P04176
Gene name |
Pah |
Protein name |
Phenylalanine-4-hydroxylase |
Names |
PAH, Phe-4-monooxygenase |
Species |
Rattus norvegicus (Rat) |
KEGG Pathway |
|
EC number |
1.14.16.1: With reduced pteridine as one donor, and incorporation of one atom of oxygen |
Protein Class |
AROMATIC AMINO ACID HYDROXYLASE (PTHR11473) |
Descriptions
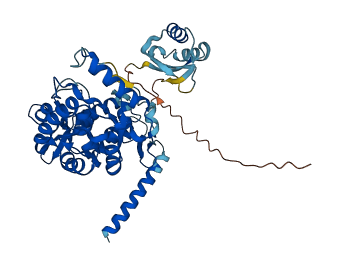
Mammalian phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH) is a multidomain homo-multimeric protein whose dysfunction causes the most common inborn error in amino acid metabolism, phenylketonuria (PKU), and milder forms of hyperphenylalaninemia. PAH catalyzes the hydroxylation of phenylalanine (Phe) to tyrosine, using nonheme iron and the cosubstrates tetrahydrobiopterin and molecular oxygen. Phe allosterically activates PAH by binding to the regulatory domain. Phosphorylation at Ser16 potentiates the effects of Phe, with phosphorylated PAH achieving full activation at lower Phe concentrations than the unphosphorylated protein. Allosteric activation by Phe is accompanied by major conformational changes that move the N-terminal regulatory region away from the active site and stabilization of the tetrameric conformation.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
119-424 (Catalytic domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Ligand binding |
Assay |
Structural analysis, Deletion assay |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
References
- Arturo EC et al. (2016) "First structure of full-length mammalian phenylalanine hydroxylase reveals the architecture of an autoinhibited tetramer", Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 113, 2394-9
- Daubner SC et al. (1997) "Characterization of chimeric pterin-dependent hydroxylases: contributions of the regulatory domains of tyrosine and phenylalanine hydroxylase to substrate specificity", Biochemistry, 36, 11574-82
Autoinhibited structure
Activated structure

No variants for P04176
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for P04176 | |||||
No associated diseases with P04176
No regional properties for P04176
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| No domain, repeats, and functional sites for P04176 | |||
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 1.14.16.1 | With reduced pteridine as one donor, and incorporation of one atom of oxygen |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | PTHR11473 | AROMATIC AMINO ACID HYDROXYLASE |
| PANTHER Subfamily | PTHR11473:SF24 | PHENYLALANINE-4-HYDROXYLASE |
| PANTHER Protein Class | oxidoreductase | |
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
No GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| No GO annotations for cellular component |
4 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| amino acid binding | Binding to an amino acid, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents. |
| identical protein binding | Binding to an identical protein or proteins. |
| iron ion binding | Binding to an iron (Fe) ion. |
| phenylalanine 4-monooxygenase activity | Catalysis of the reaction |
5 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| L-phenylalanine catabolic process | The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of phenylalanine, 2-amino-3-phenylpropanoic acid. |
| L-phenylalanine metabolic process | The chemical reactions and pathways involving L-phenylalanine, the L-enantiomer of 2-amino-3-phenylpropanoic acid, i.e. (2S)-2-amino-3-phenylpropanoic acid. |
| protein hydroxylation | The addition of a hydroxy group to a protein amino acid. |
| tyrosine biosynthetic process | The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of tyrosine, an aromatic amino acid, 2-amino-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoic acid. |
| tyrosine biosynthetic process, by oxidation of phenylalanine | The conversion of phenylalanine to tyrosine. |
4 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P17289 | TH | Tyrosine 3-monooxygenase | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| Q2KIH7 | PAH | Phenylalanine-4-hydroxylase | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| P00439 | PAH | Phenylalanine-4-hydroxylase | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P16331 | Pah | Phenylalanine-4-hydroxylase | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MAAVVLENGV | LSRKLSDFGQ | ETSYIEDNSN | QNGAISLIFS | LKEEVGALAK | VLRLFEENDI |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| NLTHIESRPS | RLNKDEYEFF | TYLDKRTKPV | LGSIIKSLRN | DIGATVHELS | RDKEKNTVPW |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| FPRTIQELDR | FANQILSYGA | ELDADHPGFK | DPVYRARRKQ | FADIAYNYRH | GQPIPRVEYT |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| EEEKQTWGTV | FRTLKALYKT | HACYEHNHIF | PLLEKYCGFR | EDNIPQLEDV | SQFLQTCTGF |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| RLRPVAGLLS | SRDFLGGLAF | RVFHCTQYIR | HGSKPMYTPE | PDICHELLGH | VPLFSDRSFA |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| QFSQEIGLAS | LGAPDEYIEK | LATIYWFTVE | FGLCKEGDSI | KAYGAGLLSS | FGELQYCLSD |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| KPKLLPLELE | KTACQEYSVT | EFQPLYYVAE | SFSDAKEKVR | TFAATIPRPF | SVRYDPYTQR |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | |||
| VEVLDNTQQL | KILADSINSE | VGILCNALQK | IKS |