P05696
Gene name |
Prkca (Pkca) |
Protein name |
Protein kinase C alpha type |
Names |
PKC-A, PKC-alpha |
Species |
Rattus norvegicus (Rat) |
KEGG Pathway |
|
EC number |
2.7.11.13: Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
Protein Class |
|
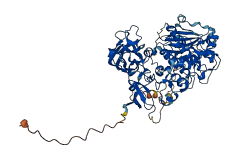
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
328-668 (Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, Classical Protein Kinase C alpha) |
Relief mechanism |
Ligand binding |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
480-503 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
328-668 (Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, Classical Protein Kinase C alpha) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
References
- Steinberg SF (2008) "Structural basis of protein kinase C isoform function", Physiological reviews, 88, 1341-78
- Sommese RF et al. (2017) "The Role of Regulatory Domains in Maintaining Autoinhibition in the Multidomain Kinase PKCα", The Journal of biological chemistry, 292, 2873-2880
- Pears CJ et al. (1990) "Mutagenesis of the pseudosubstrate site of protein kinase C leads to activation", European journal of biochemistry, 194, 89-94
- Smith MK et al. (1990) "Specificities of autoinhibitory domain peptides for four protein kinases. Implications for intact cell studies of protein kinase function", The Journal of biological chemistry, 265, 1837-40
- Slater SJ et al. (2002) "Regulation of PKC alpha activity by C1-C2 domain interactions", The Journal of biological chemistry, 277, 15277-85
- Jones AC et al. (2020) "Hypothesis: Unifying model of domain architecture for conventional and novel protein kinase C isozymes", IUBMB life, 72, 2584-2590
- Kirwan AF et al. (2003) "Inhibition of protein kinase C catalytic activity by additional regions within the human protein kinase Calpha-regulatory domain lying outside of the pseudosubstrate sequence", The Biochemical journal, 373, 571-81
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

8 structures for P05696
No variants for P05696
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for P05696 | |||||
No associated diseases with P05696
12 regional properties for P05696
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | C2 domain | 158 - 277 | IPR000008 |
| domain | Protein kinase domain | 339 - 597 | IPR000719 |
| domain | Protein kinase C-like, phorbol ester/diacylglycerol-binding domain | 36 - 87 | IPR002219-1 |
| domain | Protein kinase C-like, phorbol ester/diacylglycerol-binding domain | 101 - 153 | IPR002219-2 |
| active_site | Serine/threonine-protein kinase, active site | 459 - 471 | IPR008271 |
| binding_site | Protein kinase, ATP binding site | 345 - 368 | IPR017441 |
| domain | Protein kinase, C-terminal | 624 - 658 | IPR017892 |
| domain | Diacylglycerol/phorbol-ester binding | 34 - 48 | IPR020454-1 |
| domain | Diacylglycerol/phorbol-ester binding | 50 - 59 | IPR020454-2 |
| domain | Diacylglycerol/phorbol-ester binding | 63 - 74 | IPR020454-3 |
| domain | Diacylglycerol/phorbol-ester binding | 140 - 152 | IPR020454-4 |
| domain | Classical Protein Kinase C alpha, catalytic domain | 328 - 668 | IPR034663 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.11.13 | Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
21 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| alphav-beta3 integrin-PKCalpha complex | A protein complex that consists of an alphav-beta3 integrin complex bound to protein kinase C alpha. |
| apical part of cell | The region of a polarized cell that forms a tip or is distal to a base. For example, in a polarized epithelial cell, the apical region has an exposed surface and lies opposite to the basal lamina that separates the epithelium from other tissue. |
| axon | The long process of a neuron that conducts nerve impulses, usually away from the cell body to the terminals and varicosities, which are sites of storage and release of neurotransmitter. |
| calyx of Held | The terminal specialization of a calyciferous axon which forms large synapses in the mammalian auditory central nervous system. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| dendrite | A neuron projection that has a short, tapering, morphology. Dendrites receive and integrate signals from other neurons or from sensory stimuli, and conduct nerve impulses towards the axon or the cell body. In most neurons, the impulse is conveyed from dendrites to axon via the cell body, but in some types of unipolar neuron, the impulse does not travel via the cell body. |
| endoplasmic reticulum | The irregular network of unit membranes, visible only by electron microscopy, that occurs in the cytoplasm of many eukaryotic cells. The membranes form a complex meshwork of tubular channels, which are often expanded into slitlike cavities called cisternae. The ER takes two forms, rough (or granular), with ribosomes adhering to the outer surface, and smooth (with no ribosomes attached). |
| intercalated disc | A complex cell-cell junction at which myofibrils terminate in cardiomyocytes; mediates mechanical and electrochemical integration between individual cardiomyocytes. The intercalated disc contains regions of tight mechanical attachment (fasciae adherentes and desmosomes) and electrical coupling (gap junctions) between adjacent cells. |
| membrane | A lipid bilayer along with all the proteins and protein complexes embedded in it an attached to it. |
| membrane raft | Any of the small (10-200 nm), heterogeneous, highly dynamic, sterol- and sphingolipid-enriched membrane domains that compartmentalize cellular processes. Small rafts can sometimes be stabilized to form larger platforms through protein-protein and protein-lipid interactions. |
| mitochondrial membrane | Either of the lipid bilayers that surround the mitochondrion and form the mitochondrial envelope. |
| mitochondrion | A semiautonomous, self replicating organelle that occurs in varying numbers, shapes, and sizes in the cytoplasm of virtually all eukaryotic cells. It is notably the site of tissue respiration. |
