathway |
hsa:2534 |
EC number |
2.7.10.2: Protein-tyrosine kinases |
Protein Class |
|
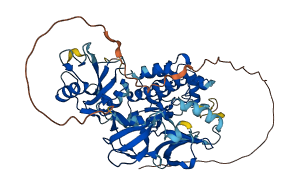
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
271-524 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Partner binding |
Assay |
|
Target domain |
271-524 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Partner binding |
Assay |
|
Target domain |
271-524 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
Target domain |
271-524 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
PTM |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
407-431 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
271-524 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
References
- Register AC et al. (2014) "SH2-catalytic domain linker heterogeneity influences allosteric coupling across the SFK family", Biochemistry, 53, 6910-23
- Boggon TJ et al. (2004) "Structure and regulation of Src family kinases", Oncogene, 23, 7918-27
- Saharinen P et al. (2003) "Autoinhibition of Jak2 tyrosine kinase is dependent on specific regions in its pseudokinase domain", Molecular biology of the cell, 14, 1448-59
- Wang Q et al. (2010) "Multicolor monitoring of dysregulated protein kinases in chronic myelogenous leukemia", ACS chemical biology, 5, 887-95
- Sotirellis N et al. (1995) "Autophosphorylation induces autoactivation and a decrease in the Src homology 2 domain accessibility of the Lyn protein kinase", The Journal of biological chemistry, 270, 29773-80
- Williams NK et al. (2009) "Crystal structures of the Lyn protein tyrosine kinase domain in its Apo- and inhibitor-bound state", The Journal of biological chemistry, 284, 284-291
- Brian BF 4th et al. (2022) "SH3-domain mutations selectively disrupt Csk homodimerization or PTPN22 binding", Scientific reports, 12, 5875
- Hantschel O et al. (2003) "A myristoyl/phosphotyrosine switch regulates c-Abl", Cell, 112, 845-57
- Walkenhorst J et al. (1996) "Analysis of human c-Abl tyrosine kinase activity and regulation in S. pombe", Oncogene, 12, 1513-20
- Pluk H et al. (2002) "Autoinhibition of c-Abl", Cell, 108, 247-59
- Woodring PJ et al. (2001) "Inhibition of c-Abl tyrosine kinase activity by filamentous actin", The Journal of biological chemistry, 276, 27104-10
- Prieto-Echagüe V et al. (2010) "Cancer-associated mutations activate the nonreceptor tyrosine kinase Ack1", The Journal of biological chemistry, 285, 10605-15
- Choi I et al. (2016) "LRRK2 Inhibits FAK Activity by Promoting FERM-mediated Autoinhibition of FAK and Recruiting the Tyrosine Phosphatase, SHP-2", Experimental neurobiology, 25, 269-276
- Lietha D et al. (2007) "Structural basis for the autoinhibition of focal adhesion kinase", Cell, 129, 1177-87
- Engen JR et al. (2008) "Structure and dynamic regulation of Src-family kinases", Cellular and molecular life sciences : CMLS, 65, 3058-73
- Alvarado JJ et al. (2010) "Crystal structure of the Src family kinase Hck SH3-SH2 linker regulatory region supports an SH3-dominant activation mechanism", The Journal of biological chemistry, 285, 35455-61
- Laham LE et al. (2000) "The activation loop in Lck regulates oncogenic potential by inhibiting basal kinase activity and restricting substrate specificity", Oncogene, 19, 3961-70
- Furlan G et al. (2014) "Phosphatase CD45 both positively and negatively regulates T cell receptor phosphorylation in reconstituted membrane protein clusters", The Journal of biological chemistry, 289, 28514-25
- Hong E et al. (2004) "Solution structure and backbone dynamics of the non-receptor protein-tyrosine kinase-6 Src homology 2 domain", The Journal of biological chemistry, 279, 29700-8
- Ko S et al. (2009) "Structural basis of the auto-inhibition mechanism of nonreceptor tyrosine kinase PTK6", Biochemical and biophysical research communications, 384, 236-42
- Qiu H et al. (2002) "Regulation of the nonreceptor tyrosine kinase Brk by autophosphorylation and by autoinhibition", The Journal of biological chemistry, 277, 34634-41
- Bond PJ et al. (2011) "Molecular mechanism of selective recruitment of Syk kinases by the membrane antigen-receptor complex", The Journal of biological chemistry, 286, 25872-81
- Brdicka T et al. (2005) "Intramolecular regulatory switch in ZAP-70: analogy with receptor tyrosine kinases", Molecular and cellular biology, 25, 4924-33
- Kulathu Y et al. (2009) "Autoinhibition and adapter function of Syk", Immunological reviews, 232, 286-99
- Ma W et al. (2009) "Mutation profile of JAK2 transcripts in patients with chronic myeloproliferative neoplasias", The Journal of molecular diagnostics : JMD, 11, 49-53
- Williams JC et al. (1997) "The 2.35 A crystal structure of the inactivated form of chicken Src: a dynamic molecule with multiple regulatory interactions", Journal of molecular biology, 274, 757-75
- Meng Y et al. (2014) "Locking the active conformation of c-Src kinase through the phosphorylation of the activation loop", Journal of molecular biology, 426, 423-35
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

50 structures for P06241
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1A0N | NMR | - | B | 80-148 | PDB |
| 1AOT | NMR | - | F | 143-248 | PDB |
| 1AOU | NMR | - | F | 143-248 | PDB |
| 1AVZ | X-ray | 300 A | C | 85-141 | PDB |
| 1AZG | NMR | - | B | 82-148 | PDB |
| 1EFN | X-ray | 250 A | A/C | 86-143 | PDB |
| 1FYN | X-ray | 230 A | A | 81-142 | PDB |
| 1G83 | X-ray | 260 A | A/B | 82-246 | PDB |
| 1M27 | X-ray | 250 A | C | 84-144 | PDB |
| 1NYF | NMR | - | A | 82-148 | PDB |
| 1NYG | NMR | - | A | 82-148 | PDB |
| 1SHF | X-ray | 190 A | A/B | 84-142 | PDB |
| 1ZBJ | NMR | - | A | 84-142 | PDB |
| 2DQ7 | X-ray | 280 A | X | 261-537 | PDB |
| 2MQI | NMR | - | A | 148-248 | PDB |
| 2MRJ | NMR | - | A | 148-248 | PDB |
| 2MRK | NMR | - | PDB | ||
| 3H0F | X-ray | 261 A | A | 73-142 | PDB |
| 3H0H | X-ray | 176 A | A | 73-142 | PDB |
| 3H0I | X-ray | 220 A | A/B | 73-142 | PDB |
| 3UA6 | X-ray | 185 A | A/B | 81-143 | PDB |
| 3UA7 | X-ray | 150 A | A/B/C/D | 81-143 | PDB |
| 4D8D | X-ray | 252 A | A/C | 84-141 | PDB |
| 4EIK | X-ray | 160 A | A | 81-143 | PDB |
| 4U17 | X-ray | 199 A | A/B/C | 148-248 | PDB |
| 4U1P | X-ray | 140 A | A | 148-248 | PDB |
| 4ZNX | X-ray | 210 A | A/B/C/D | 84-141 | PDB |
| 5ZAU | NMR | - | A | 85-141 | PDB |
| 6EDF | X-ray | 140 A | A | 83-146 | PDB |
| 6IPY | X-ray | 134 A | A | 82-144 | PDB |
