P02649
Gene name |
APOE |
Protein name |
Apolipoprotein E |
Names |
Apo-E |
Species |
Homo sapiens (Human) |
KEGG Pathway |
hsa:348 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
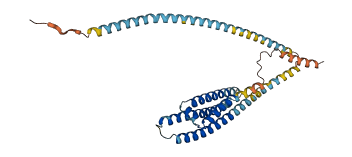
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

29 structures for P02649
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1B68 | X-ray | 200 A | A | 19-209 | PDB |
| 1BZ4 | X-ray | 185 A | A | 40-183 | PDB |
| 1EA8 | X-ray | 195 A | A | 19-209 | PDB |
| 1GS9 | X-ray | 170 A | A | 19-183 | PDB |
| 1H7I | X-ray | 190 A | A | 19-209 | PDB |
| 1LE2 | X-ray | 300 A | A | 41-184 | PDB |
| 1LE4 | X-ray | 250 A | A | 41-184 | PDB |
| 1LPE | X-ray | 225 A | A | 41-184 | PDB |
| 1NFN | X-ray | 180 A | A | 19-209 | PDB |
| 1NFO | X-ray | 200 A | A | 19-209 | PDB |
| 1OEF | NMR | - | A | 281-304 | PDB |
| 1OEG | NMR | - | A | 285-307 | PDB |
| 1OR2 | X-ray | 250 A | A | 19-183 | PDB |
| 1OR3 | X-ray | 173 A | A | 19-183 | PDB |
| 2KC3 | NMR | - | A | 19-201 | PDB |
| 2KNY | NMR | - | A | 147-167 | PDB |
| 2L7B | NMR | - | A | 19-317 | PDB |
| 6IWB | X-ray | 250 A | A/C | 41-186 | PDB |
| 6NCN | X-ray | 182 A | A | 19-180 | PDB |
| 6NCO | X-ray | 171 A | A | 19-180 | PDB |
| 7FCR | X-ray | 140 A | A | 19-209 | PDB |
| 7FCS | X-ray | 160 A | A | 19-209 | PDB |
| 7UVJ | X-ray | 199 A | A/B | 40-183 | PDB |
| 8AX8 | X-ray | 155 A | A | 19-317 | PDB |
| 8AX9 | X-ray | 155 A | A | 19-317 | PDB |
| 8CDY | X-ray | 190 A | A | 19-317 | PDB |
| 8CE0 | X-ray | 175 A | A | 19-317 | PDB |
| 8GRX | EM | 300 A | A/C | 41-180 | PDB |
| AF-P02649-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
398 variants for P02649
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
rs121918392 RCV000019429 VAR_000645 CA127499 |
21 | E>K | HYPERLIPOPROTEINEMIA, TYPE III, AND ATHEROSCLEROSIS ASSOCIATED WITH APOE5 ApoE5; associated with hyperlipoproteinemia and atherosclerosis; increased binding to LDL receptor [ClinVar, UniProt] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar UniProt 1000Genomes ExAC TOPMed dbSNP gnomAD |
|
RCV002225641 RCV000019443 rs201672011 VAR_000646 RCV000019453 CA041327 |
31 | E>K | Familial type 3 hyperlipoproteinemia HLPP3; ApoE4 Philadelphia, ApoE5 French-Canadian and ApoE5-type; only ApoE4 Philadelphia is associated with HLPP3 [ClinVar, UniProt] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar UniProt 1000Genomes ExAC TOPMed dbSNP gnomAD |
|
rs121918399 CA127525 VAR_042734 RCV000019468 RCV002496418 |
43 | R>C | Alzheimer disease 3 Lipoprotein glomerulopathy (lpg) Lipoprotein glomerulopathy LPG; ApoE2 Kyoto [ClinVar, Ensembl, UniProt] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar UniProt ExAC dbSNP gnomAD |
|
RCV001195944 rs769452 RCV000429606 RCV002379036 CA041808 RCV000019456 VAR_000647 RCV001175124 |
46 | L>P | Alzheimer disease 4 APOE4(-)-FREIBURG Familial hypercholesterolemia found in a patient with hypercholesterolemia; unknown pathological significance; ApoE4 Freiburg [ClinVar, UniProt] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar UniProt 1000Genomes ESP ExAC TOPMed dbSNP gnomAD |
|
CA127515 VAR_000648 rs28931576 RCV000019457 |
60 | T>A | APOE3(-)-FREIBURG ApoE3 Freiburg [ClinVar, UniProt] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar UniProt ExAC TOPMed dbSNP gnomAD |
|
RCV000019459 CA042275 VAR_000651 rs28931577 |
117 | A>T | APOE3 VARIANT ApoE3* [ClinVar, UniProt] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar UniProt Ensembl dbSNP |
|
RCV000074336 rs587778876 CA345321 |
122 | L>M | Major depressive disorder [ClinVar] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar Ensembl dbSNP |
|
rs429358 RCV000856604 RCV000019447 |
130 | C>= | Alzheimer disease 3, protection against, due to APOE3-Christchurch APOE3 ISOFORM [ClinVar] | Yes |
ClinVar dbSNP |
|
rs429358 CA127512 RCV000019455 RCV000019448 RCV000019458 RCV001262791 RCV000826089 RCV000019438 RCV000991302 VAR_000652 RCV000845581 RCV001195807 RCV000292119 RCV000019456 RCV001175124 |
130 | C>R | Alzheimer disease 4 Primary degenerative dementia of the Alzheimer type, presenile onset Lipoprotein glomerulopathy APOE4(-)-FREIBURG Familial type 3 hyperlipoproteinemia Alzheimer disease Alzheimer disease 2 Familial hypercholesterolemia HLPP3 and AD2; ApoE4, ApoE3 Leiden, ApoE3**, ApoE5-Frankfurt and ApoE5-type; ApoE3 Leiden and ApoE3** are associated with HLPP3; ApoE4 is associated with AD2; changed protein structure; no effect on binding to LDL receptor; decreased association with HDL and enrichment in VLDL and IDL; may prevent the interaction with MAP2 and MAPT; changed interaction with APP/A4 amyloid-beta peptide; increased ability to induce APP transcription; increased C-terminal proteolytic processing in neurons; decreased function in neurite outgrowth; ApoE4 is associated with higher susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection in neurons and astrocytes [ClinVar, UniProt] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar UniProt 1000Genomes ESP ExAC TOPMed dbSNP gnomAD |
|
RCV000019434 rs397514254 |
139 | E>missing | Familial type 3 hyperlipoproteinemia [ClinVar] | Yes |
ClinVar dbSNP |
|
rs1969863273 RCV001175125 |
141 | Q>R | Familial type 3 hyperlipoproteinemia [ClinVar] | Yes |
ClinVar dbSNP |
|
rs267606664 RCV001262660 RCV001579351 RCV000019439 VAR_000653 CA041273 RCV002476210 |
145 | G>D | Alzheimer disease 3 Hyperlipoproteinemia due to APOE1 found in a patient with hypercholesterolemia; unknown pathological significance; ApoE1 Weisgraber [ClinVar, UniProt] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar UniProt ESP ExAC TOPMed dbSNP gnomAD |
| VAR_000654 | 145 | G>GEVQAMLG | HLPP3; ApoE3 Leiden; no effect on glycosylation [UniProt] | Yes | UniProt |
|
rs587778877 CA345323 RCV000074337 |
151 | L>M | Major depressive disorder [ClinVar] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar ExAC dbSNP gnomAD |
|
rs28931578 VAR_000655 CA127517 RCV000019460 |
152 | R>Q | APOE2 VARIANT ApoE2-type; no hyperlipidemia [ClinVar, UniProt] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar UniProt TOPMed dbSNP gnomAD |
|
CA9506071 rs121918393 VAR_000657 |
154 | R>C | HLPP3; ApoE2-type [UniProt] | Yes |
ClinGen UniProt ExAC TOPMed dbSNP gnomAD |
|
RCV000019430 RCV000856604 rs121918393 CA127501 VAR_000656 |
154 | R>S | Alzheimer disease 3, protection against, due to APOE3-Christchurch Familial type 3 hyperlipoproteinemia HLPP3; ApoE2 Christchurch; decreased binding to LDL receptor [ClinVar, UniProt] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar UniProt ExAC TOPMed dbSNP gnomAD |
|
rs387906567 CA041132 RCV000019438 VAR_000658 |
160 | R>C | Familial type 3 hyperlipoproteinemia HLPP3; ApoE3** [ClinVar, UniProt] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar UniProt dbSNP gnomAD |
|
RCV000019443 CA127502 VAR_000659 rs769455 RCV000019432 RCV002326680 RCV001777143 RCV000884152 |
163 | R>C | Familial type 3 hyperlipoproteinemia HLPP3; also found in a patient with hypercholesterolemia; ApoE4 Philadelphia and ApoE2-type [ClinVar, UniProt] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar UniProt 1000Genomes ESP ExAC TOPMed dbSNP gnomAD |
|
RCV000019449 CA127513 VAR_000660 RCV002250463 rs121918397 |
163 | R>H | Lipoprotein glomerulopathy (lpg) Familial type 3 hyperlipoproteinemia Lipoprotein glomerulopathy HLPP3; unknown pathological significance; ApoE Kochi [Ensembl, ClinVar, UniProt] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar UniProt dbSNP gnomAD |
|
VAR_042735 rs121918397 CA127524 RCV000019466 |
163 | R>P | Lipoprotein glomerulopathy (lpg) Lipoprotein glomerulopathy LPG; ApoE2 Sendai; decreased binding to LDL receptor; induces intraglomerular deposition of ApoE-containing lipoproteins [Ensembl, ClinVar, UniProt] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar UniProt dbSNP gnomAD |
|
rs121918394 VAR_000662 RCV000019440 CA127506 |
164 | K>E | Familial type 3 hyperlipoproteinemia HLPP3; ApoE1 Harrisburg; decreased binding to LDL receptor; probable dominant negative effect; decreased in vitro binding to heparin [ClinVar, UniProt] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar UniProt dbSNP gnomAD |
|
rs121918394 VAR_000661 RCV001804151 CA127507 |
164 | K>Q | Hyperlipoproteinemia, type III, due to APOE2 HLPP3; ApoE2** [ClinVar, UniProt] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar UniProt dbSNP gnomAD |
|
RCV003221804 rs515726148 RCV000202536 RCV002336246 |
167 | L>missing | Sea-blue histiocyte syndrome [ClinVar] | Yes |
ClinVar dbSNP |
| VAR_035015 | 167 | L>del | SBHD; also found in patients with a diagnosis of familial combined hyperlipidemia [UniProt] | Yes | UniProt |
|
RCV000019459 CA042396 VAR_000663 rs267606662 |
170 | A>P | APOE3 VARIANT ApoE3*; decreased binding to LDL receptor [ClinVar, UniProt] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar UniProt Ensembl dbSNP |
|
RCV000019428 RCV000346955 RCV000845582 RCV001529800 RCV000019452 rs7412 VAR_000664 RCV001262472 RCV000019454 RCV000019439 CA127498 RCV000211178 |
176 | R>C | Familial type 3 hyperlipoproteinemia Hyperlipoproteinemia due to APOE1 HLPP3; ApoE2, ApoE2 Fukuoka, ApoE1 Weisgraber and ApoE3**; ApoE3** is associated with HLPP3; changed protein structure; decreased binding to LDLR and other lipoprotein receptors; decreased in vitro binding to heparin; no effect on distribution among plasma lipoproteins [ClinVar, UniProt] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar UniProt 1000Genomes ESP ExAC TOPMed dbSNP gnomAD |
|
RCV000856605 RCV000019445 CA127510 rs121918396 |
228 | W>* | Familial type 3 hyperlipoproteinemia HYPERLIPOPROTEINEMIA, TYPE III, ASSOCIATED WITH APOE3(WASHINGTON) [ClinVar] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar TOPMed dbSNP gnomAD |
| VAR_081136 | 228 | W>del | HLPP3; ApoE3 Washington [UniProt] | Yes | UniProt |
|
RCV000019452 rs267606663 CA041342 VAR_000665 |
242 | R>Q | Familial type 3 hyperlipoproteinemia ApoE2 Fukuoka [ClinVar, UniProt] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar UniProt ExAC dbSNP gnomAD |
|
rs121918395 CA127508 VAR_000666 RCV000019442 |
246 | R>C | Variant assessed as Somatic; 0.0 impact. APOE2-DUNEDIN ApoE2 Dunedin [NCI-TCGA, ClinVar, UniProt] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar UniProt ESP ExAC NCI-TCGA TOPMed dbSNP gnomAD |
|
RCV001579858 VAR_000667 rs199768005 CA041472 RCV000019454 RCV001701092 |
254 | V>E | Familial type 3 hyperlipoproteinemia ApoE2 WG [ClinVar, UniProt] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar UniProt ESP ExAC TOPMed dbSNP gnomAD |
|
rs140808909 RCV000019435 CA040712 |
262 | E>K | HYPERLIPOPROTEINEMIA, TYPE III, AND ATHEROSCLEROSIS ASSOCIATED WITH APOE7 [ClinVar] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar 1000Genomes ExAC TOPMed dbSNP gnomAD |
| VAR_000668 | 262 | E>KK | HLPP3; ApoE7 Suita [UniProt] | Yes | UniProt |
|