| neuron projection | A prolongation or process extending from a nerve cell, e.g. an axon or dendrite. |
| neuronal cell body | The portion of a neuron that includes the nucleus, but excludes cell projections such as axons and dendrites. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| perinuclear region of cytoplasm | Cytoplasm situated near, or occurring around, the nucleus. |
| photoreceptor outer segment | The outer segment of a vertebrate photoreceptor that contains a stack of membrane discs embedded with photoreceptor proteins. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| presynaptic cytosol | The region of the cytosol consisting of all cytosol that is part of the presynapse. |
| protein-containing complex | A stable assembly of two or more macromolecules, i.e. proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates or lipids, in which at least one component is a protein and the constituent parts function together. |
11 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| calcium-dependent protein kinase C activity | Calcium-dependent catalysis of the reaction: ATP + a protein = ADP + a phosphoprotein. |
| enzyme binding | Binding to an enzyme, a protein with catalytic activity. |
| histone kinase activity (H3-T6 specific) | Catalysis of the transfer of a phosphate group to the threonine-6 residue of the N-terminal tail of histone H3. |
| integrin binding | Binding to an integrin. |
| protein kinase activity | Catalysis of the phosphorylation of an amino acid residue in a protein, usually according to the reaction: a protein + ATP = a phosphoprotein + ADP. |
| protein kinase C activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + a protein = ADP + a phosphoprotein. This reaction requires diacylglycerol. |
| protein serine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate. |
| protein serine/threonine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate, and ATP + protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate. |
| protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + a protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate; ATP + a protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate; and ATP + a protein tyrosine = ADP + protein tyrosine phosphate. |
| zinc ion binding | Binding to a zinc ion (Zn). |
66 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| aging | A developmental process that is a deterioration and loss of function over time. Aging includes loss of functions such as resistance to disease, homeostasis, and fertility, as well as wear and tear. Aging includes cellular senescence, but is more inclusive. May precede death and may succeed developmental maturation (GO:0021700). |
| angiogenesis | Blood vessel formation when new vessels emerge from the proliferation of pre-existing blood vessels. |
| cell adhesion | The attachment of a cell, either to another cell or to an underlying substrate such as the extracellular matrix, via cell adhesion molecules. |
| cellular calcium ion homeostasis | Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady state of calcium ions at the level of a cell. |
| cellular response to carbohydrate stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a carbohydrate stimulus. |
| central nervous system neuron axonogenesis | Generation of a long process from a neuron whose cell body resides in the central nervous system. The process carries efferent (outgoing) action potentials from the cell body towards target cells. |
| chondrocyte differentiation | The process in which a chondroblast acquires specialized structural and/or functional features of a chondrocyte. A chondrocyte is a polymorphic cell that forms cartilage. |
| desmosome assembly | A cellular process that results in the aggregation, arrangement and bonding together of a set of components to form a desmosome. A desmosome is a patch-like intercellular junction found in vertebrate tissues, consisting of parallel zones of two cell membranes, separated by an space of 25-35 nm, and having dense fibrillar plaques in the subjacent cytoplasm. |
| establishment of protein localization | The directed movement of a protein to a specific location. |
| histone H3-T6 phosphorylation | OBSOLETE. The modification of histone H3 by the addition of an phosphate group to a threonine residue at position 6 of the histone. |
| induction of positive chemotaxis | Any process that initiates the directed movement of a motile cell or organism towards a higher concentration in a concentration gradient of a specific chemical. |
| intracellular signal transduction | The process in which a signal is passed on to downstream components within the cell, which become activated themselves to further propagate the signal and finally trigger a change in the function or state of the cell. |
| intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals in which an intracellular signal is conveyed to trigger the apoptotic death of a cell. The pathway starts with reception of an intracellular signal (e.g. DNA damage, endoplasmic reticulum stress, oxidative stress etc.), and ends when the execution phase of apoptosis is triggered. The intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway is crucially regulated by permeabilization of the mitochondrial outer membrane (MOMP). |
| learning or memory | The acquisition and processing of information and/or the storage and retrieval of this information over time. |
| negative regulation of anion channel activity | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate, or extent of the anion channel activity. |
| negative regulation of cell population proliferation | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the rate or extent of cell proliferation. |
| negative regulation of glial cell apoptotic process | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate, or extent of glial cell apoptotic process. |