| 6IPZ | X-ray | 158 A | Z | 82-144 | PDB |
| 7A2J | X-ray | 150 A | A/B | 83-142 | PDB |
| 7A2K | X-ray | 150 A | A/B/C/D | 83-142 | PDB |
| 7A2L | X-ray | 190 A | A/B | 83-142 | PDB |
| 7A2M | X-ray | 150 A | A/B | 83-142 | PDB |
| 7A2N | X-ray | 140 A | A/B/C/D | 83-142 | PDB |
| 7A2O | X-ray | 094 A | A | 83-142 | PDB |
| 7A2P | X-ray | 090 A | A | 83-143 | PDB |
| 7A2Q | X-ray | 094 A | A | 83-143 | PDB |
| 7A2R | X-ray | 105 A | A | 83-143 | PDB |
| 7A2S | X-ray | 102 A | A | 83-143 | PDB |
| 7A2T | X-ray | 122 A | A | 83-143 | PDB |
| 7A2U | X-ray | 170 A | A | 83-142 | PDB |
| 7A2V | X-ray | 181 A | A | 83-142 | PDB |
| 7A2W | X-ray | 099 A | A | 83-142 | PDB |
| 7A2X | X-ray | 092 A | A | 83-142 | PDB |
| 7A2Y | X-ray | 097 A | A | 83-142 | PDB |
| 7A2Z | X-ray | 114 A | A | 83-142 | PDB |
| 7UD6 | X-ray | 259 A | A | 86-141 | PDB |
| AF-P06241-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
186 variants for P06241
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
rs1800846906 RCV001270202 |
69 | S>C | Premature ovarian failure [ClinVar] | Yes |
ClinVar dbSNP |
|
rs932933882 CA144884560 |
5 | Q>H | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA3963807 rs758583081 |
8 | D>E | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1342849795 CA365517560 |
9 | K>E | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs753638188 CA3963806 |
11 | A>T | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA365517495 rs1216229096 |
12 | T>A | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
COSM1725728 COSM1725729 rs140762956 CA144884550 |
15 | T>M | liver [Cosmic] | No |
ClinGen cosmic curated ESP gnomAD |
|
CA917834844 rs1583358301 |
15 | T>P | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs752645540 CA3963803 |
19 | D>N | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA3963801 rs759104731 |
20 | G>C | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA365517341 rs759104731 |
20 | G>S | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs944200359 CA144884545 |
25 | S>G | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA3963800 rs113851622 |
29 | R>C | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA3963799 rs766059845 |
29 | R>H | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA3963798 rs762635372 |
30 | Y>C | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs773768130 CA3963797 |
34 | P>A | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA365517073 rs1294520439 |
35 | T>I | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA3963796 rs770281251 |
38 | H>Y | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA365516922 rs201335932 |
43 | G>A | No |
ClinGen ESP TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA144884518 rs201335932 |
43 | G>D | No |
ClinGen ESP TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA144884521 rs144813746 |
43 | G>R | No |
ClinGen ESP |
|
|
COSM1439857 rs144813746 COSM1439856 CA144884527 |
43 | G>S | large_intestine [Cosmic] | No |
ClinGen cosmic curated ESP |
|
CA144884516 rs201335932 |
43 | G>V | No |
ClinGen ESP TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs768994990 CA3963793 |
44 | V>G | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA144884514 rs924981581 |
45 | T>N | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1391967192 CA365516896 |
45 | T>P | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1420125743 CA365516753 |
54 | H>Y | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs376211530 CA3963789 |
55 | A>T | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA365516723 rs1374104837 |
56 | A>P | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1374104837 CA365516724 |
56 | A>T | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs755877937 COSM1144001 COSM593907 CA3963787 |
57 | G>R | lung [Cosmic] | No |
ClinGen cosmic curated ExAC gnomAD |
|
CA365515952 rs1163825202 |
58 | G>D | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA3963785 rs781216797 |
58 | G>R | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA3963783 rs751093740 |
59 | Q>R | No |
ClinGen ExAC |
|
|
rs765972374 CA3963782 |
62 | T>A | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA3963780 rs62620251 |
63 | V>I | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA144884482 rs769705565 |
65 | G>R | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA365515851 rs1229456829 |
66 | G>S | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1452241969 CA365515814 |
68 | N>S | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs762290632 CA3963778 |
70 | S>L | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs761032788 CA3963775 |
73 | T>M | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA144884466 rs1014698570 |
76 | L>S | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
COSM1207698 rs746134687 CA3963772 COSM1207699 |
77 | R>C | large_intestine [Cosmic] | No |
ClinGen cosmic curated ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
rs779126684 CA3963771 |
77 | R>H | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA3963769 rs376255649 |
78 | T>M | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs376255649 CA3963770 |
78 | T>R | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA365514678 rs1403522537 |
83 | G>E | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1183701507 CA365514670 |
84 | V>G | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA365514649 rs1583349053 |
88 | V>M | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs747019456 CA3963749 |
91 | Y>H | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1349795944 CA365514621 |
92 | D>G | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA3963748 rs373967031 |
92 | D>N | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
COSM1544672 COSM1544673 rs764943142 CA144882371 |
96 | R>Q | lung [Cosmic] | No |
ClinGen cosmic curated Ensembl |
|
CA3963746 rs370573757 |
97 | T>P | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC |
|
|
CA365514556 rs1334899277 |
102 | S>G | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs778511334 CA3963745 |
103 | F>V | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs902458478 CA144882341 |
104 | H>Q | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA365514527 rs1276587324 |
106 | G>R | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1159797492 CA365514520 |
107 | E>Q | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1354857291 CA365514506 |