rs190853081 RCV000019435 CA041004 |
263 | E>K | HYPERLIPOPROTEINEMIA, TYPE III, AND ATHEROSCLEROSIS ASSOCIATED WITH APOE7 [ClinVar] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar 1000Genomes ExAC TOPMed dbSNP gnomAD |
|
RCV000019455 RCV002483522 CA041514 VAR_000669 rs267606661 RCV001565388 |
269 | R>G | Alzheimer disease 3 Familial type 3 hyperlipoproteinemia ApoE3 HB [ClinVar, UniProt] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar UniProt ExAC TOPMed dbSNP gnomAD |
|
rs121918398 VAR_000671 CA127519 RCV000019461 |
292 | R>H | APOE4 VARIANT ApoE4 PD [ClinVar, UniProt] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar UniProt dbSNP gnomAD |
|
rs28931579 CA127521 VAR_000672 RCV000019462 |
314 | S>R | APOE4(+) ApoE4 HG [ClinVar, UniProt] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar UniProt ExAC TOPMed dbSNP gnomAD |
|
CA9505925 rs777551553 |
5 | W>* | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA406301950 rs1568615382 |
6 | A>T | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA9505926 rs754318486 |
7 | A>V | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs923895447 CA308883668 |
8 | L>* | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs779278130 CA9505928 |
9 | L>P | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1599950832 CA406302083 |
10 | V>G | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA406302071 rs1461741495 |
10 | V>I | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA9505931 rs144354013 |
11 | T>A | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA9505930 rs144354013 |
11 | T>S | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA406302118 rs1381224336 |
12 | F>L | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA9505932 rs747078681 |
12 | F>Y | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA406302138 rs1568615443 |
13 | L>R | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA308883691 rs559532612 |
14 | A>T | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes |
|
|
rs752693941 CA308883724 |
15 | G>* | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs533904656 CA9505967 |
18 | A>P | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs533904656 CA9505966 |
18 | A>T | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
| TCGA novel | 19 | K>R | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
|
rs1456562720 CA406302412 |
22 | Q>H | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA9505969 rs776242156 |
23 | A>V | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA406302420 rs1394832846 |
24 | V>L | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA406302419 rs1394832846 |
24 | V>M | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA406302425 rs1440976751 |
25 | E>K | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs764929617 CA9505972 |
28 | P>L | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA9505975 rs752079771 |
33 | R>C | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1212454788 CA406302480 |
33 | R>H | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
| TCGA novel | 33 | R>L | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
|
rs1249808975 CA406302495 |
35 | Q>R | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
| TCGA novel | 36 | T>S | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
|
CA9505978 rs142480126 |
37 | E>K | Variant assessed as Somatic; 0.0 impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC NCI-TCGA gnomAD |
|
CA406303216 rs1301411037 |
38 | W>L | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs756353413 COSM3960197 CA9505979 |
39 | Q>R | lung [Cosmic] | No |
ClinGen cosmic curated ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
rs1599951908 CA406303267 |
41 | G>D | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs749406635 CA9505981 |
41 | G>S | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA9505983 rs371694216 |
43 | R>H | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs371694216 CA406303313 |
43 | R>P | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA9505985 rs768684471 |
44 | W>* | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1599951966 CA406303348 |
45 | E>G | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs769452 CA406303362 |
46 | L>Q | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA406303377 rs1439276876 |
48 | L>V | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1599952025 CA406303392 |
49 | G>D | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs1599952017 CA406303387 |
49 | G>S | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA9505987 rs11542029 |
50 | R>C | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs11542029 CA9505988 |
50 | R>G | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA9505991 rs762461580 |
50 | R>H | Variant assessed as Somatic; 0.0 impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No |
ClinGen ExAC NCI-TCGA TOPMed gnomAD |
|
rs762461580 CA9505989 |
50 | R>L | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs762461580 CA9505990 |
50 | R>P | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs11542029 RCV000520712 CA406303398 |
50 | R>S | No |
ClinGen ClinVar ExAC dbSNP gnomAD |
|
|
rs752790054 CA9505994 |
56 | R>H | Variant assessed as Somatic; 0.0 impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No |
ClinGen ExAC NCI-TCGA TOPMed gnomAD |
|
rs28931576 CA406303469 |
60 | T>S | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1599952129 CA406303491 |
63 | E>D | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA406303486 rs1265280650 |
63 | E>Q | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
VAR_014114 rs370594287 CA9505996 |
64 | Q>H | confirmed at protein level [UniProt] | No |
ClinGen UniProt 1000Genomes ESP ExAC TOPMed dbSNP gnomAD |
|
rs780035531 CA9505998 |
67 | E>K | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1052163943 CA406303522 |
68 | E>* | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1418355128 CA406303526 |
68 | E>D | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA308884581 rs1052163943 |
68 | E>K | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1184253344 CA406303525 |
68 | E>V | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA9506000 rs768780599 |
69 | L>P | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA406303530 rs768780599 |
69 | L>Q | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1426176730 CA406303534 |
70 | L>F | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA406303535 rs1599952206 |
70 | L>H | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA308884592 rs757100480 |
72 | S>P | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs757100480 CA406303546 |
72 | S>T | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA406303551 rs1599952234 |
73 | Q>K | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA406303556 rs1164895411 |
73 | Q>R | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs769366285 CA9506003 |
74 | V>A | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs747975000 CA9506002 |
74 | V>F | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed |
|
|
rs747975000 CA308884594 |
74 | V>I | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed |
|
|
CA9506005 rs762703669 |
76 | Q>R | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA9506006 rs770545391 |
77 | E>K | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA9506025 rs774000134 |
80 | A>E | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs557845700 CA308885232 |
82 | M>I | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes |
|
|
rs1407867184 CA406303629 |
82 | M>R | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs767980905 CA406303638 |
83 | D>E | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA308885238 rs1023086190 |
84 | E>K | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA406303654 rs1434287349 |
86 | M>V | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1334600571 CA406303671 |
88 | E>Q | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA406303675 rs1183932967 |
88 | E>V | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs368210726 CA9506028 |
89 | L>S | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA406303685 rs1278944082 |
90 | K>E | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA406303691 rs1377553244 |
90 | K>N | Variant assessed as Somatic; 0.0 impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No |
ClinGen NCI-TCGA gnomAD |
|
rs1241692890 CA406303692 |
91 | A>T | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1300558735 CA406303702 |
92 | Y>C | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA406303712 rs371331933 |
93 | K>N | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs761285934 CA406303709 |
93 | K>R | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA9506029 rs761285934 |
93 | K>T | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA9506031 rs776830091 |
94 | S>* | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1238105907 CA406303729 |
96 | L>P | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs527236160 RCV000132772 |
98 | E>missing | No |
ClinVar dbSNP |
|
|
CA406303740 rs1440786605 |
98 | E>* | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA406303739 rs1440786605 |
98 | E>K | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1180612218 CA406303747 VAR_000649 |
99 | Q>K | ApoE5 Frankfurt [UniProt] | No |
ClinGen UniProt dbSNP gnomAD |
|
rs577618688 CA9506033 |
99 | Q>R | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1599952958 CA406303764 |
101 | T>I | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs11083750 CA308885271 |
102 | P>L | Variant assessed as Somatic; 0.0 impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC NCI-TCGA TOPMed gnomAD |
|
rs11083750 CA308885274 |
102 | P>Q | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
VAR_000650 rs11083750 RCV000019458 CA042073 |
102 | P>R | ApoE5-type; no hyperlipidemia [UniProt] | No |
ClinGen ClinVar UniProt ESP ExAC TOPMed dbSNP gnomAD |
|
rs11542040 CA308885268 |
102 | P>T | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA406303768 rs1327865483 CA406303769 |
103 | V>L | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs767382895 CA9506035 |
104 | A>T | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1448845160 CA406303777 |
104 | A>V | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1369662219 CA406303787 |
106 | E>Q | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs749160976 CA9506039 |
108 | R>Q | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA308885296 rs1050106163 |
108 | R>W | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No |
ClinGen Ensembl NCI-TCGA |
|
CA406303804 rs1599953056 |
109 | A>T | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA406303808 rs1330045687 |
109 | A>V | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA9506042 rs778348297 |
110 | R>Q | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
