O88554
Gene name |
Parp2 (Adprt2, Adprtl2, Aspartl2) |
Protein name |
Poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase 2 |
Names |
PARP-2 , mPARP-2 , EC 2.4.2.30 , ADP-ribosyltransferase diphtheria toxin-like 2 , ARTD2 , DNA ADP-ribosyltransferase PARP2 , EC 2.4.2.- , NAD, + ADP-ribosyltransferase 2 , ADPRT-2 , Poly[ADP-ribose] synthase 2 , pADPRT-2 , Protein poly-ADP-ribosyltransferase PARP2 , EC 2.4.2.- |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:11546 |
EC number |
2.4.2.30: Pentosyltransferases |
Protein Class |
|
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
332-559 (ART domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Ligand binding, Others |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

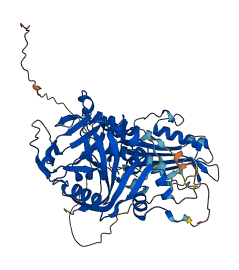
2 structures for O88554
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1GS0 | X-ray | 280 A | A/B | 207-557 | PDB |
| AF-O88554-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
35 variants for O88554
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs217203552 | 10 | S>P | No | EVA | |
| rs3389323083 | 23 | N>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3389247015 | 33 | P>S | No | EVA | |
| rs224024136 | 46 | P>S | No | EVA | |
| rs246589245 | 53 | A>T | No | EVA | |
| rs255096927 | 59 | N>K | No | EVA | |
| rs224000098 | 60 | R>Q | No | EVA | |
| rs230728336 | 61 | D>E | No | EVA | |
| rs31020030 | 82 | L>V | No | EVA | |
| rs3389330911 | 110 | K>Q | No | EVA | |
| rs3389319650 | 153 | K>Q | No | EVA | |
| rs31094122 | 177 | V>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3389334388 | 180 | K>* | No | EVA | |
| rs3404841645 | 190 | A>G | No | EVA | |
| rs3389279356 | 206 | P>H | No | EVA | |
| rs36436211 | 209 | Q>K | No | EVA | |
| rs3389323102 | 234 | M>I | No | EVA | |
| rs36397441 | 249 | A>E | No | EVA | |
| rs36397441 | 249 | A>G | No | EVA | |
| rs3389279396 | 273 | A>E | No | EVA | |
| rs3404322797 | 300 | E>G | No | EVA | |
| rs3404322797 | 300 | E>V | No | EVA | |
| rs3389326272 | 303 | L>P | No | EVA | |
| rs3389326300 | 329 | G>C | No | EVA | |
| rs3389307811 | 332 | H>N | No | EVA | |
| rs3389307753 | 353 | N>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3405077307 | 437 | I>N | No | EVA | |
| rs236322907 | 460 | L>F | No | EVA | |
| rs3389249404 | 465 | E>D | No | EVA | |
| rs3389307793 | 467 | A>T | No | EVA | |
| rs3405077375 | 476 | E>K | No | EVA | |
| rs3389326037 | 479 | P>T | No | EVA | |
| rs13470699 | 486 | R>Q | No | EVA | |
| rs3404638205 | 486 | R>W | No | EVA | |
| rs3389307824 | 507 | L>M | No | EVA |
No associated diseases with O88554
9 regional properties for O88554
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Protein kinase domain | 74 - 332 | IPR000719 |
| domain | EF-hand domain | 375 - 446 | IPR002048-1 |
| domain | EF-hand domain | 447 - 516 | IPR002048-2 |
| active_site | Serine/threonine-protein kinase, active site | 194 - 206 | IPR008271 |
| binding_site | Protein kinase, ATP binding site | 80 - 107 | IPR017441 |
| binding_site | EF-Hand 1, calcium-binding site | 388 - 400 | IPR018247-1 |
| binding_site | EF-Hand 1, calcium-binding site | 424 - 436 | IPR018247-2 |
| binding_site | EF-Hand 1, calcium-binding site | 460 - 472 | IPR018247-3 |
| binding_site | EF-Hand 1, calcium-binding site | 494 - 506 | IPR018247-4 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.4.2.30 | Pentosyltransferases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
4 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| nucleolus | A small, dense body one or more of which are present in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. It is rich in RNA and protein, is not bounded by a limiting membrane, and is not seen during mitosis. Its prime function is the transcription of the nucleolar DNA into 45S ribosomal-precursor RNA, the processing of this RNA into 5.8S, 18S, and 28S components of ribosomal RNA, and the association of these components with 5S RNA and proteins synthesized outside the nucleolus. This association results in the formation of ribonucleoprotein precursors; these pass into the cytoplasm and mature into the 40S and 60S subunits of the ribosome. |
| nucleoplasm | That part of the nuclear content other than the chromosomes or the nucleolus. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| site of DNA damage | A region of a chromosome at which DNA damage has occurred. DNA damage signaling and repair proteins accumulate at the lesion to respond to the damage and repair the DNA to form a continuous DNA helix. |
12 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| chromatin binding | Binding to chromatin, the network of fibers of DNA, protein, and sometimes RNA, that make up the chromosomes of the eukaryotic nucleus during interphase. |
| damaged DNA binding | Binding to damaged DNA. |
| NAD DNA ADP-ribosyltransferase activity | Catalysis of the transfer of the ADP-ribose group of NAD+ to a residue in double-stranded DNA. |
| NAD+ ADP-ribosyltransferase activity | Catalysis of the reaction |
| NAD+- protein-aspartate ADP-ribosyltransferase activity | Catalysis of the reaction |
| NAD+-protein ADP-ribosyltransferase activity | Catalysis of the reaction |
| NAD+-protein-glutamate ADP-ribosyltransferase activity | Catalysis of the reaction |
| NAD+-protein-serine ADP-ribosyltransferase activity | Catalysis of the reaction |
| nucleosome binding | Binding to a nucleosome, a complex comprised of DNA wound around a multisubunit core and associated proteins, which forms the primary packing unit of DNA into higher order structures. |
| nucleotidyltransferase activity | Catalysis of the transfer of a nucleotidyl group to a reactant. |
| poly-ADP-D-ribose binding | Binding to polymeric ADP-D-ribose, a polymer that is composed of poly-ADP-D-ribose units linked through 1,2-glycosidic bonds at the ribose ring. |