108 | K>N | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs367543111 CA225606 RCV000084665 |
111 | I>M | No |
ClinGen ClinVar Ensembl dbSNP |
|
|
CA365514468 rs1314045748 |
114 | S>G | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA365514455 rs1417100825 |
115 | S>L | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs774471526 CA3963735 |
117 | G>V | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA365514159 rs1431899285 |
120 | W>R | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs766363948 CA3963734 |
123 | R>C | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA3963733 rs763274490 |
123 | R>H | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA365514134 rs763274490 |
123 | R>L | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1199978400 CA365514128 |
124 | S>F | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1459480269 CA365514113 |
127 | T>A | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA365514110 rs1393179519 |
127 | T>S | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA3963732 rs370983835 |
129 | E>K | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA3963731 rs370983835 |
129 | E>Q | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA365514095 rs1425536603 |
130 | T>A | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA3963730 rs746811848 |
130 | T>R | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs902952398 CA144880125 |
131 | G>A | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA365514077 rs1475630951 |
133 | I>L | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1249602922 CA365514060 |
135 | S>I | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA3963728 rs199837003 |
138 | V>L | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA365514019 rs1468202652 |
141 | V>G | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1273956318 CA365514014 |
142 | D>G | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1306312823 CA365514003 |
144 | I>V | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA365513997 rs778635709 |
145 | Q>* | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs778635709 CA3963726 |
145 | Q>E | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA144880102 rs778635709 |
145 | Q>K | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA3963712 rs762073611 |
150 | Y>N | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA3963711 rs775487661 |
154 | L>F | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1370545141 CA365513905 |
156 | R>Q | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA144878591 rs990452762 |
164 | L>S | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA365513817 rs1171571796 |
169 | P>R | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs770859434 CA3963707 |
170 | R>G | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs748749207 CA3963706 |
170 | R>K | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA3963704 rs769389395 |
175 | I>V | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs866100904 CA144878562 |
176 | R>H | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs201537647 CA144878561 |
177 | E>Q | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes |
|
|
rs1392459562 CA365513702 |
185 | Y>C | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA3963677 rs753926758 |
189 | I>F | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA365513673 rs1370673690 |
190 | R>C | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs756342493 COSM1439851 COSM1439852 CA3963675 |
190 | R>H | large_intestine [Cosmic] | No |
ClinGen cosmic curated ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
rs1427788940 CA365513655 |
192 | W>* | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1465963577 CA365513550 COSM281268 COSM3156578 |
206 | R>C | large_intestine [Cosmic] | No |
ClinGen cosmic curated gnomAD |
|
CA3963672 rs773177629 |
210 | N>D | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA144878036 rs562373735 |
210 | N>S | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA3963670 rs761344763 |
214 | Y>C | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs776054256 CA3963669 |
216 | T>S | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1325644126 CA365513479 |
217 | T>P | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA365513473 rs1298055854 |
218 | R>G | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA365513472 rs1298055854 |
218 | R>W | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA365513424 rs1325355118 |
225 | Q>* | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA365513404 rs1406059725 |
228 | V>I | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA3963667 rs77439992 |
229 | Q>H | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA365513388 rs1461865526 |
230 | H>R | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA3963649 rs763590929 |
236 | A>G | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1484568929 CA365512968 |
240 | C>R | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA3963648 rs760289292 |
241 | R>C | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs775187751 CA3963647 |
244 | V>I | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA3963646 rs771578344 |
247 | H>D | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs547882184 CA144876906 |
250 | M>L | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA3963645 rs746244610 |
254 | T>A | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA365512782 rs1391023705 |
256 | L>V | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1307588137 CA365512686 |
270 | S>T | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1058134 CA144876891 |
272 | Q>K | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs1414723028 CA365512651 |
275 | K>R | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs774796125 CA3963643 |
287 | M>L | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs750858351 CA3963584 |
292 | G>E | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA3963583 rs74391161 |
294 | T>K | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA3963581 rs776982828 |
295 | K>N | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs762425590 CA3963582 |
295 | K>R | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs764616446 CA3963580 |
296 | V>L | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1407998435 CA365509539 |
298 | I>M | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1348043585 CA365509530 |