| TCGA novel | 111 | L>M | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
|
rs745552623 CA9506043 |
112 | S>Y | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA9506044 rs771594795 |
113 | K>E | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA406303825 rs1167428194 |
113 | K>T | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA406303830 rs1169728519 |
114 | E>K | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA406303838 rs1424027593 |
115 | L>M | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1466963971 CA406303841 |
115 | L>R | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1413443775 CA406303845 |
116 | Q>* | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs372938213 CA406303853 |
117 | A>E | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA9506046 rs372938213 |
117 | A>V | Variant assessed as Somatic; 0.0 impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC NCI-TCGA gnomAD |
|
CA308885365 rs947015878 |
118 | A>V | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No |
ClinGen NCI-TCGA TOPMed |
|
CA9506048 rs777291619 |
119 | Q>P | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1429543001 CA406303870 |
120 | A>D | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1324343215 CA406303868 |
120 | A>S | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA9506049 rs11542037 |
121 | R>W | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs587778876 CA406303877 |
122 | L>V | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
| TCGA novel | 123 | G>A | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
|
CA406303884 rs1356186009 |
123 | G>D | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA406303882 rs1271901056 |
123 | G>R | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA308885402 rs937063425 VAR_016789 |
124 | A>V | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. ApoE3 Basel [NCI-TCGA, UniProt] | No |
ClinGen UniProt NCI-TCGA TOPMed dbSNP |
|
CA406303892 rs993409614 |
125 | D>H | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA308885407 rs993409614 |
125 | D>N | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA9506052 rs763313394 |
128 | D>N | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA308885445 rs752600356 |
129 | V>L | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA9506054 rs752600356 |
129 | V>M | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1367830766 CA406303929 |
130 | C>Y | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1458301734 CA406303934 |
131 | G>C | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA406303937 rs1599953294 |
131 | G>D | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs1458301734 CA406303936 |
131 | G>S | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs11542041 CA9506055 |
132 | R>C | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1263042140 CA406303941 |
132 | R>H | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA406303943 rs1263042140 |
132 | R>L | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs11542041 CA308885481 |
132 | R>S | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA406303959 rs753798476 |
135 | Q>L | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA9506056 rs753798476 |
135 | Q>R | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1341982092 CA406303966 |
136 | Y>C | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs573658040 CA9506058 |
137 | R>C | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs573658040 CA406303971 |
137 | R>G | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA308885519 rs11542035 |
137 | R>H | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs543363163 CA406303975 |
138 | G>C | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA406303976 rs1246120787 |
138 | G>D | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs543363163 CA9506059 |
138 | G>S | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA308885532 rs41382345 |
139 | E>V | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA406303986 CA9506061 rs779569800 |
140 | V>L | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA9506062 rs779569800 |
140 | V>M | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1162012100 CA406304000 |
142 | A>T | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA9506064 CA9506063 rs768925016 |
143 | M>L | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA406304013 rs1287096724 |
144 | L>I | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA406304018 rs267606664 |
145 | G>A | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs748703149 CA308885595 |
145 | G>C | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA406304017 rs748703149 |
145 | G>R | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs748703149 CA9506065 |
145 | G>S | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA406304022 rs1189593420 |
146 | Q>* | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1032082950 CA308885618 |
148 | T>I | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs762933906 CA9506068 |
149 | E>D | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1438607869 CA406304041 |
149 | E>K | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA308885645 rs11542034 |
150 | E>G | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs1289377244 CA406304058 |
151 | L>R | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs28931578 CA406304060 |
152 | R>L | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs28931578 CA308885664 |
152 | R>P | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs531939919 CA9506070 |
152 | R>W | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1599953509 CA406304064 |
153 | V>A | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs990344075 CA308885673 |
153 | V>M | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
RCV000417087 rs200703101 CA16044403 |
154 | R>L | No |
ClinGen ClinVar Ensembl dbSNP |
|
|
rs200703101 CA308885705 |
154 | R>P | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA406304068 rs1018669382 |
155 | L>F | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1018669382 CA308885718 |
155 | L>V | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA308885722 rs954186991 |
156 | A>S | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs954186991 CA308885721 |
156 | A>T | Variant assessed as Somatic; 0.0 impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No |
ClinGen NCI-TCGA TOPMed gnomAD |
|
CA406304081 rs1483485796 |
157 | S>F | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs998239069 CA308885728 |
157 | S>T | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA308885733 rs868094551 |
158 | H>N | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA406304083 rs868094551 |
158 | H>Y | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA308885734 rs867004984 |
159 | L>M | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA406304092 rs1457217956 |
159 | L>P | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA406304095 rs387906567 |
160 | R>G | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA406304096 rs1452005331 |
160 | R>H | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs867215645 CA308885740 |
161 | K>N | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA406304106 rs1377830202 |
162 | L>M | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA406304124 rs1332591068 |
165 | R>L | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA406304121 rs1402219759 |
165 | R>W | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA406304137 rs867594573 |
168 | R>C | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA9506074 rs376170967 |
168 | R>H | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs867594573 CA308885772 |
168 | R>S | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1300930146 CA406304143 |
169 | D>Y | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1599953786 CA406304161 |
171 | D>E | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA406304154 rs1249355043 |
171 | D>N | Variant assessed as Somatic; 0.0 impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No |
ClinGen NCI-TCGA gnomAD |
|
rs757859088 CA9506075 |
172 | D>E | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA308885778 rs988698841 |
172 | D>N | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1190120890 CA406304173 |
174 | Q>K | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA406304209 rs1421977676 |
179 | V>A | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1403079937 CA406304216 |
180 | Y>* | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA9506076 rs751200677 |
180 | Y>H | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1434405741 CA406304219 |
181 | Q>E | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA9506077 CA406304224 rs754627330 |
181 | Q>H | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1434405741 CA406304218 |
181 | Q>K | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA308885811 rs796443813 |
182 | A>P | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs796443813 CA308885815 |
182 | A>S | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1388704077 CA406304230 CA406304229 |
183 | G>R | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA308885824 rs981058595 |
184 | A>D | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA406304236 rs1276509170 |
184 | A>S | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA406304235 rs1276509170 COSM3787717 |
184 | A>T | pancreas [Cosmic] | No |
ClinGen cosmic curated gnomAD |
|
CA406304243 rs1339651557 |
185 | R>H | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1339651557 CA406304244 |
185 | R>P | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1332509626 CA406304258 |
187 | G>A | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1332509626 CA406304259 |
187 | G>V | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA308885826 rs11542032 |
189 | E>K | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA406304266 rs11542032 |
189 | E>Q | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA406304270 rs1402325936 |
189 | E>V | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA308885840 rs937011116 |
190 | R>C | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1265472491 CA406304278 |
191 | G>S | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1599953984 CA406304285 |
192 | L>V | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA9506079 rs748506927 |
193 | S>R | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1599954003 CA406304298 |
194 | A>T | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs1380773651 CA406304307 |
195 | I>F | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA406304312 rs1184454715 |
195 | I>M | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA9506080 rs770485817 |
196 | R>C | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA9506081 rs778425259 |