| poly-ADP-D-ribose modification-dependent protein binding | Binding to a protein upon poly-ADP-ribosylation of the target protein. |
12 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| base-excision repair | In base excision repair, an altered base is removed by a DNA glycosylase enzyme, followed by excision of the resulting sugar phosphate. The small gap left in the DNA helix is filled in by the sequential action of DNA polymerase and DNA ligase. |
| decidualization | The cellular and vascular changes occurring in the endometrium of the pregnant uterus just after the onset of blastocyst implantation. This process involves the proliferation and differentiation of the fibroblast-like endometrial stromal cells into large, polyploid decidual cells that eventually form the maternal component of the placenta. |
| DNA ADP-ribosylation | The covalent attachment of an ADP-ribosyl group to a residue in double-stranded DNA. |
| DNA repair | The process of restoring DNA after damage. Genomes are subject to damage by chemical and physical agents in the environment (e.g. UV and ionizing radiations, chemical mutagens, fungal and bacterial toxins, etc.) and by free radicals or alkylating agents endogenously generated in metabolism. DNA is also damaged because of errors during its replication. A variety of different DNA repair pathways have been reported that include direct reversal, base excision repair, nucleotide excision repair, photoreactivation, bypass, double-strand break repair pathway, and mismatch repair pathway. |
| DNA repair-dependent chromatin remodeling | A chromatin remodeling process that allows DNA repair enzyme to access genomic DNA and repair DNA lesions. |
| double-strand break repair | The repair of double-strand breaks in DNA via homologous and nonhomologous mechanisms to reform a continuous DNA helix. |
| extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals in which a signal is conveyed from the cell surface to trigger the apoptotic death of a cell. The pathway starts with either a ligand binding to a cell surface receptor, or a ligand being withdrawn from a cell surface receptor (e.g. in the case of signaling by dependence receptors), and ends when the execution phase of apoptosis is triggered. |
| hippocampal neuron apoptotic process | Any apoptotic process that occurs in a hippocampal neuron. |
| positive regulation of cell growth involved in cardiac muscle cell development | Any process that increases the rate, frequency, or extent of the growth of a cardiac muscle cell, where growth contributes to the progression of the cell over time from its initial formation to its mature state. |
| protein auto-ADP-ribosylation | The ADP-ribosylation by a protein of one or more of its own amino acid residues, or residues on an identical protein. |
| protein poly-ADP-ribosylation | The transfer of multiple ADP-ribose residues from NAD to a protein amino acid, forming a poly(ADP-ribose) chain. |
| response to oxygen-glucose deprivation | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of the deprivation of oxygen and glucose. |
14 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P18493 | PARP1 | Poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase 1 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| P26446 | PARP1 | Poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase 1 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P35875 | Parp | Poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| P09874 | PARP1 | Poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q9Y6F1 | PARP3 | Protein mono-ADP-ribosyltransferase PARP3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9UGN5 | PARP2 | Poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| O50017 | PARP2 | Poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase 2 | Zea mays (Maize) | SS |
| P11103 | Parp1 | Poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P27008 | Parp1 | Poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q0JMY1 | PARP2-B | Poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase 2-B | Oryza sativa subsp. japonica (Rice) | SS |
| Q5Z8Q9 | PARP2-A | Poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase 2-A | Oryza sativa subsp. japonica (Rice) | SS |
| Q11207 | PARP2 | Poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase 2 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| Q9ZP54 | PARP1 | Poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase 1 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| Q5RHR0 | parp1 | Poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase 1 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MAPRRQRSGS | GRRVLNEAKK | VDNGNKATED | DSPPGKKMRT | CQRKGPMAGG | KDADRTKDNR |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| DSVKTLLLKG | KAPVDPECAA | KLGKAHVYCE | GDDVYDVMLN | QTNLQFNNNK | YYLIQLLEDD |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| AQRNFSVWMR | WGRVGKTGQH | SLVTCSGDLN | KAKEIFQKKF | LDKTKNNWED | RENFEKVPGK |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| YDMLQMDYAA | STQDESKTKE | EETLKPESQL | DLRVQELLKL | ICNVQTMEEM | MIEMKYDTKR |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| APLGKLTVAQ | IKAGYQSLKK | IEDCIRAGQH | GRALVEACNE | FYTRIPHDFG | LSIPPVIRTE |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| KELSDKVKLL | EALGDIEIAL | KLVKSERQGL | EHPLDQHYRN | LHCALRPLDH | ESNEFKVISQ |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| YLQSTHAPTH | KDYTMTLLDV | FEVEKEGEKE | AFREDLPNRM | LLWHGSRLSN | WVGILSHGLR |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| VAPPEAPITG | YMFGKGIYFA | DMSSKSANYC | FASRLKNTGL | LLLSEVALGQ | CNELLEANPK |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| AQGLLRGKHS | TKGMGKMAPS | PAHFITLNGS | TVPLGPASDT | GILNPEGYTL | NYNEFIVYSP |
| 550 | |||||
| NQVRMRYLLK | IQFNFLQLW |