299 | K>R | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA365509465 rs1484267673 |
303 | P>L | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA365509425 rs1238046784 |
306 | M>K | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs746081172 CA3963576 |
306 | M>V | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs773096270 CA3963575 |
307 | S>A | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA365509384 rs1359936085 |
309 | E>K | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA225596 rs367543108 RCV000084662 |
315 | A>G | No |
ClinGen ClinVar Ensembl dbSNP |
|
|
rs200994286 CA144874844 |
317 | I>V | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs373817482 CA3963569 |
324 | D>N | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA3963566 rs750014610 |
333 | V>L | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs150687315 CA144874820 |
334 | S>F | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA3963564 rs757587326 |
341 | V>I | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA365508716 rs1326474009 |
345 | M>V | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs768772210 CA3963553 |
354 | L>I | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1583318435 CA365506516 |
357 | G>R | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs1562475555 CA365506445 |
361 | A>S | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs1036974418 CA144874077 |
361 | A>V | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA3963551 rs371036122 |
365 | P>S | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA365506303 rs1410454124 |
368 | V>M | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA365506194 rs1364706330 |
371 | A>T | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA365506035 rs1476189949 |
374 | V>L | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs376486970 CA3963530 |
376 | A>T | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA3963527 rs756490869 |
381 | I>V | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA3963524 rs755454152 |
382 | E>Q | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA365505745 rs1230972545 |
383 | R>C | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs138034632 CA144873949 |
383 | R>H | No |
ClinGen ESP gnomAD |
|
|
rs751647014 CA3963523 |
392 | R>* | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA3963520 rs146616109 |
400 | N>S | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1310208336 CA365505181 |
401 | G>V | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs765507873 CA3963519 |
402 | L>F | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA365505163 rs1276905617 |
402 | L>H | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1276905617 CA365505148 |
402 | L>R | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1399641483 CA365505091 |
403 | I>M | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA365505068 rs1342905891 |
404 | C>G | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1223286930 CA365504732 |
413 | R>* | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA145301580 rs1801109 |
438 | A>D | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs752601385 CA3963500 |
441 | G>R | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1583291085 CA365373002 |
443 | F>V | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs1801121 CA145301555 VAR_014661 |
445 | I>F | No |
ClinGen UniProt Ensembl dbSNP |
|
|
rs766184115 CA3963496 |
449 | V>M | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA365372852 rs1270581627 |
452 | F>S | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA365372765 rs780676443 |
459 | L>V | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs747793778 CA3963492 |
461 | T>A | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1012190969 CA145296463 |
475 | V>M | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs1322366187 CA365368564 |
476 | L>P | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs771152377 CA3963466 |
488 | P>L | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA3963463 rs756230899 |
490 | D>N | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1241865669 CA365367944 |
493 | I>V | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1368550683 CA365367825 |
496 | H>Q | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs779707578 CA3963461 |
500 | I>T | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA3963460 rs758371153 |
505 | K>R | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
VAR_041706 CA3963458 RCV000971753 rs28763975 |
506 | D>E | No |
ClinGen ClinVar UniProt 1000Genomes ESP ExAC TOPMed dbSNP gnomAD |
|
|
CA3963457 rs761344686 |
507 | P>T | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed |
|
|
rs774087768 CA145296412 |
516 | L>F | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA3963454 rs140423768 |
517 | Q>E | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA3963449 rs142454848 |
530 | Q>H | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC gnomAD |
No associated diseases with P06241
9 regional properties for P06241
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Protein kinase domain | 271 - 524 | IPR000719 |
| domain | SH2 domain | 147 - 246 | IPR000980 |
| domain | Serine-threonine/tyrosine-protein kinase, catalytic domain | 271 - 520 | IPR001245 |
| domain | SH3 domain | 82 - 143 | IPR001452 |
| active_site | Tyrosine-protein kinase, active site | 386 - 398 | IPR008266 |
| binding_site | Protein kinase, ATP binding site | 277 - 299 | IPR017441 |
| domain | Tyrosine-protein kinase, catalytic domain | 271 - 520 | IPR020635 |
| domain | Fyn/Yrk, SH3 domain | 85 - 140 | IPR035750 |
| domain | Fyn/Yrk, SH2 domain | 145 - 245 | IPR047924 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.10.2 | Protein-tyrosine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
15 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| actin filament | A filamentous structure formed of a two-stranded helical polymer of the protein actin and associated proteins. Actin filaments are a major component of the contractile apparatus of skeletal muscle and the microfilaments of the cytoskeleton of eukaryotic cells. The filaments, comprising polymerized globular actin molecules, appear as flexible structures with a diameter of 5-9 nm. They are organized into a variety of linear bundles, two-dimensional networks, and three dimensional gels. In the cytoskeleton they are most highly concentrated in the cortex of the cell just beneath the plasma membrane. |
