O54748
Gene name |
Stk3 (Mst2) |
Protein name |
Serine/threonine-protein kinase 3 |
Names |
Mammalian STE20-like protein kinase 2, MST-2, STE20-like kinase MST2 |
Species |
Rattus norvegicus (Rat) |
KEGG Pathway |
rno:65189 |
EC number |
2.7.11.1: Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
Protein Class |
|
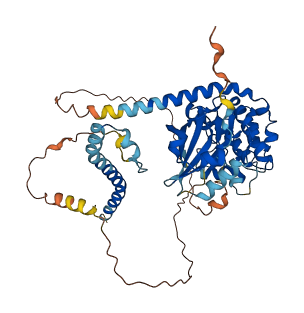
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
27-278 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Cleavage |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
163-186 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
27-278 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
References
- Avruch J et al. (2011) "Mst1/2 signalling to Yap: gatekeeper for liver size and tumour development", British journal of cancer, 104, 24-32
- Zhou D et al. (2011) "Mst1 and Mst2 protein kinases restrain intestinal stem cell proliferation and colonic tumorigenesis by inhibition of Yes-associated protein (Yap) overabundance", Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 108, E1312-20
- Creasy CL et al. (1996) "The Ste20-like protein kinase, Mst1, dimerizes and contains an inhibitory domain", The Journal of biological chemistry, 271, 21049-53
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for O54748
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-O54748-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for O54748
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for O54748 | |||||
No associated diseases with O54748
1 regional properties for O54748
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Protein kinase domain | 27 - 278 | IPR000719 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.11.1 | Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
3 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| protein-containing complex | A stable assembly of two or more macromolecules, i.e. proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates or lipids, in which at least one component is a protein and the constituent parts function together. |
7 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| identical protein binding | Binding to an identical protein or proteins. |
| magnesium ion binding | Binding to a magnesium (Mg) ion. |
| protein kinase activity | Catalysis of the phosphorylation of an amino acid residue in a protein, usually according to the reaction: a protein + ATP = a phosphoprotein + ADP. |
| protein serine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate. |
| protein serine/threonine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate, and ATP + protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate. |
| protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + a protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate; ATP + a protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate; and ATP + a protein tyrosine = ADP + protein tyrosine phosphate. |
23 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cell differentiation involved in embryonic placenta development | The process in which a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of the embryonic placenta. |
| central nervous system development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the central nervous system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The central nervous system is the core nervous system that serves an integrating and coordinating function. In vertebrates it consists of the brain and spinal cord. In those invertebrates with a central nervous system it typically consists of a brain, cerebral ganglia and a nerve cord. |
| endocardium development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the endocardium over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The endocardium is an anatomical structure comprised of an endothelium and an extracellular matrix that forms the innermost layer of tissue of the heart, and lines the heart chambers. |
| hepatocyte apoptotic process | Any apoptotic process in a hepatocyte, the main structural component of the liver. |
| hippo signaling | The series of molecular signals mediated by the serine/threonine kinase Hippo or one of its orthologs. In Drosophila, Hippo in complex with the scaffold protein Salvador (Sav), phosphorylates and activates Warts (Wts), which in turn phosphorylates and inactivates the Yorkie (Yki) transcriptional activator. The core fly components hippo, sav, wts and mats are conserved in mammals as STK4/3 (MST1/2), SAV1/WW45, LATS1/2 and MOB1. |
| intracellular signal transduction | The process in which a signal is passed on to downstream components within the cell, which become activated themselves to further propagate the signal and finally trigger a change in the function or state of the cell. |
| negative regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway | Any process that decreases the rate, frequency, or extent of the Wnt signaling pathway through beta-catenin, the series of molecular signals initiated by binding of a Wnt protein to a frizzled family receptor on the surface of the target cell, followed by propagation of the signal via beta-catenin, and ending with a change in transcription of target genes. |
| negative regulation of cell population proliferation | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the rate or extent of cell proliferation. |
| negative regulation of organ growth | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of growth of an organ of an organism. |
| neural tube formation | The formation of a tube from the flat layer of ectodermal cells known as the neural plate. This will give rise to the central nervous system. |
| positive regulation of apoptotic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell death by apoptotic process. |
| positive regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of activity of a transcription factor, any factor involved in the initiation or regulation of transcription. |
| positive regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway via death domain receptors | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway via death domain receptors. |
| positive regulation of fat cell differentiation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of adipocyte differentiation. |
| positive regulation of JNK cascade | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction mediated by the JNK cascade. |
| positive regulation of protein binding | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of protein binding. |
| positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of protein kinase B signaling, a series of reactions mediated by the intracellular serine/threonine kinase protein kinase B. |
| primitive hemopoiesis | A first transient wave of blood cell production that, in vertebrates, gives rise to erythrocytes (red blood cells) and myeloid cells. |
| protein phosphorylation | The process of introducing a phosphate group on to a protein. |
| protein stabilization | Any process involved in maintaining the structure and integrity of a protein and preventing it from degradation or aggregation. |
| protein tetramerization | The formation of a protein tetramer, a macromolecular structure consisting of four noncovalently associated identical or nonidentical subunits. |
| regulation of cell differentiation involved in embryonic placenta development | Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of cell differentiation that contributes to the progression of the placenta over time, from its initial condition to its mature state. |
| regulation of MAPK cascade | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction mediated by the MAP kinase (MAPK) cascade. |
14 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q5E9L6 | STK4 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase 4 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| Q5ZJK4 | STK4 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase 4 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q13043 | STK4 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase 4 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q13188 | STK3 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase 3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q9JI11 | Stk4 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase 4 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9JI10 | Stk3 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase 3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| D4A280 | Pak5 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 5 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q64303 | Pak2 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 2 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q62829 | Pak3 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 3 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P35465 | Pak1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| A4K2T0 | STK4 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase 4 | Macaca mulatta (Rhesus macaque) | PR |
| Q9NB31 | cst-1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase cst-1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| Q6P3Q4 | stk4 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase 4 | Xenopus tropicalis (Western clawed frog) (Silurana tropicalis) | SS |
| Q7ZUQ3 | stk3 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase 3 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MEQPPAPKSK | LKKLSEDSLT | KQPEEVFDVL | EKLGEGSYGS | VFKAIHKESG | QVVAIKQVPV |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| ESDVQEIIKE | ISIMQQCDSP | YVVKYYGSYF | KNTDLWIVME | YCGAGSVSDI | IRLRNKTLTE |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| DEIATILKST | LKGLEYLHFM | RKIHRDIKAG | NILLNTEGHA | KLADFGVAGQ | LTDTMAKRNT |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| VIGTPFWMAP | EVIQEIGYNC | VADIWSLGIT | SIEMAEGKPP | YADIHPMRAI | FMIPTNPPPT |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| FRKPELWSDD | FTDFVKKCLV | KSPEQRATAT | QLLQHPFIKN | AKPVSILREL | ITEGMEIKAK |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| RHEEQQRELE | DEEENSDEDE | LDSHTMVKTS | SEGVGTMRAT | STMSEGAQTM | IEHNSTMLES |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| DLGTMVINSE | DEEEEDGTMK | RNATSPQVQR | PSFMDYFDKQ | DFKNKSHENC | DQSMREPCPM |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| SNNVFPDNWR | VPQDGDFDFL | KNLSLEELQM | RLKALDPMME | REIEELHQRY | SAKRQPILDA |
| 490 | |||||
| MDAKKRRQQN | F |