| negative regulation of glucose import | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the import of the hexose monosaccharide glucose into a cell or organelle. |
| negative regulation of heart contraction | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of heart contraction. |
| negative regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of insulin receptor signaling. |
| negative regulation of MAPK cascade | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction mediated by the MAPKKK cascade. |
| negative regulation of protein kinase activity | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of protein kinase activity. |
| negative regulation of protein phosphorylation | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the rate of addition of phosphate groups to amino acids within a protein. |
| negative regulation of translation | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of proteins by the translation of mRNA or circRNA. |
| neutrophil chemotaxis | The directed movement of a neutrophil cell, the most numerous polymorphonuclear leukocyte found in the blood, in response to an external stimulus, usually an infection or wounding. |
| peptidyl-serine autophosphorylation | The phosphorylation by a protein of one or more of its own serine amino acid residues, or a serine residue on an identical protein. |
| peptidyl-serine phosphorylation | The phosphorylation of peptidyl-serine to form peptidyl-O-phospho-L-serine. |
| peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation | The phosphorylation of peptidyl-threonine to form peptidyl-O-phospho-L-threonine. |
| positive regulation of angiogenesis | Any process that activates or increases angiogenesis. |
| positive regulation of blood vessel endothelial cell migration | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the migration of the endothelial cells of blood vessels. |
| positive regulation of bone resorption | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of bone resorption. |
| positive regulation of cardiac muscle hypertrophy | Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of the enlargement or overgrowth of all or part of the heart due to an increase in size (not length) of individual cardiac muscle fibers, without cell division. |
| positive regulation of cell adhesion | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell adhesion. |
| positive regulation of cell migration | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell migration. |
| positive regulation of dense core granule biogenesis | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of dense core granule biogenesis. |
| positive regulation of endothelial cell migration | Any process that increases the rate, frequency, or extent of the orderly movement of an endothelial cell into the extracellular matrix to form an endothelium. |
| positive regulation of endothelial cell proliferation | Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of endothelial cell proliferation. |
| positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction mediated by the ERK1 and ERK2 cascade. |
| positive regulation of exocytosis | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of exocytosis. |
| positive regulation of inflammatory response | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the inflammatory response. |
| positive regulation of lipopolysaccharide-mediated signaling pathway | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of signaling in response to detection of lipopolysaccharide. |
| positive regulation of macrophage differentiation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of macrophage differentiation. |
| positive regulation of mitotic cell cycle | Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of progression through the mitotic cell cycle. |
| positive regulation of protein phosphorylation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of addition of phosphate groups to amino acids within a protein. |
| positive regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation | Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of smooth muscle cell proliferation. |
| positive regulation of synapse assembly | Any process that activates, maintains or increases the frequency, rate or extent of synapse assembly, the aggregation, arrangement and bonding together of a set of components to form a synapse. |
| presynaptic modulation of chemical synaptic transmission | Any process, acting in the presynapse that results in modulation of chemical synaptic transmission. |
| protein autophosphorylation | The phosphorylation by a protein of one or more of its own amino acid residues (cis-autophosphorylation), or residues on an identical protein (trans-autophosphorylation). |
| protein phosphorylation | The process of introducing a phosphate group on to a protein. |
| regulation of muscle contraction | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of muscle contraction. |
| regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the phosphorylation of peptidyl-tyrosine. |
| regulation of platelet aggregation | Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of platelet aggregation. Platelet aggregation is the adhesion of one platelet to one or more other platelets via adhesion molecules. |
| regulation of receptor-mediated endocytosis | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of receptor mediated endocytosis, the uptake of external materials by cells, utilizing receptors to ensure specificity of transport. |
| regulation of response to osmotic stress | Any process that modulates the rate or extent of the response to osmotic stress. |
| regulation of synaptic vesicle exocytosis | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of synaptic vesicle exocytosis. |
| regulation of the force of heart contraction | Any process that modulates the extent of heart contraction, changing the force with which blood is propelled. |