196 | R>H | Variant assessed as Somatic; 0.0 impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No |
ClinGen ExAC NCI-TCGA gnomAD |
|
CA406304324 rs1303558981 |
197 | E>G | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA406304331 rs1426426514 |
198 | R>C | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1048982607 CA308885889 |
198 | R>L | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs916989869 CA308885893 |
199 | L>R | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1164213063 CA406304341 |
200 | G>R | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs11542030 CA308885900 |
205 | Q>R | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA406304402 rs1385100920 |
206 | G>D | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs749750245 CA9506082 |
207 | R>C | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA406304410 rs1459489355 |
207 | R>H | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA406304411 rs1459489355 |
207 | R>P | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs749750245 CA406304406 |
207 | R>S | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs770942678 CA9506083 |
208 | V>L | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs770942678 CA308885904 |
208 | V>M | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA308885916 rs1047319304 |
209 | R>Q | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA406304422 rs1459595735 |
209 | R>W | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA406304440 rs1376916580 |
211 | A>T | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1227709957 CA406304462 |
213 | V>G | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA9506085 rs759721023 |
214 | G>S | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA308885927 rs11542027 |
215 | S>F | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA406304507 rs1466115957 |
218 | G>D | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1488379910 CA406304503 |
218 | G>R | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA406304502 rs1488379910 |
218 | G>S | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs941248161 CA406304513 |
219 | Q>* | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs941248161 CA308885934 |
219 | Q>E | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1265743589 CA406304532 |
220 | P>L | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1471997722 CA406304541 |
221 | L>P | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1181840153 CA406304550 |
222 | Q>* | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1181840153 CA406304547 |
222 | Q>K | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA308885935 rs1039633588 |
222 | Q>L | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA406304555 rs1039633588 |
222 | Q>R | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1425703838 CA406304592 |
224 | R>L | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA406304589 rs1425703838 |
224 | R>P | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs547472686 CA308885936 |
225 | A>T | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1360151558 CA406304634 |
227 | A>S | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA406304670 rs1299844242 |
229 | G>R | Variant assessed as Somatic; 0.0 impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No |
ClinGen NCI-TCGA gnomAD |
|
rs1357260388 CA406304682 |
229 | G>V | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs567353589 CA308885947 |
230 | E>K | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1237339516 CA406304711 |
231 | R>Q | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1381171305 CA406304708 |
231 | R>W | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs554251788 CA406304732 |
233 | R>C | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs554251788 CA308885948 |
233 | R>G | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA406304738 rs1307832357 |
233 | R>H | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1241924076 CA406304743 |
234 | A>T | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1276043726 CA406304752 |
234 | A>V | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1238565583 CA406304762 |
235 | R>Q | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA9506087 rs530010303 |
235 | R>W | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA406304783 rs1555790637 |
236 | M>I | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs1335550286 CA406304791 |
237 | E>K | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs892532644 CA308885963 |
238 | E>D | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs761592007 CA9506088 |
239 | M>I | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1391215146 CA406304841 |
240 | G>D | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1440369210 CA406304839 |
240 | G>R | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA308885968 rs1009671345 |
241 | S>N | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA406304856 rs1237443001 |
241 | S>R | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs387906568 CA308885969 |
242 | R>G | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs267606663 CA9506089 |
242 | R>P | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA406304858 rs387906568 |
242 | R>W | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA406304869 rs1413700881 |
243 | T>N | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA406304889 rs1334498236 |
245 | D>N | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1330553726 CA406304912 |
246 | R>P | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs121918395 CA406304904 |
246 | R>S | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA406304959 rs1221046029 |
248 | D>E | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs762906934 CA406304961 |
249 | E>* | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs765845034 CA9506091 |
249 | E>G | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA406304965 rs762906934 |
249 | E>K | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA9506090 rs762906934 |
249 | E>Q | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1453797593 CA406305024 |
252 | E>D | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA9506093 rs780984110 |
255 | A>V | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA406305114 rs1197351070 |
256 | E>V | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA406305153 rs1599954391 |
257 | V>G | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs1003367097 CA308886000 |
258 | R>C | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
COSM1183264 CA9506095 rs756564996 |
258 | R>H | large_intestine [Cosmic] | No |
ClinGen cosmic curated ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
rs778237451 CA9506096 |
259 | A>P | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA406305164 rs778237451 |
259 | A>T | Variant assessed as Somatic; 0.0 impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No |
ClinGen ExAC NCI-TCGA gnomAD |
|
rs1245215443 CA406305223 |
262 | E>G | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1463848099 CA406305269 |
265 | A>T | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA406305283 rs1350058178 |
266 | Q>E | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1466737235 CA406305305 |
267 | Q>* | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs745950059 CA9506098 |
267 | Q>R | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA9506100 rs267606661 |
269 | R>C | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
| VAR_000670 | 270 | L>E | ApoE1 HE; requires 2 nucleotide substitutions [UniProt] | No | UniProt |
| TCGA novel | 272 | A>D | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
|
rs1217176327 CA406305380 |
272 | A>T | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs951182634 CA308886041 |
273 | E>G | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA9506102 rs551256627 |
274 | A>G | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1599954500 CA406305426 |
274 | A>T | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA406305437 rs551256627 |
274 | A>V | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA9506103 rs371110159 |
276 | Q>* | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA406305500 rs1199910165 |
277 | A>V | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA9506104 rs762845923 |
278 | R>C | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA9506106 rs767339630 |
278 | R>H | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed |
|
|
CA406305515 COSM1525698 rs767339630 |
278 | R>L | lung Variant assessed as Somatic; 0.0 impact. [Cosmic, NCI-TCGA] | No |
ClinGen cosmic curated ExAC NCI-TCGA TOPMed |
|
CA406305528 rs1476757984 |
279 | L>F | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1599954557 CA406305562 |
281 | S>G | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA406305567 rs1479320041 |
281 | S>N | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA406305575 rs1463421531 |
281 | S>R | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA308886085 rs778901516 |
282 | W>C | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA308886090 rs954301448 |
283 | F>L | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA9506108 rs759118026 |
284 | E>D | No |
ClinGen ExAC |
|
|
CA9506107 rs773797268 |
284 | E>G | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA406305632 rs1396111554 |
284 | E>K | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No |
ClinGen NCI-TCGA gnomAD |
|
rs1358158446 CA406305652 |
285 | P>H | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA406305644 rs1325189389 |
285 | P>T | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA9506110 rs750138933 |
286 | L>M | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs755792921 CA9506111 |
287 | V>M | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1568618190 CA406305685 |
289 | D>A | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA406305691 rs77903069 |
289 | D>E | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes TOPMed |
|
|
CA406305706 rs1282920511 |
290 | M>I | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA406305704 rs1282294107 |
290 | M>K | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1599954673 CA406305720 |
291 | Q>H | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs1599954663 CA406305717 |
291 | Q>R | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs1355806321 CA406305723 |
292 | R>C | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA406305756 rs557715042 |
294 | W>* | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs557715042 CA9506112 |
294 | W>C | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA9506113 rs754211171 |
295 | A>T | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA9506115 rs757764781 |
296 | G>R | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA9506114 rs757764781 |
296 | G>W | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA308886167 rs1039600156 |