| cell body | The portion of a cell bearing surface projections such as axons, dendrites, cilia, or flagella that includes the nucleus, but excludes all cell projections. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| dendrite | A neuron projection that has a short, tapering, morphology. Dendrites receive and integrate signals from other neurons or from sensory stimuli, and conduct nerve impulses towards the axon or the cell body. In most neurons, the impulse is conveyed from dendrites to axon via the cell body, but in some types of unipolar neuron, the impulse does not travel via the cell body. |
| endosome | A vacuole to which materials ingested by endocytosis are delivered. |
| extrinsic component of cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane | The component of a plasma membrane consisting of gene products and protein complexes that are loosely bound to its cytoplasmic surface, but not integrated into the hydrophobic region. |
| glial cell projection | A prolongation or process extending from a glial cell. |
| membrane raft | Any of the small (10-200 nm), heterogeneous, highly dynamic, sterol- and sphingolipid-enriched membrane domains that compartmentalize cellular processes. Small rafts can sometimes be stabilized to form larger platforms through protein-protein and protein-lipid interactions. |
| mitochondrion | A semiautonomous, self replicating organelle that occurs in varying numbers, shapes, and sizes in the cytoplasm of virtually all eukaryotic cells. It is notably the site of tissue respiration. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| perinuclear endoplasmic reticulum | The portion of endoplasmic reticulum, the intracellular network of tubules and cisternae, that occurs near the nucleus. The lumen of the perinuclear endoplasmic reticulum is contiguous with the nuclear envelope lumen (also called perinuclear space), the region between the inner and outer nuclear membranes. |
| perinuclear region of cytoplasm | Cytoplasm situated near, or occurring around, the nucleus. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| postsynaptic density | An electron dense network of proteins within and adjacent to the postsynaptic membrane of an asymmetric, neuron-neuron synapse. Its major components include neurotransmitter receptors and the proteins that spatially and functionally organize them such as anchoring and scaffolding molecules, signaling enzymes and cytoskeletal components. |
| Schaffer collateral - CA1 synapse | A synapse between the Schaffer collateral axon of a CA3 pyramidal cell and a CA1 pyramidal cell. |
19 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| alpha-tubulin binding | Binding to the microtubule constituent protein alpha-tubulin. |
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| disordered domain specific binding | Binding to a disordered domain of a protein. |
| enzyme binding | Binding to an enzyme, a protein with catalytic activity. |
| ephrin receptor binding | Binding to an ephrin receptor. |
| growth factor receptor binding | Binding to a growth factor receptor. |
| identical protein binding | Binding to an identical protein or proteins. |
| metal ion binding | Binding to a metal ion. |
| non-membrane spanning protein tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + protein L-tyrosine = ADP + protein L-tyrosine phosphate by a non-membrane spanning protein. |
| phospholipase activator activity | Increases the activity of a phospholipase, an enzyme that catalyzes of the hydrolysis of a glycerophospholipid. |
| phospholipase binding | Binding to a phospholipase. |
| protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + a protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate; ATP + a protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate; and ATP + a protein tyrosine = ADP + protein tyrosine phosphate. |
| protein tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + a protein tyrosine = ADP + protein tyrosine phosphate. |
| scaffold protein binding | Binding to a scaffold protein. Scaffold proteins are crucial regulators of many key signaling pathways. Although not strictly defined in function, they are known to interact and/or bind with multiple members of a signaling pathway, tethering them into complexes. |
| signaling receptor binding | Binding to one or more specific sites on a receptor molecule, a macromolecule that undergoes combination with a hormone, neurotransmitter, drug or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell function. |
| tau protein binding | Binding to tau protein. tau is a microtubule-associated protein, implicated in Alzheimer's disease, Down Syndrome and ALS. |
| tau-protein kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + tau-protein = ADP + O-phospho-tau-protein. |
| transmembrane transporter binding | Binding to a transmembrane transporter, a protein or protein complex that enables the transfer of a substance, usually a specific substance or a group of related substances, from one side of a membrane to the other. |
| type 5 metabotropic glutamate receptor binding | Binding to a type 5 metabotropic glutamate receptor. |
55 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| activated T cell proliferation | The expansion of a T cell population following activation by an antigenic stimulus. |
| adaptive immune response | An immune response mediated by cells expressing specific receptors for antigen produced through a somatic diversification process, and allowing for an enhanced secondary response to subsequent exposures to the same antigen (immunological memory). |
| axon guidance | The chemotaxis process that directs the migration of an axon growth cone to a specific target site in response to a combination of attractive and repulsive cues. |
| calcium ion transport | The directed movement of calcium (Ca) ions into, out of or within a cell, or between cells, by means of some agent such as a transporter or pore. |
| cell differentiation | The process in which relatively unspecialized cells, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cells, acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate and its subsequent development to the mature state. |
| cellular response to amyloid-beta | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a amyloid-beta stimulus. |
