Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
157-401 (DID domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Partner binding |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
References
- Lammers M et al. (2005) "The regulation of mDia1 by autoinhibition and its release by Rho*GTP", The EMBO journal, 24, 4176-87
- Otomo T et al. (2010) "Crystal structure of the Formin mDia1 in autoinhibited conformation", PloS one, 5,
- Otomo T et al. (2005) "Structural basis of Rho GTPase-mediated activation of the formin mDia1", Molecular cell, 18, 273-81
- Kitzing TM et al. (2007) "Positive feedback between Dia1, LARG, and RhoA regulates cell morphology and invasion", Genes & development, 21, 1478-83
- Mizuno H et al. (2018) "Helical rotation of the diaphanous-related formin mDia1 generates actin filaments resistant to cofilin", Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 115, E5000-E5007
- Seth A et al. (2006) "Autoinhibition regulates cellular localization and actin assembly activity of the diaphanous-related formins FRLalpha and mDia1", The Journal of cell biology, 174, 701-13
- Lash LL et al. (2013) "Small-molecule intramimics of formin autoinhibition: a new strategy to target the cytoskeletal remodeling machinery in cancer cells", Cancer research, 73, 6793-803
- Deacon SW et al. (2008) "Chemical inhibition through conformational stabilization of Rho GTPase effectors", Handbook of experimental pharmacology, , 431-60
- Orshanskiy IA et al. (2015) "[Molecular Dynamics of N- and C-terminal Interactions during Autoinhibition and Activation of Formin mDial]", Biofizika, 60, 451-6
- Lammers M et al. (2008) "Specificity of interactions between mDia isoforms and Rho proteins", The Journal of biological chemistry, 283, 35236-46
- Copeland SJ et al. (2007) "The diaphanous inhibitory domain/diaphanous autoregulatory domain interaction is able to mediate heterodimerization between mDia1 and mDia2", The Journal of biological chemistry, 282, 30120-30
- Alberts AS (2001) "Identification of a carboxyl-terminal diaphanous-related formin homology protein autoregulatory domain", The Journal of biological chemistry, 276, 2824-30
- Maiti S et al. (2012) "Structure and activity of full-length formin mDia1", Cytoskeleton (Hoboken, N.J.), 69, 393-405
- Gould CJ et al. (2011) "The formin DAD domain plays dual roles in autoinhibition and actin nucleation", Current biology : CB, 21, 384-90
- Goode BL et al. (2007) "Mechanism and function of formins in the control of actin assembly", Annual review of biochemistry, 76, 593-627
- Higgs HN (2005) "Formin proteins: a domain-based approach", Trends in biochemical sciences, 30, 342-53
- Nezami A et al. (2010) "Crystal structure of a complex between amino and carboxy terminal fragments of mDia1: insights into autoinhibition of diaphanous-related formins", PloS one, 5,
- Kovar DR (2006) "Molecular details of formin-mediated actin assembly", Current opinion in cell biology, 18, 11-7
- Li F et al. (2005) "Dissecting requirements for auto-inhibition of actin nucleation by the formin, mDia1", The Journal of biological chemistry, 280, 6986-92
- Copeland JW et al. (2004) "Homo-oligomerization is essential for F-actin assembly by the formin family FH2 domain", The Journal of biological chemistry, 279, 50250-6
- Bai CX et al. (2008) "Activation of TRPP2 through mDia1-dependent voltage gating", The EMBO journal, 27, 1345-56
- Li F et al. (2003) "The mouse Formin mDia1 is a potent actin nucleation factor regulated by autoinhibition", Current biology : CB, 13, 1335-40
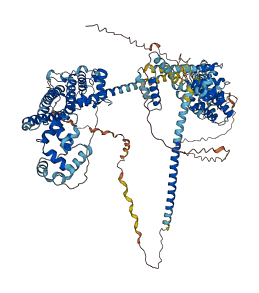
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for O70566
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-O70566-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
14 variants for O70566
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs218501571 | 72 | Y>S | No | Ensembl | |
| rs238439533 | 74 | T>A | No | Ensembl | |
| rs29116447 | 79 | I>F | No | Ensembl | |
| rs221676640 | 148 | L>P | No | Ensembl | |
| rs240566703 | 617 | I>M | No | Ensembl | |
| rs864289100 | 740 | L>R | No | Ensembl | |
| rs1134181080 | 817 | A>T | No | Ensembl | |
| rs1134720661 | 818 | C>F | No | Ensembl | |
| rs29115138 | 826 | S>G | No | Ensembl | |
| rs1133460747 | 829 | R>I | No | Ensembl | |
| rs29112923 | 884 | K>Q | No | Ensembl | |
| rs238447772 | 906 | A>D | No | Ensembl | |
| rs864284296 | 1015 | K>E | No | Ensembl | |
| rs1134732480 | 1031 | L>M | No | Ensembl |
No associated diseases with O70566
5 regional properties for O70566
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Formin, FH3 domain | 288 - 479 | IPR010472 |
| domain | Formin, GTPase-binding domain | 90 - 283 | IPR010473 |
| domain | Diaphanous autoregulatory (DAD) domain | 1048 - 1078 | IPR014767 |
| domain | Rho GTPase-binding/formin homology 3 (GBD/FH3) domain | 90 - 463 | IPR014768 |
| domain | Formin, FH2 domain | 625 - 1068 | IPR015425 |