297 | L>P | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA406305798 rs1367811482 |
299 | E>Q | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs780067631 CA9506118 |
300 | K>N | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA9506117 rs758487955 |
300 | K>R | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA406305847 rs1418673754 |
301 | V>G | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1378119160 CA406305837 |
301 | V>L | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA406305832 rs1378119160 |
301 | V>M | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA406305874 rs1298395482 |
303 | A>S | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs539470710 CA9506120 |
304 | A>G | No |
ClinGen ExAC |
|
|
rs1340326154 CA406305916 |
305 | V>G | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA9506122 rs749102800 |
305 | V>M | Variant assessed as Somatic; 0.0 impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No |
ClinGen ExAC NCI-TCGA TOPMed gnomAD |
|
CA406305927 rs1245628517 |
306 | G>D | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs770562611 CA9506123 |
307 | T>I | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA406305949 rs1599954804 |
308 | S>R | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs1351828960 CA406305965 |
309 | A>T | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA9506125 rs759501381 |
311 | P>A | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1486760107 CA406305996 |
312 | V>L | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs775113061 CA406306076 |
318 | H>S | No |
ClinGen ExAC |
4 associated diseases with P02649
[MIM: 617347]: Hyperlipoproteinemia 3 (HLPP3)
A disorder characterized by the accumulation of intermediate-density lipoprotein particles (IDL or broad-beta-lipoprotein) rich in cholesterol. Clinical features include xanthomas, yellowish lipid deposits in the palmar crease, or less specific on tendons and on elbows. The disorder rarely manifests before the third decade in men. In women, it is usually expressed only after the menopause. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1361196, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1674745, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2101409, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22481068, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2556398, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26802169, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2738044, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7635945, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8287539}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. The vast majority of the patients are homozygous for APOE*2 alleles. More severe cases of HLPP3 have also been observed in individuals heterozygous for rare APOE variants. The influence of APOE on lipid levels is often suggested to have major implications for the risk of coronary artery disease (CAD). Individuals carrying the common APOE*4 variant are at higher risk of CAD.
[MIM: 104310]: Alzheimer disease 2 (AD2)
A late-onset form of Alzheimer disease. Alzheimer disease is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by progressive dementia, loss of cognitive abilities, and deposition of fibrillar amyloid proteins as intraneuronal neurofibrillary tangles, extracellular amyloid plaques and vascular amyloid deposits. The major constituents of these plaques are neurotoxic amyloid-beta protein 40 and amyloid-beta protein 42, that are produced by the proteolysis of the transmembrane APP protein. The cytotoxic C-terminal fragments (CTFs) and the caspase-cleaved products, such as C31, are also implicated in neuronal death. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10903326, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11258893, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11447277, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28111074, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2987927, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7891887, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7972031, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8071364, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8346443, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8367470, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8939961}. Note=Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. The APOE*4 allele (APOE form E4) is genetically associated with the common late onset familial and sporadic forms of Alzheimer disease. Risk for AD increased from 20% to 90% and mean age at onset decreased from 84 to 68 years with increasing number of APOE*4 alleles in 42 families with late onset AD. Thus APOE*4 gene dose is a major risk factor for late onset AD and, in these families, homozygosity for APOE*4 was virtually sufficient to cause AD by age 80. The mechanism by which APOE*4 participates in pathogenesis is not known. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:8346443}.
[MIM: 269600]: Sea-blue histiocyte disease (SBHD)
Characterized by splenomegaly, mild thrombocytopenia and, in the bone marrow, numerous histiocytes containing cytoplasmic granules which stain bright blue with the usual hematologic stains. The syndrome is the consequence of an inherited metabolic defect analogous to Gaucher disease and other sphingolipidoses. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11095479, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16094309, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22481068, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22949395, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24267230, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26802169}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.
[MIM: 611771]: Lipoprotein glomerulopathy (LPG)
Uncommon kidney disease characterized by proteinuria, progressive kidney failure, and distinctive lipoprotein thrombi in glomerular capillaries. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10432380, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10903326, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18077821, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9176854}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.
Without disease ID
- A disorder characterized by the accumulation of intermediate-density lipoprotein particles (IDL or broad-beta-lipoprotein) rich in cholesterol. Clinical features include xanthomas, yellowish lipid deposits in the palmar crease, or less specific on tendons and on elbows. The disorder rarely manifests before the third decade in men. In women, it is usually expressed only after the menopause. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1361196, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1674745, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2101409, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22481068, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2556398, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26802169, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2738044, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7635945, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8287539}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. The vast majority of the patients are homozygous for APOE*2 alleles. More severe cases of HLPP3 have also been observed in individuals heterozygous for rare APOE variants. The influence of APOE on lipid levels is often suggested to have major implications for the risk of coronary artery disease (CAD). Individuals carrying the common APOE*4 variant are at higher risk of CAD.
- A late-onset form of Alzheimer disease. Alzheimer disease is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by progressive dementia, loss of cognitive abilities, and deposition of fibrillar amyloid proteins as intraneuronal neurofibrillary tangles, extracellular amyloid plaques and vascular amyloid deposits. The major constituents of these plaques are neurotoxic amyloid-beta protein 40 and amyloid-beta protein 42, that are produced by the proteolysis of the transmembrane APP protein. The cytotoxic C-terminal fragments (CTFs) and the caspase-cleaved products, such as C31, are also implicated in neuronal death. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10903326, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11258893, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11447277, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28111074, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2987927, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7891887, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7972031, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8071364, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8346443, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8367470, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8939961}. Note=Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. The APOE*4 allele (APOE form E4) is genetically associated with the common late onset familial and sporadic forms of Alzheimer disease. Risk for AD increased from 20% to 90% and mean age at onset decreased from 84 to 68 years with increasing number of APOE*4 alleles in 42 families with late onset AD. Thus APOE*4 gene dose is a major risk factor for late onset AD and, in these families, homozygosity for APOE*4 was virtually sufficient to cause AD by age 80. The mechanism by which APOE*4 participates in pathogenesis is not known. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:8346443}.
- Characterized by splenomegaly, mild thrombocytopenia and, in the bone marrow, numerous histiocytes containing cytoplasmic granules which stain bright blue with the usual hematologic stains. The syndrome is the consequence of an inherited metabolic defect analogous to Gaucher disease and other sphingolipidoses. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11095479, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16094309, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22481068, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22949395, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24267230, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26802169}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.
- Uncommon kidney disease characterized by proteinuria, progressive kidney failure, and distinctive lipoprotein thrombi in glomerular capillaries. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10432380, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10903326, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18077821, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9176854}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.
