O70145
Gene name |
Ncf2 |
Protein name |
Neutrophil cytosol factor 2 |
Names |
NCF-2, 67 kDa neutrophil oxidase factor, NADPH oxidase activator 2, Neutrophil NADPH oxidase factor 2, p67-phox |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:17970 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
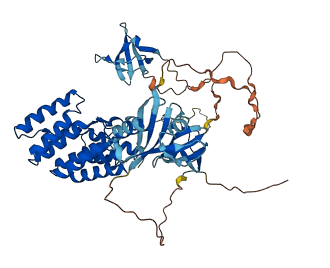
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for O70145
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-O70145-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
24 variants for O70145
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs31180149 | 23 | K>N | No | EVA | |
| rs223849895 | 31 | E>A | No | EVA | |
| rs3388507076 | 72 | V>M | No | EVA | |
| rs3388507521 | 75 | F>V | No | EVA | |
| rs3388506927 | 111 | I>N | No | EVA | |
| rs3388507466 | 169 | Q>L | No | EVA | |
| rs3388503868 | 173 | E>K | No | EVA | |
| rs3390815158 | 223 | Q>H | No | EVA | |
| rs3388503151 | 255 | T>M | No | EVA | |
| rs3388506903 | 288 | L>H | No | EVA | |
| rs232746001 | 343 | L>P | No | EVA | |
| rs215150189 | 372 | S>C | No | EVA | |
| rs215150189 | 372 | S>G | No | EVA | |
| rs3390796566 | 375 | R>Q | No | EVA | |
| rs3388503857 | 389 | T>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3388503857 | 389 | T>S | No | EVA | |
| rs31178388 | 394 | R>Q | No | EVA | |
| rs258207904 | 399 | H>P | No | EVA | |
| rs3388503833 | 414 | G>R | No | EVA | |
| rs3388503216 | 418 | N>T | No | EVA | |
| rs3388503841 | 441 | R>K | No | EVA | |
| rs3388508861 | 444 | S>* | No | EVA | |
| rs3388507187 | 464 | I>V | No | EVA | |
| rs265670655 | 512 | G>E | No | EVA |
No associated diseases with O70145
10 regional properties for O70145
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | PB1 domain | 350 - 428 | IPR000270 |
| repeat | Tetratricopeptide repeat 1 | 71 - 99 | IPR001440 |
| domain | SH3 domain | 240 - 299 | IPR001452-1 |
| domain | SH3 domain | 456 - 515 | IPR001452-2 |
| repeat | Tetratricopeptide repeat | 37 - 70 | IPR019734-1 |
| repeat | Tetratricopeptide repeat | 71 - 104 | IPR019734-2 |
| repeat | Tetratricopeptide repeat | 121 - 154 | IPR019734-3 |
| domain | Neutrophil cytosol factor 2, PB1 domain | 350 - 428 | IPR034885 |
| domain | Neutrophil cytosol factor 2, SH3 domain | 460 - 511 | IPR034889 |
| domain | Neutrophil cytosol factor 2, SH3 domain 1 | 244 - 297 | IPR035546 |
5 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| acrosomal vesicle | A structure in the head of a spermatozoon that contains acid hydrolases, and is concerned with the breakdown of the outer membrane of the ovum during fertilization. It lies just beneath the plasma membrane and is derived from the lysosome. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| membrane | A lipid bilayer along with all the proteins and protein complexes embedded in it an attached to it. |
| NADPH oxidase complex | A enzyme complex of which the core is a heterodimer composed of a light (alpha) and heavy (beta) chain, and requires several other water-soluble proteins of cytosolic origin for activity. Functions in superoxide generation by the NADPH-dependent reduction of O2. |
4 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| protein C-terminus binding | Binding to a protein C-terminus, the end of a peptide chain at which the 1-carboxyl function of a constituent amino acid is not attached in peptide linkage to another amino-acid residue. |
| small GTPase binding | Binding to a small monomeric GTPase. |
| superoxide-generating NAD(P)H oxidase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: NAD(P)H + O2 = NAD(P)H + O2-. |
| superoxide-generating NADPH oxidase activator activity | Increases the activity of the enzyme superoxide-generating NADPH oxidase. |
12 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cellular response to hormone stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a hormone stimulus. |
