O35799
Gene name |
Hfe |
Protein name |
Hereditary hemochromatosis protein homolog |
Names |
RT1-CAFE |
Species |
Rattus norvegicus (Rat) |
KEGG Pathway |
rno:29199 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
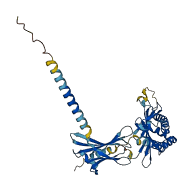
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for O35799
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-O35799-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for O35799
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for O35799 | |||||
No associated diseases with O35799
8 regional properties for O35799
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | MHC class I alpha chain, alpha1 alpha2 domains | 88 - 117 | IPR001039-1 |
| domain | MHC class I alpha chain, alpha1 alpha2 domains | 127 - 143 | IPR001039-2 |
| domain | MHC class I alpha chain, alpha1 alpha2 domains | 147 - 164 | IPR001039-3 |
| domain | MHC class I alpha chain, alpha1 alpha2 domains | 193 - 211 | IPR001039-4 |
| conserved_site | Immunoglobulin/major histocompatibility complex, conserved site | 293 - 299 | IPR003006 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin C1-set | 231 - 305 | IPR003597 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin-like domain | 220 - 309 | IPR007110 |
| domain | MHC class I-like antigen recognition-like | 31 - 212 | IPR011161 |
12 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| apical part of cell | The region of a polarized cell that forms a tip or is distal to a base. For example, in a polarized epithelial cell, the apical region has an exposed surface and lies opposite to the basal lamina that separates the epithelium from other tissue. |
| basal part of cell | The region of a cell situated near the base. For example, in a polarized epithelial cell, the basal surface rests on the basal lamina that separates the epithelium from other tissue. |
| cytoplasmic vesicle | A vesicle found in the cytoplasm of a cell. |
| early endosome | A membrane-bounded organelle that receives incoming material from primary endocytic vesicles that have been generated by clathrin-dependent and clathrin-independent endocytosis; vesicles fuse with the early endosome to deliver cargo for sorting into recycling or degradation pathways. |
| external side of plasma membrane | The leaflet of the plasma membrane that faces away from the cytoplasm and any proteins embedded or anchored in it or attached to its surface. |
| extracellular space | That part of a multicellular organism outside the cells proper, usually taken to be outside the plasma membranes, and occupied by fluid. |
| HFE-transferrin receptor complex | A protein complex containing at least HFE and a transferrin receptor (either TFR1/TFRC or TFR2), proposed to play a role in the sensing of transferrin-bound Fe (Fe2-Tf) on the plasma membrane to regulate hepcidin transcription. |
| integral component of membrane | The component of a membrane consisting of the gene products and protein complexes having at least some part of their peptide sequence embedded in the hydrophobic region of the membrane. |
| perinuclear region of cytoplasm | Cytoplasm situated near, or occurring around, the nucleus. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| recycling endosome | An organelle consisting of a network of tubules that functions in targeting molecules, such as receptors transporters and lipids, to the plasma membrane. |
| terminal web | An actin-rich cytoskeletal network located beneath the microvilli of the apical plasma membrane of polarized epithelial cells. In addition to actin filaments, the terminal web may contain actin-binding proteins, myosin motor proteins, and intermediate filaments. The terminal web can function as a contractile structure that influences the spatial distribution of microvilli as well as the development and morphogenesis of tissues containing polarized epithelial cells. |
4 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| beta-2-microglobulin binding | Binding to beta-2-microglobulin. |
| co-receptor binding | Binding to a coreceptor. A coreceptor acts in cooperation with a primary receptor to transmit a signal within the cell. |
| signaling receptor binding | Binding to one or more specific sites on a receptor molecule, a macromolecule that undergoes combination with a hormone, neurotransmitter, drug or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell function. |
| transferrin receptor binding | Binding to a transferrin receptor. |
31 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| acute-phase response | An acute inflammatory response that involves non-antibody proteins whose concentrations in the plasma increase in response to infection or injury of homeothermic animals. |
| BMP signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by the binding of a member of the BMP (bone morphogenetic protein) family to a receptor on the surface of a target cell, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| cellular iron ion homeostasis | Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady state of iron ions at the level of a cell. |
| cellular response to iron ion | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an iron ion stimulus. |
| cellular response to iron ion starvation | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of deprivation of iron ions. |
| female pregnancy | The set of physiological processes that allow an embryo or foetus to develop within the body of a female animal. It covers the time from fertilization of a female ovum by a male spermatozoon until birth. |
| hormone biosynthetic process | The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of any hormone, naturally occurring substances secreted by specialized cells that affects the metabolism or behavior of other cells possessing functional receptors for the hormone. |
| iron ion homeostasis | Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady state of iron ions within an organism or cell. |
| iron ion import across plasma membrane | The directed movement of iron ions from outside of a cell, across the plasma membrane and into the cytosol. |
| liver regeneration | The regrowth of lost or destroyed liver. |
| multicellular organismal iron ion homeostasis | Any process involved in the maintenance of the distribution of iron stores within tissues and organs of a multicellular organism. |
| negative regulation of antigen processing and presentation of endogenous peptide antigen via MHC class I | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of antigen processing and presentation of endogenous peptide antigen via MHC class I. |
| negative regulation of CD8-positive, alpha-beta T cell activation | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of CD8-positive, alpha-beta T cell activation. |