No regional properties for P02649
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| No domain, repeats, and functional sites for P02649 | |||
Functions
30 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| blood microparticle | A phospholipid microvesicle that is derived from any of several cell types, such as platelets, blood cells, endothelial cells, or others, and contains membrane receptors as well as other proteins characteristic of the parental cell. Microparticles are heterogeneous in size, and are characterized as microvesicles free of nucleic acids. |
| chylomicron | A large lipoprotein particle (diameter 75-1200 nm) composed of a central core of triglycerides and cholesterol surrounded by a protein-phospholipid coating. The proteins include one molecule of apolipoprotein B-48 and may include a variety of apolipoproteins, including APOAs, APOCs and APOE. Chylomicrons are found in blood or lymph and carry lipids from the intestines into other body tissues. |
| clathrin-coated endocytic vesicle membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding a clathrin-coated endocytic vesicle. |
| collagen-containing extracellular matrix | An extracellular matrix consisting mainly of proteins (especially collagen) and glycosaminoglycans (mostly as proteoglycans) that provides not only essential physical scaffolding for the cellular constituents but can also initiate crucial biochemical and biomechanical cues required for tissue morphogenesis, differentiation and homeostasis. The components are secreted by cells in the vicinity and form a sheet underlying or overlying cells such as endothelial and epithelial cells. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| dendrite | A neuron projection that has a short, tapering, morphology. Dendrites receive and integrate signals from other neurons or from sensory stimuli, and conduct nerve impulses towards the axon or the cell body. In most neurons, the impulse is conveyed from dendrites to axon via the cell body, but in some types of unipolar neuron, the impulse does not travel via the cell body. |
| discoidal high-density lipoprotein particle | A newly formed high-density lipoprotein particle; consists of a phospholipid bilayer surrounded by two or more APOA1 molecules. The discoidal HDL particle is formed when lipid-free or lipid-poor APOA1 acquires phospholipids and unesterified cholesterol from either cell membranes or triglyceride-rich lipoproteins (undergoing lipolysis by lipoprotein lipase). |
| early endosome | A membrane-bounded organelle that receives incoming material from primary endocytic vesicles that have been generated by clathrin-dependent and clathrin-independent endocytosis; vesicles fuse with the early endosome to deliver cargo for sorting into recycling or degradation pathways. |
| endocytic vesicle lumen | The volume enclosed by the membrane of an endocytic vesicle. |
| endoplasmic reticulum | The irregular network of unit membranes, visible only by electron microscopy, that occurs in the cytoplasm of many eukaryotic cells. The membranes form a complex meshwork of tubular channels, which are often expanded into slitlike cavities called cisternae. The ER takes two forms, rough (or granular), with ribosomes adhering to the outer surface, and smooth (with no ribosomes attached). |
| endoplasmic reticulum lumen | The volume enclosed by the membranes of the endoplasmic reticulum. |
| extracellular exosome | A vesicle that is released into the extracellular region by fusion of the limiting endosomal membrane of a multivesicular body with the plasma membrane. Extracellular exosomes, also simply called exosomes, have a diameter of about 40-100 nm. |
| extracellular matrix | A structure lying external to one or more cells, which provides structural support, biochemical or biomechanical cues for cells or tissues. |
| extracellular region | The space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite. |
| extracellular space | That part of a multicellular organism outside the cells proper, usually taken to be outside the plasma membranes, and occupied by fluid. |
| extracellular vesicle | Any vesicle that is part of the extracellular region. |
| glutamatergic synapse | A synapse that uses glutamate as a neurotransmitter. |
| Golgi apparatus | A membrane-bound cytoplasmic organelle of the endomembrane system that further processes the core oligosaccharides (e.g. N-glycans) added to proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum and packages them into membrane-bound vesicles. The Golgi apparatus operates at the intersection of the secretory, lysosomal, and endocytic pathways. |
| high-density lipoprotein particle | A lipoprotein particle with a high density (typically 1.063-1.21 g/ml) and a diameter of 5-10 nm that contains APOAs and may contain APOCs and APOE; found in blood and carries lipids from body tissues to the liver as part of the reverse cholesterol transport process. |
| intermediate-density lipoprotein particle | A triglyceride-rich lipoprotein particle that typically contains APOB100, APOE and APOCs and has a density of 1.006-1.019 g/ml and a diameter of between 25-30 nm. IDL particles are found in blood and are formed by the delipidation of very-low-density lipoprotein particles (VLDL). IDL particles are removed from blood by the liver, following binding to the APOE receptor, or are converted to low-density lipoprotein (LDL). |
| lipoprotein particle | A spherical particle containing non-covalently associated proteins and lipids. Examples are plasma lipoprotein particles which transport lipids in the blood or lymph. |
| low-density lipoprotein particle | A lipoprotein particle, rich in cholesterol esters and low in triglycerides that is typically composed of APOB100 and APOE and has a density of 1.02-1.06 g/ml and a diameter of between 20-25 nm. LDL particles are formed from VLDL particles (via IDL) by the loss of triglyceride and gain of cholesterol ester. They transport endogenous cholesterol (and to some extent triglycerides) from peripheral tissues back to the liver. |
| melanosome | A tissue-specific, membrane-bounded cytoplasmic organelle within which melanin pigments are synthesized and stored. Melanosomes are synthesized in melanocyte cells. |
| membrane | A lipid bilayer along with all the proteins and protein complexes embedded in it an attached to it. |
| multivesicular body | A type of endosome in which regions of the limiting endosomal membrane invaginate to form internal vesicles; membrane proteins that enter the internal vesicles are sequestered from the cytoplasm. |
| neuronal cell body | The portion of a neuron that includes the nucleus, but excludes cell projections such as axons and dendrites. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| synaptic cleft | The narrow gap that separates the presynaptic and postsynaptic membranes, into which neurotransmitter is released. |
| very-low-density lipoprotein particle | A triglyceride-rich lipoprotein particle that is typically composed of APOB100, APOE and APOCs and has a density of about 1.006 g/ml and a diameter of between 20-80 nm. It is found in blood and transports endogenous products (newly synthesized cholesterol and triglycerides) from the liver. |
21 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| amyloid-beta binding | Binding to an amyloid-beta peptide/protein. |
| antioxidant activity | Inhibition of the reactions brought about by dioxygen (O2) or peroxides. Usually the antioxidant is effective because it can itself be more easily oxidized than the substance protected. The term is often applied to components that can trap free radicals, thereby breaking the chain reaction that normally leads to extensive biological damage. |
| cholesterol transfer activity | Removes cholesterol from a membrane or a monolayer lipid particle, transports it through the aqueous phase while protected in a hydrophobic pocket, and brings it to an acceptor membrane or lipid particle. |
| enzyme binding | Binding to an enzyme, a protein with catalytic activity. |
| heparan sulfate proteoglycan binding | Binding to a heparan sulfate proteoglycan, any proteoglycan containing heparan sulfate as the glycosaminoglycan carbohydrate unit. |
| heparin binding | Binding to heparin, a member of a group of glycosaminoglycans found mainly as an intracellular component of mast cells and which consist predominantly of alternating alpha-(1->4)-linked D-galactose and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine-6-sulfate residues. |
| identical protein binding | Binding to an identical protein or proteins. |
| lipid binding | Binding to a lipid. |
| lipid transporter activity | Enables the directed movement of lipids into, out of or within a cell, or between cells. |
| lipoprotein particle binding | Binding to a lipoprotein particle. A lipoprotein particle, also known as a lipoprotein, is a clathrate complex consisting of a lipid enwrapped in a protein host without covalent binding in such a way that the complex has a hydrophilic outer surface consisting of all the protein and the polar ends of any phospholipids. |
| low-density lipoprotein particle receptor binding | Binding to a low-density lipoprotein receptor. |
| metal chelating activity | The formation of bonds from two or more atoms within the same ligand to a metal atom in complexes in which the metal is part of a ring. |
| phosphatidylcholine-sterol O-acyltransferase activator activity | Increases the activity of phosphatidylcholine-sterol O-acyltransferase, an enzyme that converts cholesterol and phosphatidylcholine (lecithins) to cholesteryl esters and lyso-phosphatidylcholines. |
| phospholipid binding | Binding to a phospholipid, a class of lipids containing phosphoric acid as a mono- or diester. |
| protein dimerization activity | The formation of a protein dimer, a macromolecular structure consists of two noncovalently associated identical or nonidentical subunits. |
| protein homodimerization activity | Binding to an identical protein to form a homodimer. |
| protein-containing complex binding | Binding to a macromolecular complex. |
| signaling receptor binding | Binding to one or more specific sites on a receptor molecule, a macromolecule that undergoes combination with a hormone, neurotransmitter, drug or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell function. |
| structural molecule activity | The action of a molecule that contributes to the structural integrity of a complex or its assembly within or outside a cell. |
| tau protein binding | Binding to tau protein. tau is a microtubule-associated protein, implicated in Alzheimer's disease, Down Syndrome and ALS. |
| very-low-density lipoprotein particle receptor binding | Binding to a very-low-density lipoprotein receptor. |
112 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| AMPA glutamate receptor clustering | The glutamate receptor clustering process in which alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionate (AMPA) receptors are localized to distinct domains in the cell membrane. |
| amyloid precursor protein metabolic process | The chemical reactions and pathways involving amyloid precursor protein (APP), the precursor of amyloid-beta, a glycoprotein associated with Alzheimer's disease. |
| artery morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structures of arterial blood vessels are generated and organized. Arteries are blood vessels that transport blood from the heart to the body and its organs. |