| cellular response to glycine | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a glycine stimulus. |
| cellular response to L-glutamate | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a L-glutamate(1-) stimulus. |
| cellular response to platelet-derived growth factor stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a platelet-derived growth factor stimulus. |
| cellular response to transforming growth factor beta stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a transforming growth factor beta stimulus. |
| dendrite morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structures of a dendrite are generated and organized. |
| dendritic spine maintenance | The organization process that preserves a dendritic spine in a stable functional or structural state. A dendritic spine is a specialized protrusion from a neuronal dendrite and is involved in synaptic transmission. |
| detection of mechanical stimulus involved in sensory perception of pain | The series of events involved in the perception of pain in which a mechanical stimulus is received and converted into a molecular signal. |
| ephrin receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by ephrin binding to its receptor, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| Fc-gamma receptor signaling pathway involved in phagocytosis | An Fc-gamma receptor signaling pathway that contributes to the endocytic engulfment of external particulate material by phagocytes. |
| feeding behavior | Behavior associated with the intake of food. |
| forebrain development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the forebrain over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The forebrain is the anterior of the three primary divisions of the developing chordate brain or the corresponding part of the adult brain (in vertebrates, includes especially the cerebral hemispheres, the thalamus, and the hypothalamus and especially in higher vertebrates is the main control center for sensory and associative information processing, visceral functions, and voluntary motor functions). |
| heart process | A circulatory system process carried out by the heart. The heart is a hollow, muscular organ, which, by contracting rhythmically, keeps up the circulation of the blood. The heart is a hollow, muscular organ, which, by contracting rhythmically, keeps up the circulation of the blood. |
| innate immune response | Innate immune responses are defense responses mediated by germline encoded components that directly recognize components of potential pathogens. |
| intracellular signal transduction | The process in which a signal is passed on to downstream components within the cell, which become activated themselves to further propagate the signal and finally trigger a change in the function or state of the cell. |
| learning | Any process in an organism in which a relatively long-lasting adaptive behavioral change occurs as the result of experience. |
| leukocyte migration | The movement of a leukocyte within or between different tissues and organs of the body. |
| modulation of chemical synaptic transmission | Any process that modulates the frequency or amplitude of synaptic transmission, the process of communication from a neuron to a target (neuron, muscle, or secretory cell) across a synapse. Amplitude, in this case, refers to the change in postsynaptic membrane potential due to a single instance of synaptic transmission. |
| negative regulation of dendritic spine maintenance | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of dendritic spine maintenance. |
| negative regulation of gene expression | Any process that decreases the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product (protein or RNA). |
| negative regulation of hydrogen peroxide biosynthetic process | Any process that decreases the rate, frequency or extent of hydrogen peroxide biosynthesis. The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), a potentially harmful byproduct of aerobic cellular respiration which can cause damage to DNA. |
| negative regulation of inflammatory response to antigenic stimulus | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate, or extent of an inflammatory response to an antigenic stimulus. |
| negative regulation of oxidative stress-induced cell death | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of oxidative stress-induced cell death. |
| negative regulation of protein catabolic process | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of protein catabolic process. |
| negative regulation of protein ubiquitination | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the addition of ubiquitin groups to a protein. |
| neuron migration | The characteristic movement of an immature neuron from germinal zones to specific positions where they will reside as they mature. |
| peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation | The phosphorylation of peptidyl-tyrosine to form peptidyl-O4'-phospho-L-tyrosine. |
| positive regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity. |
| positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling. |
| positive regulation of neuron death | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of neuron death. |
| positive regulation of neuron projection development | Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of neuron projection development. Neuron projection development is the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron projection over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A neuron projection is any process extending from a neural cell, such as axons or dendrites (collectively called neurites). |
| positive regulation of protein localization to membrane | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of protein localization to membrane. |
| positive regulation of protein localization to nucleus | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of protein localization to nucleus. |
| positive regulation of protein targeting to membrane | Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of the process of directing proteins towards a membrane, usually using signals contained within the protein. |
| positive regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the introduction of a phosphate group to a tyrosine residue of a STAT (Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription) protein. |