| negative regulation of receptor binding | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a protein or other molecule binding to a receptor. |
| negative regulation of signaling receptor activity | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a signaling receptor activity. |
| negative regulation of T cell antigen processing and presentation | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate, or extent of T cell antigen processing and presentation. |
| negative regulation of T cell cytokine production | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate, or extent of T cell cytokine production. |
| negative regulation of ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process. |
| positive regulation of ferrous iron binding | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of ferrous iron binding. |
| positive regulation of gene expression | Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product (protein or RNA). |
| positive regulation of pathway-restricted SMAD protein phosphorylation | Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of pathway-restricted SMAD protein phosphorylation. Pathway-restricted SMAD proteins and common-partner SMAD proteins are involved in the transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathways. |
| positive regulation of peptide hormone secretion | Any process that increases the rate, frequency, or extent of the regulated release of a peptide hormone from secretory granules. |
| positive regulation of protein binding | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of protein binding. |
| positive regulation of receptor binding | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a protein or other molecule binding to a receptor. |
| positive regulation of receptor-mediated endocytosis | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of receptor mediated endocytosis, the uptake of external materials by cells, utilizing receptors to ensure specificity of transport. |
| positive regulation of signaling receptor activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of signaling receptor activity. |
| positive regulation of transferrin receptor binding | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transferrin receptor binding. |
| regulation of iron ion transport | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the directed movement of iron ions (Fe) into, out of or within a cell, or between cells, by means of some agent such as a transporter or pore. |
| regulation of protein localization to cell surface | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of protein localization to the cell surface. |
| response to iron ion | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an iron ion stimulus. |
| response to iron ion starvation | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a starvation stimulus, deprivation of iron ion. |
37 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P68428 | Histone H3.2 | Triticum aestivum (Wheat) | PR | |
| Q5E9F8 | H3-3B | Histone H3.3 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| P68432 | Histone H3.1 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR | |
| P84227 | Histone H3.2 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR | |
| P84247 | H3-X | Histone H3.3 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | PR |
| P84229 | H3-VIII | Histone H3.2 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | PR |
| P02299 | His3 | Histone H3 | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | PR |
| Q71H73 | Histone H3.3 | Vitis vinifera (Grape) | PR | |
| P84243 | H3-3B | Histone H3.3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q71DI3 | H3C13 | Histone H3.2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P68431 | H3C12 | Histone H3.1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q16695 | H3-4 | Histone H3.1t | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P69246 | H3C4 | Histone H3.2 | Zea mays (Maize) | PR |
| P84228 | H3c15 | Histone H3.2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P68433 | H3c11 | Histone H3.1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P84244 | H3-3b | Histone H3.3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q71LE2 | H3-3A | Histone H3.3 | Sus scrofa (Pig) | PR |
| P84245 | H3-3b | Histone H3.3 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q6LED0 | Histone H3.1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR | |
| Q63493 | Cd1d | Antigen-presenting glycoprotein CD1d | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P13599 | Fcgrt | IgG receptor FcRn large subunit p51 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q0JCT1 | H3 | Histone H3.3 | Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) | PR |
| Q2RAD9 | H3R-21 | Histone H3.2 | Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) | PR |
| Q27490 | his-70 | Histone H3.3-like type 1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| Q10453 | his-71 | Histone H3.3 type 1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| Q27532 | his-74 | Histone H3.3-like type 2 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| P08898 | his-2 | Histone H3 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| P59226 | HTR2 | Histone H3.1 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9FX60 | At1g13370 | Histone H3-like 1 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9FXI7 | MGH3 | Histone H3-like 2 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9LR02 | At1g75600 | Histone H3-like 3 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| P59169 | HTR4 | Histone H3.3 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9FKQ3 | At5g65350 | Histone H3-like 5 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q6P823 | TGas113e22.1 | Histone H3.3 | Xenopus tropicalis (Western clawed frog) (Silurana tropicalis) | PR |
| Q28D37 | TGas081o10.1 | Histone H3.2 | Xenopus tropicalis (Western clawed frog) (Silurana tropicalis) | PR |
| Q6PI20 | h3f3a | Histone H3.3 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | PR |
| Q4QRF4 | zgc:113984; | Histone H3.2 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MDRSAGLPVR | LLLLLLLLLL | WSVAPQALRP | GSHSLRYLFM | GASKPDLGLP | FFEALGYVDD |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| QLFVSYNHES | RRAEPRAPWI | LGQTSSQLWL | QLSQSLKGWD | YMFIVDFWTI | MGNYNHSKVT |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| KLRVVPESHI | LQVILGCEVH | EDNSTSGFWK | YGYDGQDHLE | FCPKTLNWSA | AEPRAWATKM |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| EWEEHRIRAR | QSRDYLQRDC | PQQLKQVLEL | QRGVLGQQVP | TLVKVTRHWA | STGTSLRCQA |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| LNFFPQNITM | RWLKDSQPLD | AKDVNPENVL | PNGDGTYQGW | LTLAVAPGEE | TRFSCQVEHP |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | |
| GLDQPLTATW | EPSRSQDMII | GIISGITICA | IFFVGILILV | LRKRKVSGGT | MGDYVLTECE |