3 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| endoplasmic reticulum | The irregular network of unit membranes, visible only by electron microscopy, that occurs in the cytoplasm of many eukaryotic cells. The membranes form a complex meshwork of tubular channels, which are often expanded into slitlike cavities called cisternae. The ER takes two forms, rough (or granular), with ribosomes adhering to the outer surface, and smooth (with no ribosomes attached). |
| intracellular membrane-bounded organelle | Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane. |
| nucleolus | A small, dense body one or more of which are present in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. It is rich in RNA and protein, is not bounded by a limiting membrane, and is not seen during mitosis. Its prime function is the transcription of the nucleolar DNA into 45S ribosomal-precursor RNA, the processing of this RNA into 5.8S, 18S, and 28S components of ribosomal RNA, and the association of these components with 5S RNA and proteins synthesized outside the nucleolus. This association results in the formation of ribonucleoprotein precursors; these pass into the cytoplasm and mature into the 40S and 60S subunits of the ribosome. |
2 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| actin binding | Binding to monomeric or multimeric forms of actin, including actin filaments. |
| small GTPase binding | Binding to a small monomeric GTPase. |
2 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| actin filament polymerization | Assembly of actin filaments by the addition of actin monomers to a filament. |
| oogenesis | The complete process of formation and maturation of an ovum or female gamete from a primordial female germ cell. Examples of this process are found in Mus musculus and Drosophila melanogaster. |
8 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P48608 | dia | Protein diaphanous | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | EV |
| O60610 | DIAPH1 | Protein diaphanous homolog 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q9NSV4 | DIAPH3 | Protein diaphanous homolog 3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| O60879 | DIAPH2 | Protein diaphanous homolog 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| O08808 | Diaph1 | Protein diaphanous homolog 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| Q9Z207 | Diaph3 | Protein diaphanous homolog 3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| F1LVW7 | Diaph3 | Protein diaphanous homolog 3 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| F1M775 | Diaph1 | Protein diaphanous homolog 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MEELGAAASG | AGGGGGGGEE | HGGGRSNKRG | AGNRAANEEE | TRNKPKLRDR | ITSFRKSATK |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| REKPVIQHSI | DYQTAVVEIP | PALIVHDDRS | LILSEKEVLD | LFEKMMEDMN | LNEEKKAPLR |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| KKDFSIKREM | VVQYISATSK | SIVGSKVLGG | LKNSKHEFTL | SSQEYVHELR | SGISDEKLLN |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| CLESLRVSLT | SHPVSWVNNF | GYEGLGVLLD | VLEKLLDKKQ | QENIDKKNQY | KVIQCLKAFM |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| NNKFGLQRIL | GDERSLLLLA | RAIDPKQQNM | MTEIVKILSA | ICIVGEENIL | DKLLGGITAA |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| AELNNRERFS | PIVEGLENNE | ALHLQVACMQ | FINALVTSPY | DLDFRIHLRN | EFLRCGLKAM |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| LPTLKEIENE | GLDIQLRVFE | ENKEDDLSEL | SHRLNDIRAE | MDDINEVYHL | LYNMLKDTAA |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| EPYLLSILQH | FLLIRNDYYI | RPQYYKIIEE | CVSQIVLHCS | GMDPDFKYRQ | RIDFDFTHLL |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| DACVNKAKVE | ENEQKAMEFS | KKFDEEFTAR | QEAQAELQKR | DEKIKELETE | IQQLRGQGVP |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| SAIPGPPPPP | PLPGAGPCPP | PPPPPPPPPP | LPGVVPPPPP | PLPGMPGIPP | PPPPPLSGVP |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| PPPPPPGGVF | PLLSGPIELP | YGMKQKKLYK | PDIPMKRINW | SKIEPKELSE | NCVWLKLKEE |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| KYENADLFAK | LALTFPSQMK | GQRNTEAAEE | NRSGPPKKKV | KELRILDTKT | AQNLSIFLGS |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| YRMPYEEIKN | IILEVNEEML | SEALIQNLVK | YLPDQNALRE | LAQLKSEYDD | LCEPEQFGVV |
| 790 | 800 | 810 | 820 | 830 | 840 |
| MSTVKMLRPR | LTSILFKLTF | EEHVNNIKPS | IIAVTLACEE | LKKSESFKRL | LELILLVGNY |
| 850 | 860 | 870 | 880 | 890 | 900 |
| MNSGSRNAQS | LGFKINFLCK | IKDTKSADQK | STLLHFLAEI | CDEKYRDILK | FPDELEHVES |
| 910 | 920 | 930 | 940 | 950 | 960 |
| AGKVSAQILK | SNLVAMEQSI | LHLEKNIKNF | PPAESHHDKF | VEKMMSFTQN | AREQYDKLST |
| 970 | 980 | 990 | 1000 | 1010 | 1020 |
| MHSNMLKLYE | SLGEYFIFDP | NTVNMEEFFG | DLNTFRTLFL | EALKENHKRK | EMEEKSRRAK |
| 1030 | 1040 | 1050 | 1060 | 1070 | 1080 |
| LAKEKAEQEK | LERQKKKKQL | IDINKEGDET | GVMDNLLEAL | QSGAAFRDRR | KRIPRNPDNR |
| 1090 | |||||
| RPPLERSRSR | HNGAMSSK |