| protein autophosphorylation | The phosphorylation by a protein of one or more of its own amino acid residues (cis-autophosphorylation), or residues on an identical protein (trans-autophosphorylation). |
| protein phosphorylation | The process of introducing a phosphate group on to a protein. |
| regulation of calcium ion import across plasma membrane | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of calcium ion import across plasma membrane. |
| regulation of cell shape | Any process that modulates the surface configuration of a cell. |
| regulation of glutamate receptor signaling pathway | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of glutamate receptor signaling pathway. |
| regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the phosphorylation of peptidyl-tyrosine. |
| response to amyloid-beta | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a amyloid-beta stimulus. |
| response to ethanol | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an ethanol stimulus. |
| response to hydrogen peroxide | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) stimulus. |
| response to singlet oxygen | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a singlet oxygen stimulus. Singlet oxygen is a dioxygen (O2) molecule in which two 2p electrons have similar spin. Singlet oxygen is more highly reactive than the form in which these electrons are of opposite spin, and it is produced in mutant chloroplasts lacking carotenoids and by leukocytes during metabolic burst. |
| stimulatory C-type lectin receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by the binding of C-type lectin to its receptor on the surface of a target cell, and resulting in cellular activation. |
| T cell costimulation | The process of providing, via surface-bound receptor-ligand pairs, a second, antigen-independent, signal in addition to that provided by the T cell receptor to augment T cell activation. |
| T cell receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by the cross-linking of an antigen receptor on a T cell. |
| transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by an extracellular ligand binding to a receptor on the surface of the target cell where the receptor possesses tyrosine kinase activity, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by a ligand binding to a vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) on the surface of the target cell, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
90 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q0VBZ0 | CSK | Tyrosine-protein kinase CSK | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| Q3ZC95 | BTK | Tyrosine-protein kinase | Bos taurus (Bovine) | EV SS |
| A0JNB0 | FYN | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| P42683 | LCK | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase LCK | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P41239 | CSK | Tyrosine-protein kinase CSK | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P00523 | SRC | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | EV |
| Q02977 | YRK | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Yrk | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q8JH64 | BTK | Tyrosine-protein kinase BTK | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P09324 | YES1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase Yes | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q75R65 | JAK2 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK2 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q05876 | FYN | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q24592 | hop | Tyrosine-protein kinase hopscotch | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | PR |
| P08630 | Btk | Tyrosine-protein kinase Btk | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| Q9V9J3 | Src42A | Tyrosine-protein kinase Src42A | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| P00528 | Src64B | Tyrosine-protein kinase Src64B | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| P23458 | JAK1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| O60674 | JAK2 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P52333 | JAK3 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P29597 | TYK2 | Non-receptor tyrosine-protein kinase TYK2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P43405 | SYK | Tyrosine-protein kinase SYK | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P43403 | ZAP70 | Tyrosine-protein kinase ZAP-70 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q13882 | PTK6 | Protein-tyrosine kinase 6 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P09769 | FGR | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fgr | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P07948 | LYN | Tyrosine-protein kinase Lyn | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P12931 | SRC | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P06239 | LCK | Tyrosine-protein kinase Lck | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P51451 | BLK | Tyrosine-protein kinase Blk | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P08631 | HCK | Tyrosine-protein kinase HCK | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P07947 | YES1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase Yes | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P42685 | FRK | Tyrosine-protein kinase FRK | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q08881 | ITK | Tyrosine-protein kinase ITK/TSK | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q06187 | BTK | Tyrosine-protein kinase BTK | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P51813 | BMX | Cytoplasmic tyrosine-protein kinase BMX | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P42680 | TEC | Tyrosine-protein kinase Tec | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P42679 | MATK | Megakaryocyte-associated tyrosine-protein kinase | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P41240 | CSK | Tyrosine-protein kinase CSK | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q14289 | PTK2B | Protein-tyrosine kinase 2-beta | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q05397 | PTK2 | Focal adhesion kinase 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q13470 | TNK1 | Non-receptor tyrosine-protein kinase TNK1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q07912 | TNK2 | Activated CDC42 kinase 