| NADP catabolic process | The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide phosphate, a coenzyme involved in many redox and biosynthetic reactions; catabolism may be of either the oxidized form, NADP, or the reduced form, NADPH. |
| phagocytosis | A vesicle-mediated transport process that results in the engulfment of external particulate material by phagocytes and their delivery to the lysosome. The particles are initially contained within phagocytic vacuoles (phagosomes), which then fuse with primary lysosomes to effect digestion of the particles. |
| positive regulation of blood pressure | Any process in which the force of blood traveling through the circulatory system is increased. |
| positive regulation of neuron apoptotic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell death of neurons by apoptotic process. |
| regulation of reactive oxygen species biosynthetic process | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of reactive oxygen species biosynthetic process. |
| respiratory burst | A phase of elevated metabolic activity, during which oxygen consumption increases; this leads to the production, by an NADH dependent system, of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), superoxide anions and hydroxyl radicals. |
| response to glucose | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a glucose stimulus. |
| response to lipopolysaccharide | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a lipopolysaccharide stimulus; lipopolysaccharide is a major component of the cell wall of gram-negative bacteria. |
| response to organic cyclic compound | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an organic cyclic compound stimulus. |
| superoxide anion generation | The enzymatic generation of superoxide, the superoxide anion O2- (superoxide free radical), or any compound containing this species, by a cell in response to environmental stress, thereby mediating the activation of various stress-inducible signaling pathways. |
| superoxide metabolic process | The chemical reactions and pathways involving superoxide, the superoxide anion O2- (superoxide free radical), or any compound containing this species. |
8 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O77775 | NCF2 | Neutrophil cytosol factor 2 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| Q5HYK7 | SH3D19 | SH3 domain-containing protein 19 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q6XZF7 | DNMBP | Dynamin-binding protein | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q86UR1 | NOXA1 | NADPH oxidase activator 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P19878 | NCF2 | Neutrophil cytosol factor 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q8CJ00 | Noxa1 | NADPH oxidase activator 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| A7E3N7 | Noxa1 | NADPH oxidase activator 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| A7E3N2 | Ncf2 | Neutrophil cytosol factor 2 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MSLAEAIRLW | NEGVLAADKK | DWKGALEAFS | EVQDPHSRIC | FNIGCVNTIL | ENLQAAEQAF |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| TKSINRDKHS | AVAYFQRGML | YYRMEKYDLA | IKDLKEALTQ | LRGNQLIDYK | ILGLQFKLFA |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| CEVLYNIALM | HAKKEEWKKA | EEQLALATNM | KSEPRHSKID | KAMESIWKQK | LFEPVVIPVG |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| RLFRPNERQV | AQLAKKDYLG | KATVVASVVH | QDNFSGFAPL | QPQSAEPPPR | PKTPEIFRAL |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| EGEAHRVLFG | FVPETPEELQ | VMPGNIVFVL | KKGSDNWATV | MFNGQKGLVP | CNYLEPVELR |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| IHPQSQPQED | TSPESDIPPP | PNSSPPGRLQ | LSPGHKQKEP | KELKLSVPMP | YMLKVHYKYT |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| VVMETRLGLP | YSQLRNMVSK | KLALSPEHTK | LSYRRRDSHE | LLLLSEESMK | DAWGQVKNYC |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| LTLWCEHTVG | DQGLIDEPIQ | RENSDASKQT | TEPQPKEGTQ | VVAIFSYEAA | QPEDLEFVEG |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | ||
| DVILVLSHVN | EEWLEGECKG | KVGIFPKAFV | EGCAAKNLEG | IPREV |