| response to antibiotic | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an antibiotic stimulus. An antibiotic is a chemical substance produced by a microorganism which has the capacity to inhibit the growth of or to kill other microorganisms. |
| response to corticosterone | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a corticosterone stimulus. Corticosterone is a 21 carbon steroid hormone of the corticosteroid type, produced in the cortex of the adrenal glands. In many species, corticosterone is the principal glucocorticoid, involved in regulation of fuel metabolism, immune reactions, and stress responses. |
| response to estradiol | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of stimulus by estradiol, a C18 steroid hormone hydroxylated at C3 and C17 that acts as a potent estrogen. |
| response to ethanol | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an ethanol stimulus. |
| response to interleukin-1 | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an interleukin-1 stimulus. |
| response to mechanical stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a mechanical stimulus. |
| response to organic cyclic compound | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an organic cyclic compound stimulus. |
| response to peptide hormone | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a peptide hormone stimulus. A peptide hormone is any of a class of peptides that are secreted into the blood stream and have endocrine functions in living animals. |
| response to reactive oxygen species | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a reactive oxygen species stimulus. Reactive oxygen species include singlet oxygen, superoxide, and oxygen free radicals. |
| response to toxic substance | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a toxic stimulus. |
28 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P24583 | PKC1 | Protein kinase C-like 1 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) | SS |
| P05128 | PRKCG | Protein kinase C gamma type | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| P05126 | PRKCB | Protein kinase C beta type | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| P04409 | PRKCA | Protein kinase C alpha type | Bos taurus (Bovine) | EV SS |
| P13677 | inaC | Protein kinase C, eye isozyme | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| P05130 | Pkc53E | Protein kinase C, brain isozyme | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| P05129 | PRKCG | Protein kinase C gamma type | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P05771 | PRKCB | Protein kinase C beta type | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P17252 | PRKCA | Protein kinase C alpha type | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P68404 | Prkcb | Protein kinase C beta type | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P63318 | Prkcg | Protein kinase C gamma type | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P20444 | Prkca | Protein kinase C alpha type | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P63319 | Prkcg | Protein kinase C gamma type | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| O55173 | Pdpk1 | 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P09217 | Prkcz | Protein kinase C zeta type | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| F1M7Y5 | Prkci | Protein kinase C iota type | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q63433 | Pkn1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase N1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| O08874 | Pkn2 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase N2 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q64617 | Prkch | Protein kinase C eta type | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P09216 | Prkce | Protein kinase C epsilon type | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P09215 | Prkcd | Protein kinase C delta type | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P47197 | Akt2 | RAC-beta serine/threonine-protein kinase | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P47196 | Akt1 | RAC-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q63484 | Akt3 | RAC-gamma serine/threonine-protein kinase | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P68403 | Prkcb | Protein kinase C beta type | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P90980 | pkc-2 | Protein kinase C-like 2 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| A8KBH6 | prkcb | Protein kinase C beta type | Xenopus tropicalis (Western clawed frog) (Silurana tropicalis) | SS |
| Q7SY24 | prkcbb | Protein kinase C beta type | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MADVYPANDS | TASQDVANRF | ARKGALRQKN | VHEVKDHKFI | ARFFKQPTFC | SHCTDFIWGF |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| GKQGFQCQVC | CFVVHKRCHE | FVTFSCPGAD | KGPDTDDPRS | KHKFKIHTYG | SPTFCDHCGS |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| LLYGLIHQGM | KCDTCDMNVH | KQCVINVPSL | CGMDHTEKRG | RIYLKAEVTD | EKLHVTVRDA |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| KNLIPMDPNG | LSDPYVKLKL | IPDPKNESKQ | KTKTIRSTLN | PQWNESFTFK | LKPSDKDRRL |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| SVEIWDWDRT | TRNDFMGSLS | FGVSELMKMP | ASGWYKLLNQ | EEGEYYNVPI | PEGDEEGNVE |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| LRQKFEKAKL | GPAGNKVISP | SEDRKQPSNN | LDRVKLTDFN | FLMVLGKGSF | GKVMLADRKG |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| TEELYAIKIL | KKDVVIQDDD | VECTMVEKRV | LALLDKPPFL | TQLHSCFQTV | DRLYFVMEYV |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| NGGDLMYHIQ | QVGKFKEPQA | VFYAAEISIG | LFFLHKRGII | YRDLKLDNVM | LDSEGHIKIA |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| DFGMCKEHMM | DGVTTRTFCG | TPDYIAPEII | AYQPYGKSVD | WWAYGVLLYE | MLAGQPPFDG |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| EDEDELFQSI | MEHNVSYPKS | LSKEAVSICK | GLMTKHPAKR | LGCGPEGERD | VREHAFFRRI |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| DWEKLENREI | QPPFKPKVCG | KGAENFDKFF | TRGQPVLTPP | DQLVIANIDQ | SDFEGFSYVN |
| 670 | |||||
| PQFVHPILQS | AV |