O88942
Gene name |
Nfatc1 (Nfat2, Nfatc) |
Protein name |
Nuclear factor of activated T-cells, cytoplasmic 1 |
Names |
NF-ATc1, NFATc1, NFAT transcription complex cytosolic component, NF-ATc, NFATc |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
|
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
NFAT (PTHR12533) |
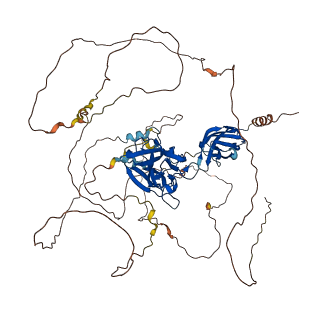
Descriptions
NFAT1 plays a role in the inducible expression of cytokine genes in T-cells. NFAT transcription factors are highly phosphorylated proteins that are regulated by the calcium-dependent phosphatase calcineurin. NFAT1 is phosphorylated on fourteen conserved phosphoserine residues in its regulatory domain (100-400), thirteen of which are dephosphorylated upon stimulation. Dephosphorylation of all thirteen residues is required to mask a nuclear export signal (NES), causes full exposure of a nuclear localization signal (NLS), and promotes transcriptional activity. Mutations in the serine-rich region (SRR-1, specifically 170-183) enhances the localization of NFAT1 to the nucleus, while the full-length NFAT1 does not move into the nucleus. This represents that the SRR-1 region inhibits the translocation of NFAT1 to the nucleus. In addition, SRR-1 region also regulates the active conformation of NFAT1.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
267-269 (NLS) |
Relief mechanism |
PTM |
Assay |
Mutagenesis experiment |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for O88942
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-O88942-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for O88942
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for O88942 | |||||
No associated diseases with O88942
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | ||
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | PTHR12533 | NFAT |
| PANTHER Subfamily | PTHR12533:SF5 | NUCLEAR FACTOR OF ACTIVATED T-CELLS, CYTOPLASMIC 1 |
| PANTHER Protein Class |
Rel homology transcription factor
immunoglobulin fold transcription factor |
|
| PANTHER Pathway Category |
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor pathway NFAT Inflammation mediated by chemokine and cytokine signaling pathway NFAT Wnt signaling pathway NFAT T cell activation NFAT B cell activation NFAT |
|
6 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| chromatin | The ordered and organized complex of DNA, protein, and sometimes RNA, that forms the chromosome. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| nuclear body | Extra-nucleolar nuclear domains usually visualized by confocal microscopy and fluorescent antibodies to specific proteins. |
| nucleoplasm | That part of the nuclear content other than the chromosomes or the nucleolus. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| transcription regulator complex | A protein complex that is capable of associating with DNA by direct binding, or via other DNA-binding proteins or complexes, and regulating transcription. |
11 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| chromatin binding | Binding to chromatin, the network of fibers of DNA, protein, and sometimes RNA, that make up the chromosomes of the eukaryotic nucleus during interphase. |
| DNA binding | Any molecular function by which a gene product interacts selectively and non-covalently with DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). |
| DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific | A DNA-binding transcription factor activity that activates or increases transcription of specific gene sets transcribed by RNA polymerase II. |
| DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific | A DNA-binding transcription factor activity that modulates the transcription of specific gene sets transcribed by RNA polymerase II. |
| DNA-binding transcription factor binding | Binding to a DNA-binding transcription factor, a protein that interacts with a specific DNA sequence (sometimes referred to as a motif) within the regulatory region of a gene to modulate transcription. |
| DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific | A DNA-binding transcription factor activity that represses or decreases the transcription of specific gene sets transcribed by RNA polymerase II. |
| mitogen-activated protein kinase p38 binding | Binding to mitogen-activated protein kinase p38, an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of phosphate from ATP to hydroxyl side chains on proteins in response to mitogen activation. |
| RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding | Binding to a specific upstream regulatory DNA sequence (transcription factor recognition sequence or binding site) located in cis relative to the transcription start site (i.e., on the same strand of DNA) of a gene transcribed by RNA polymerase II. |
| RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding | Binding to a sequence-specific DNA binding RNA polymerase II transcription factor, any of the factors that interact selectively and non-covalently with a specific DNA sequence in order to modulate transcription. |
| sequence-specific DNA binding | Binding to DNA of a specific nucleotide composition, e.g. GC-rich DNA binding, or with a specific sequence motif or type of DNA e.g. promotor binding or rDNA binding. |
| sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding | Binding to double-stranded DNA of a specific nucleotide composition, e.g. GC-rich DNA binding, or with a specific sequence motif or type of DNA, e.g. promotor binding or rDNA binding. |
30 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| aortic valve development | The progression of the aortic valve over time, from its formation to the mature structure. |
| aortic valve morphogenesis | The process in which the structure of the aortic valve is generated and organized. |
| B-1a B cell differentiation | The process in which B cells acquire the specialized features of B-1a B cells. B-1a B cells are B-1 cells that express CD5 and arise from fetal liver precursors. |
| branching involved in lymph vessel morphogenesis | The process of the coordinated growth and sprouting of lymph vessels giving rise to the organized lymphatic system. |
| calcineurin-NFAT signaling cascade | Any intracellular signal transduction in which the signal is passed on within the cell by activation of a member of the NFAT protein family as a consequence of NFAT dephosphorylation by Ca(2+)-activated calcineurin. The cascade begins with calcium-dependent activation of the phosphatase calcineurin. Calcineurin dephosphorylates multiple phosphoserine residues on NFAT, resulting in the translocation of NFAT to the nucleus. The cascade ends with regulation of transcription by NFAT. The calcineurin-NFAT cascade lies downstream of many cell surface receptors, including G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) and receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) that signal to mobilize calcium ions (Ca2+). |
| calcium ion transport | The directed movement of calcium (Ca) ions into, out of or within a cell, or between cells, by means of some agent such as a transporter or pore. |
| endocardial cushion development | The progression of a cardiac cushion over time, from its initial formation to the mature structure. The endocardial cushion is a specialized region of mesenchymal cells that will give rise to the heart septa and valves. |
| epithelial to mesenchymal transition | A transition where an epithelial cell loses apical/basolateral polarity, severs intercellular adhesive junctions, degrades basement membrane components and becomes a migratory mesenchymal cell. |
| G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle | The mitotic cell cycle transition by which a cell in G1 commits to S phase. The process begins with the build up of G1 cyclin-dependent kinase (G1 CDK), resulting in the activation of transcription of G1 cyclins. The process ends with the positive feedback of the G1 cyclins on the G1 CDK which commits the cell to S phase, in which DNA replication is initiated. |
| heart development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the heart over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The heart is a hollow, muscular organ, which, by contracting rhythmically, keeps up the circulation of the blood. |
| heart trabecula morphogenesis | The process of shaping a trabecula in the heart. A trabecula is a small, often microscopic, tissue element in the form of a small beam, strut or rod, which generally has a mechanical function. Trabecula are usually but not necessarily, composed of dense collagenous tissue. |
| heart valve development | The progression of a heart valve over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A heart valve is a structure that restricts the flow of blood to different regions of the heart and forms from an endocardial cushion. |
| heart valve morphogenesis | The process in which the structure of a heart valve is generated and organized. |
| intracellular signal transduction | The process in which a signal is passed on to downstream components within the cell, which become activated themselves to further propagate the signal and finally trigger a change in the function or state of the cell. |
| lymphangiogenesis | Lymph vessel formation when new vessels emerge from the proliferation of pre-existing vessels. |
| negative regulation of osteoblast differentiation | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of osteoblast differentiation. |