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P16591 | FER | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fer | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q6J9G0 | STYK1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase STYK1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P42684 | ABL2 | Tyrosine-protein kinase ABL2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P00519 | ABL1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase ABL1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q9R117 | Tyk2 | Non-receptor tyrosine-protein kinase TYK2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P08103 | Hck | Tyrosine-protein kinase HCK | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P16277 | Blk | Tyrosine-protein kinase Blk | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q62270 | Srms | Tyrosine-protein kinase Srms | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q64434 | Ptk6 | Protein-tyrosine kinase 6 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P05480 | Src | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| P14234 | Fgr | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fgr | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P35991 | Btk | Tyrosine-protein kinase BTK | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| P41241 | Csk | Tyrosine-protein kinase CSK | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| P25911 | Lyn | Tyrosine-protein kinase Lyn | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| Q62137 | Jak3 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q62120 | Jak2 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| P06240 | Lck | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase LCK | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P24604 | Tec | Tyrosine-protein kinase Tec | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q04736 | Yes1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase Yes | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P52332 | Jak1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q03526 | Itk | Tyrosine-protein kinase ITK/TSK | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P41242 | Matk | Megakaryocyte-associated tyrosine-protein kinase | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q922K9 | Frk | Tyrosine-protein kinase FRK | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P39688 | Fyn | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| O19064 | JAK2 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK2 | Sus scrofa (Pig) | SS |
| A1Y2K1 | FYN | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn | Sus scrofa (Pig) | SS |
| Q62662 | Frk | Tyrosine-protein kinase FRK | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q07014 | Lyn | Tyrosine-protein kinase Lyn | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P50545 | Hck | Tyrosine-protein kinase HCK | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q9WUD9 | Src | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q01621 | Lck | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase LCK | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q6P6U0 | Fgr | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fgr | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q62689 | Jak2 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK2 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q63272 | Jak3 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK3 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P32577 | Csk | Tyrosine-protein kinase CSK | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P41243 | Matk | Megakaryocyte-associated tyrosine-protein kinase | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| F1LM93 | Yes1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase Yes | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q62844 | Fyn | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| G5ECJ6 | csk-1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase csk-1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| O45539 | src-2 | Tyrosine protein-kinase src-2 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| G5EE56 | src-1 | Tyrosine protein-kinase src-1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| F4JTP5 | STY46 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase STY46 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| O22558 | STY8 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase STY8 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q2MHE4 | HT1 | Serine/threonine/tyrosine-protein kinase HT1 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q8RWL6 | STY17 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase STY17 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| A1A5H8 | yes1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase yes | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| O12990 | jak1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK1 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | PR |
| Q1JPZ3 | src | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q6EWH2 | fyna | Tyrosine-protein kinase fyna | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| F1RDG9 | fynb | Tyrosine-protein kinase fynb | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MGCVQCKDKE | ATKLTEERDG | SLNQSSGYRY | GTDPTPQHYP | SFGVTSIPNY | NNFHAAGGQG |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| LTVFGGVNSS | SHTGTLRTRG | GTGVTLFVAL | YDYEARTEDD | LSFHKGEKFQ | ILNSSEGDWW |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| EARSLTTGET | GYIPSNYVAP | VDSIQAEEWY | FGKLGRKDAE | RQLLSFGNPR | GTFLIRESET |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| TKGAYSLSIR | DWDDMKGDHV | KHYKIRKLDN | GGYYITTRAQ | FETLQQLVQH | YSERAAGLCC |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| RLVVPCHKGM | PRLTDLSVKT | KDVWEIPRES | LQLIKRLGNG | QFGEVWMGTW | NGNTKVAIKT |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| LKPGTMSPES | FLEEAQIMKK | LKHDKLVQLY | AVVSEEPIYI | VTEYMNKGSL | LDFLKDGEGR |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| ALKLPNLVDM | AAQVAAGMAY | IERMNYIHRD | LRSANILVGN | GLICKIADFG | LARLIEDNEY |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| TARQGAKFPI | KWTAPEAALY | GRFTIKSDVW | SFGILLTELV | TKGRVPYPGM | NNREVLEQVE |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | |
| RGYRMPCPQD | CPISLHELMI | HCWKKDPEER | PTFEYLQSFL | EDYFTATEPQ | YQPGENL |