| cellular calcium ion homeostasis | Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady state of calcium ions at the level of a cell. |
| cGMP-mediated signaling | Any intracellular signal transduction in which the signal is passed on within the cell via cyclic GMP (cGMP). Includes production of cGMP, and downstream effectors that further transmit the signal within the cell. |
| cholesterol catabolic process | The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of cholesterol, cholest-5-en-3 beta-ol, the principal sterol of vertebrates and the precursor of many steroids, including bile acids and steroid hormones. |
| cholesterol efflux | The directed movement of cholesterol, cholest-5-en-3-beta-ol, out of a cell or organelle. |
| cholesterol homeostasis | Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady state of cholesterol within an organism or cell. |
| cholesterol metabolic process | The chemical reactions and pathways involving cholesterol, cholest-5-en-3 beta-ol, the principal sterol of vertebrates and the precursor of many steroids, including bile acids and steroid hormones. It is a component of the plasma membrane lipid bilayer and of plasma lipoproteins and can be found in all animal tissues. |
| chylomicron remnant clearance | The process in which a chylomicron remnant is removed from the blood via receptor-mediated endocytosis into liver cells and its constituent parts degraded. |
| cytoskeleton organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures. |
| fatty acid homeostasis | Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady state of fatty acid within an organism or cell. |
| G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by a ligand binding to its receptor, in which the activated receptor promotes the exchange of GDP for GTP on the alpha-subunit of an associated heterotrimeric G-protein complex. The GTP-bound activated alpha-G-protein then dissociates from the beta- and gamma-subunits to further transmit the signal within the cell. The pathway begins with receptor-ligand interaction, and ends with regulation of a downstream cellular process. The pathway can start from the plasma membrane, Golgi or nuclear membrane. |
| gene expression | The process in which a gene's sequence is converted into a mature gene product (protein or RNA). This includes the production of an RNA transcript and its processing, translation and maturation for protein-coding genes. |
| high-density lipoprotein particle assembly | The non-covalent aggregation and arrangement of proteins and lipids to form a high-density lipoprotein particle. |
| high-density lipoprotein particle clearance | The process in which a high-density lipoprotein particle is removed from the blood via receptor-mediated endocytosis and its constituent parts degraded. |
| high-density lipoprotein particle remodeling | The acquisition, loss or modification of a protein or lipid within a high-density lipoprotein particle, including the hydrolysis of triglyceride by hepatic lipase, with the subsequent loss of free fatty acid, and the transfer of cholesterol esters from LDL to a triglyceride-rich lipoprotein particle by cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP), with the simultaneous transfer of triglyceride to LDL. |
| intermediate-density lipoprotein particle clearance | The process in which a intermediate-density lipoprotein particle is removed from the blood via receptor-mediated endocytosis and its constituent parts degraded. |
| intracellular transport | The directed movement of substances within a cell. |
| lipid transport involved in lipid storage | The directed movement of lipids into cells that is part of their accumulation and maintenance. |
| lipoprotein biosynthetic process | The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of any conjugated, water-soluble protein in which the covalently attached nonprotein group consists of a lipid or lipids. |
| lipoprotein catabolic process | The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of any conjugated, water-soluble protein in which the covalently attached nonprotein group consists of a lipid or lipids. |
| locomotory exploration behavior | The specific movement from place to place of an organism in response to a novel environment. |
| long-chain fatty acid transport | The directed movement of long-chain fatty acids into, out of or within a cell, or between cells, by means of some agent such as a transporter or pore. A long-chain fatty acid is a fatty acid with a chain length between C13 and C22. |
| long-term memory | The memory process that deals with the storage, retrieval and modification of information a long time (typically weeks, months or years) after receiving that information. This type of memory is typically dependent on gene transcription regulated by second messenger activation. |
| low-density lipoprotein particle remodeling | The acquisition, loss or modification of a protein or lipid within a low-density lipoprotein particle, including the hydrolysis of triglyceride by hepatic lipase, with the subsequent loss of free fatty acid, and the transfer of cholesterol esters from LDL to a triglyceride-rich lipoprotein particle by cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP), with the simultaneous transfer of triglyceride to LDL. |
| maintenance of location in cell | Any process in which a substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, is maintained in a specific location within, or in the membrane of, a cell, and is prevented from moving elsewhere. |
| melanosome organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of a melanosome. A melanosome is a tissue-specific, membrane-bounded cytoplasmic organelle within which melanin pigments are synthesized and stored. |
| negative regulation of amyloid fibril formation | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of amyloid fibril formation. |
| negative regulation of amyloid-beta formation | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of amyloid-beta formation. |
| negative regulation of blood coagulation | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of blood coagulation. |
| negative regulation of blood vessel endothelial cell migration | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the migration of the endothelial cells of blood vessels. |
| negative regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway | Any process that decreases the rate, frequency, or extent of the Wnt signaling pathway through beta-catenin, the series of molecular signals initiated by binding of a Wnt protein to a frizzled family receptor on the surface of the target cell, followed by propagation of the signal via beta-catenin, and ending with a change in transcription of target genes. |
| negative regulation of cholesterol biosynthetic process | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of cholesterol. |
| negative regulation of cholesterol efflux | Any process that decreases the frequency, rate or extent of cholesterol efflux. Cholesterol efflux is the directed movement of cholesterol, cholest-5-en-3-beta-ol, out of a cell or organelle. |
| negative regulation of dendritic spine development | Any process that decreases the rate, frequency, or extent of dendritic spine development, the process whose specific outcome is the progression of the dendritic spine over time, from its formation to the mature structure. |
| negative regulation of dendritic spine maintenance | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of dendritic spine maintenance. |
| negative regulation of endothelial cell migration | Any process that decreases the rate, frequency, or extent of the orderly movement of an endothelial cell into the extracellular matrix to form an endothelium. |
| negative regulation of endothelial cell proliferation | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the rate or extent of endothelial cell proliferation. |
| negative regulation of gene expression | Any process that decreases the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product (protein or RNA). |
| negative regulation of inflammatory response | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the inflammatory response. |
| negative regulation of lipid biosynthetic process | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of lipids. |
| negative regulation of lipid transport across blood-brain barrier | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of lipid transport across blood-brain barrier. |
| negative regulation of long-term synaptic potentiation | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of long-term synaptic potentiation. |
| negative regulation of MAP kinase activity | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of MAP kinase activity. |
| negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cell death by apoptotic process in neurons. |
| negative regulation of neuron death | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of neuron death. |
| negative regulation of neuron projection development | Any process that decreases the rate, frequency or extent of neuron projection development. Neuron projection development is the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron projection over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A neuron projection is any process extending from a neural cell, such as axons or dendrites (collectively called neurites). |
| negative regulation of phospholipid efflux | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of phospholipid efflux. |
| negative regulation of platelet activation | Any process that decreases the rate or frequency of platelet activation. Platelet activation is a series of progressive, overlapping events triggered by exposure of the platelets to subendothelial tissue. |
| negative regulation of postsynaptic membrane organization | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of postsynaptic membrane organization. |
| negative regulation of protein metabolic process | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of chemical reactions and pathways involving a protein. |
| negative regulation of protein secretion | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the controlled release of a protein from a cell. |
| negative regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the rate or extent of smooth muscle cell proliferation. |
| negative regulation of triglyceride metabolic process | Any process that decreases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving triglyceride, any triester of glycerol. |
| neuron projection development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron projection over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A neuron projection is any process extending from a neural cell, such as axons or dendrites (collectively called neurites). |
| nitric oxide mediated signal transduction | Any intracellular signal transduction in which the signal is passed on within the cell via nitric oxide (NO). Includes synthesis of nitric oxide, receptors/sensors for nitric oxide (such as soluble guanylyl cyclase/sGC) and downstream effectors that further transmit the signal within the cell. Nitric oxide transmits its downstream effects through either cyclic GMP (cGMP)-dependent or independent mechanisms. |
| NMDA glutamate receptor clustering | The receptor clustering process in which N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors are localized to distinct domains in the cell membrane. |