| negative regulation of stem cell proliferation | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of stem cell proliferation. |
| negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of transcription mediated by RNA polymerase II. |
| negative regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell differentiation | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of vascular smooth muscle cell differentiation. |
| osteoclast differentiation | The process in which a relatively unspecialized monocyte acquires the specialized features of an osteoclast. An osteoclast is a specialized phagocytic cell associated with the absorption and removal of the mineralized matrix of bone tissue. |
| positive regulation of gene expression | Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product (protein or RNA). |
| positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription from an RNA polymerase II promoter. |
| positive regulation of transcription, DNA-templated | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cellular DNA-templated transcription. |
| pulmonary valve development | The progression of the pulmonary valve over time, from its formation to the mature structure. |
| pulmonary valve morphogenesis | The process in which the structure of the pulmonary valve is generated and organized. |
| regulation of hair cycle | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the cyclical phases of growth (anagen), regression (catagen), quiescence (telogen), and shedding (exogen) in the life of a hair. |
| regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of transcription mediated by RNA polymerase II. |
| semi-lunar valve development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a semi-lunar valve over time, from its formation to the mature structure. |
| transition between fast and slow fiber | The process of conversion of fast-contracting muscle fibers to a slower character. This may involve slowing of contractile rate, slow myosin gene induction, increase in oxidative metabolic properties, altered electrophysiology and altered innervation. This process also regulates skeletal muscle adapatation. |
| ventricular septum morphogenesis | The developmental process in which a ventricular septum is generated and organized. A ventricular septum is an anatomical structure that separates the lower chambers (ventricles) of the heart from one another. |
6 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P98201 | NFATC1 | Nuclear factor of activated T-cells, cytoplasmic 1 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| O95644 | NFATC1 | Nuclear factor of activated T-cells, cytoplasmic 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P97305 | Nfatc3 | Nuclear factor of activated T-cells, cytoplasmic 3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q60591 | Nfatc2 | Nuclear factor of activated T-cells, cytoplasmic 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q8K120 | Nfatc4 | Nuclear factor of activated T-cells, cytoplasmic 4 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| O77638 | NFATC1 | Nuclear factor of activated T-cells, cytoplasmic 1 | Sus scrofa (Pig) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MPNTSFPVPS | KFPLGPPAAV | CGSGETLRPA | PPSGGTMKAA | EEEHYSYVSP | SVTSTLPLPT |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| AHSALPAACH | DLQTSTPGIS | AVPSANHPPS | YGGAVDSGPS | GYFLSSGNTR | PNGAPTLESP |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| RIEITSYLGL | HHGSGQFFHD | VEVEDVLPSC | KRSPSTATLH | LPSLEAYRDP | SCLSPASSLS |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| SRSCNSEASS | YESNYSYPYA | SPQTSPWQSP | CVSPKTTDPE | EGFPRSLGAC | HLLGSPRHSP |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| STSPRASITE | ESWLGARGSR | PTSPCNKRKY | SLNGRQPSCS | PHHSPTPSPH | GSPRVSVTED |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| TWLGNTTQYT | SSAIVAAINA | LTTDSTLDLG | DGVPIKSRKT | ALEHAPSVAL | KVEPAGEDLG |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| TTPPTSDFPP | EEYTFQHLRK | GAFCEQYLSV | PQASYQWAKP | KSLSPTSYMS | PSLPALDWQL |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| PSHSGPYELR | IEVQPKSHHR | AHYETEGSRG | AVKASAGGHP | IVQLHGYLEN | EPLTLQLFIG |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| TADDRLLRPH | AFYQVHRITG | KTVSTTSHEI | ILSNTKVLEI | PLLPENNMRA | IIDCAGILKL |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| RNSDIELRKG | ETDIGRKNTR | VRLVFRVHIP | QPNGRTLSLQ | VASNPIECSQ | RSAQELPLVE |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| KQSTDSYPVI | GGKKMVLSGH | NFLQDSKVIF | VEKAPDGHHV | WEMEAKTDRD | LCKPNSLVVE |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | |
| IPPFRNQRIT | SPAQVSFYVC | NGKRKRSQYQ | RFTYLPANGN | SVFLTLSSES | ELRGGFY |