| phospholipid efflux | The directed movement of a phospholipid out of a cell or organelle. |
| positive regulation by host of viral process | A process in which a host organism activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the release of a process being mediated by a virus with which it is infected. |
| positive regulation of amyloid fibril formation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of amyloid fibril formation. |
| positive regulation of amyloid-beta clearance | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of amyloid-beta clearance. |
| positive regulation of amyloid-beta formation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of amyloid-beta formation. |
| positive regulation of cholesterol efflux | Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of cholesterol efflux. Cholesterol efflux is the directed movement of cholesterol, cholest-5-en-3-beta-ol, out of a cell or organelle. |
| positive regulation of cholesterol metabolic process | Any process that increases the rate, frequency, or extent of cholesterol metabolism, the chemical reactions and pathways involving cholesterol, cholest-5-en-3 beta-ol, the principal sterol of vertebrates and the precursor of many steroids, including bile acids and steroid hormones. |
| positive regulation of CoA-transferase activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of CoA-transferase activity. |
| positive regulation of dendritic spine development | Any process that increases the rate, frequency, or extent of dendritic spine development, the process whose specific outcome is the progression of the dendritic spine over time, from its formation to the mature structure. |
| positive regulation of dendritic spine maintenance | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of dendritic spine maintenance. |
| positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cellular DNA-templated transcription. |
| positive regulation of endocytosis | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of endocytosis. |
| positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction mediated by the ERK1 and ERK2 cascade. |
| positive regulation of heparan sulfate binding | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of heparan sulfate binding. |
| positive regulation of heparan sulfate proteoglycan binding | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of heparan sulfate proteoglycan binding. |
| positive regulation of lipid biosynthetic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of lipids. |
| positive regulation of lipid transport across blood-brain barrier | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of lipid transport across blood-brain barrier. |
| positive regulation of low-density lipoprotein particle receptor catabolic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of low-density lipoprotein particle receptors. |
| positive regulation of membrane protein ectodomain proteolysis | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of membrane protein ectodomain peptidolysis. |
| positive regulation of neurofibrillary tangle assembly | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of neurofibrillary tangle assembly. |
| positive regulation of neuron death | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of neuron death. |
| positive regulation of neuron projection development | Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of neuron projection development. Neuron projection development is the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron projection over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A neuron projection is any process extending from a neural cell, such as axons or dendrites (collectively called neurites). |
| positive regulation of nitric-oxide synthase activity | Any process that activates or increases the activity of the enzyme nitric-oxide synthase. |
| positive regulation of phospholipid efflux | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of phospholipid efflux. |
| positive regulation of presynaptic membrane organization | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of presynaptic membrane organization. |
| protein import | The targeting and directed movement of proteins into a cell or organelle. Not all import involves an initial targeting event. |
| receptor-mediated endocytosis | An endocytosis process in which cell surface receptors ensure specificity of transport. A specific receptor on the cell surface binds tightly to the extracellular macromolecule (the ligand) that it recognizes; the plasma-membrane region containing the receptor-ligand complex then undergoes endocytosis, forming a transport vesicle containing the receptor-ligand complex and excluding most other plasma-membrane proteins. Receptor-mediated endocytosis generally occurs via clathrin-coated pits and vesicles. |
| regulation of amyloid fibril formation | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of amyloid fibril formation. |
| regulation of amyloid precursor protein catabolic process | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of amyloid precursor protein catabolic process. |
| regulation of amyloid-beta clearance | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of amyloid-beta clearance. |
| regulation of axon extension | Any process that modulates the rate, direction or extent of axon extension. |
| regulation of behavioral fear response | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of behavioral fear response. |
| regulation of Cdc42 protein signal transduction | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of Cdc42 protein signal transduction. |
| regulation of cellular response to very-low-density lipoprotein particle stimulus | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cellular response to very-low-density lipoprotein particle stimulus. |
| regulation of cholesterol metabolic process | Any process that modulates the rate, frequency, or extent of cholesterol metabolism, the chemical reactions and pathways involving cholesterol, cholest-5-en-3 beta-ol, the principal sterol of vertebrates and the precursor of many steroids, including bile acids and steroid hormones. |
| regulation of innate immune response | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the innate immune response, the organism's first line of defense against infection. |
| regulation of neuron death | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of neuron death. |
| regulation of neuronal synaptic plasticity | A process that modulates neuronal synaptic plasticity, the ability of neuronal synapses to change as circumstances require. They may alter function, such as increasing or decreasing their sensitivity, or they may increase or decrease in actual numbers. |
| regulation of proteasomal protein catabolic process | Any process that modulates the rate, frequency, or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of a protein or peptide by hydrolysis of its peptide bonds that is mediated by the proteasome. |
| regulation of protein metabolic process | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving a protein. |
| regulation of protein-containing complex assembly | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of protein complex assembly. |
| regulation of tau-protein kinase activity | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of tau-protein kinase activity. |
| response to caloric restriction | A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a caloric restriction, insufficient food energy intake. |
| response to dietary excess | The physiological process in which dietary excess is sensed by the central nervous system, resulting in a reduction in food intake and increased energy expenditure. |
| response to reactive oxygen species | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a reactive oxygen species stimulus. Reactive oxygen species include singlet oxygen, superoxide, and oxygen free radicals. |
| reverse cholesterol transport | The directed movement of peripheral cell cholesterol, cholest-5-en-3-beta-ol, towards the liver for catabolism. |
| synaptic transmission, cholinergic | The vesicular release of acetylcholine from a presynapse, across a chemical synapse, the subsequent activation of dopamine receptors at the postsynapse of a target cell (neuron, muscle, or secretory cell) and the effects of this activation on the postsynaptic membrane potential and ionic composition of the postsynaptic cytosol. This process encompasses both spontaneous and evoked release of neurotransmitter and all parts of synaptic vesicle exocytosis. Evoked transmission starts with the arrival of an action potential at the presynapse. |
| triglyceride homeostasis | Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady state of triglyceride within an organism or cell. |
| triglyceride metabolic process | The chemical reactions and pathways involving triglyceride, any triester of glycerol. The three fatty acid residues may all be the same or differ in any permutation. Triglycerides are important components of plant oils, animal fats and animal plasma lipoproteins. |
| triglyceride-rich lipoprotein particle clearance | The process in which a triglyceride-rich lipoprotein particle is removed from the blood via receptor-mediated endocytosis and its constituent parts degraded. |
| vasodilation | An increase in the internal diameter of blood vessels, especially arterioles or capillaries, due to relaxation of smooth muscle cells that line the vessels, and usually resulting in a decrease in blood pressure. |
| very-low-density lipoprotein particle clearance | The process in which a very-low-density lipoprotein particle is removed from the blood via receptor-mediated endocytosis and its constituent parts degraded. |
| very-low-density lipoprotein particle remodeling | The acquisition, loss or modification of a protein or lipid within a very-low-density lipoprotein particle, including the hydrolysis of triglyceride by hepatic lipase or lipoprotein lipase and the subsequent loss of free fatty acid. |
| virion assembly | A late phase of the viral life cycle during which all the components necessary for the formation of a mature virion collect at a particular site in the cell and the basic structure of the virus particle is formed. |
6 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q03247 | APOE | Apolipoprotein E | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| P18649 | APOE | Apolipoprotein E | Canis lupus familiaris (Dog) (Canis familiaris) | PR |
| Q6Q788 | APOA5 | Apolipoprotein A-V | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P08226 | Apoe | Apolipoprotein E | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q8C7G5 | Apoa5 | Apolipoprotein A-V | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P02650 | Apoe | Apolipoprotein E | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MKVLWAALLV | TFLAGCQAKV | EQAVETEPEP | ELRQQTEWQS | GQRWELALGR | FWDYLRWVQT |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| LSEQVQEELL | SSQVTQELRA | LMDETMKELK | AYKSELEEQL | TPVAEETRAR | LSKELQAAQA |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| RLGADMEDVC | GRLVQYRGEV | QAMLGQSTEE | LRVRLASHLR | KLRKRLLRDA | DDLQKRLAVY |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| QAGAREGAER | GLSAIRERLG | PLVEQGRVRA | ATVGSLAGQP | LQERAQAWGE | RLRARMEEMG |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| SRTRDRLDEV | KEQVAEVRAK | LEEQAQQIRL | QAEAFQARLK | SWFEPLVEDM | QRQWAGLVEK |
| 310 | |||||
| VQAAVGTSAA | PVPSDNH |