O35430
Gene name |
Apba1 (Mint1, X11) |
Protein name |
Amyloid-beta A4 precursor protein-binding family A member 1 |
Names |
Adapter protein X11alpha, Neuron-specific X11 protein, Neuronal Munc18-1-interacting protein 1, Mint-1 |
Species |
Rattus norvegicus (Rat) |
KEGG Pathway |
rno:83589 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
SYNTENIN RELATED (PTHR12345) |
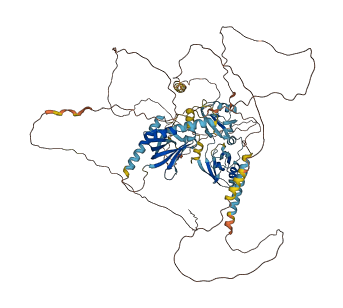
Descriptions
Mint adaptor proteins bind to the amyloid precursor protein (APP) and regulate APP processing associated with Alzheimer’s disease. The Mint1 phosphotyrosine binding (PTB) domain that binds to APP is intramolecularly inhibited by the adjacent C-terminal linker region (the autoinhibitory helix) that folds back onto the core structure of the PTB domain and sterically hinders the APP binding site. This intramolecular interaction is disrupted by mutation of Tyr633 within Mint1 autoinhibitory helix, enhancing APP binding and β-amyloid production. As a result, Mint1 undergoes a conformational transition between a closed state that does not bind APP and an open state that involves APP binding and its proteolytic processing.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
453-635 (PTB domain) |
Relief mechanism |
PTM |
Assay |
Deletion assay, Mutagenesis experiment, Structural analysis |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure
Activated structure

4 structures for O35430
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4DBB | X-ray | 190 A | A | 453-643 | PDB |
| 6KMH | X-ray | 240 A | C/D | 338-397 | PDB |
| 7XSJ | X-ray | 320 A | C | 227-303 | PDB |
| AF-O35430-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for O35430
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for O35430 | |||||
No associated diseases with O35430
No regional properties for O35430
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| No domain, repeats, and functional sites for O35430 | |||
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | ||
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | PTHR12345 | SYNTENIN RELATED |
| PANTHER Subfamily | PTHR12345:SF14 | AMYLOID-BETA A4 PRECURSOR PROTEIN-BINDING FAMILY A MEMBER 1 |
| PANTHER Protein Class | membrane trafficking regulatory protein | |
| PANTHER Pathway Category |
Alzheimer disease-amyloid secretase pathway X11alpha Alzheimer disease-amyloid secretase pathway Tip60 |
|
12 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| dendritic spine | A small, membranous protrusion from a dendrite that forms a postsynaptic compartment, typically receiving input from a single presynapse. They function as partially isolated biochemical and an electrical compartments. Spine morphology is variable:they can be thin, stubby, mushroom, or branched, with a continuum of intermediate morphologies. They typically terminate in a bulb shape, linked to the dendritic shaft by a restriction. Spine remodeling is though to be involved in synaptic plasticity. |
| glutamatergic synapse | A synapse that uses glutamate as a neurotransmitter. |
| Golgi apparatus | A membrane-bound cytoplasmic organelle of the endomembrane system that further processes the core oligosaccharides (e.g. N-glycans) added to proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum and packages them into membrane-bound vesicles. The Golgi apparatus operates at the intersection of the secretory, lysosomal, and endocytic pathways. |
| membrane | A lipid bilayer along with all the proteins and protein complexes embedded in it and attached to it. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| perinuclear region of cytoplasm | Cytoplasm situated near, or occurring around, the nucleus. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| presynaptic active zone membrane | The membrane portion of the presynaptic active zone; it is the site where docking and fusion of synaptic vesicles occurs for the release of neurotransmitters. |
| protein-containing complex | A stable assembly of two or more macromolecules, i.e. proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates or lipids, in which at least one component is a protein and the constituent parts function together. |
| Schaffer collateral - CA1 synapse | A synapse between the Schaffer collateral axon of a CA3 pyramidal cell and a CA1 pyramidal cell. |
5 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| amyloid-beta binding | Binding to an amyloid-beta peptide/protein. |
| PDZ domain binding | Binding to a PDZ domain of a protein, a domain found in diverse signaling proteins. |
| phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate binding | Binding to phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate, a derivative of phosphatidylinositol in which the inositol ring is phosphorylated at the 4' and 5' positions. |
| protein kinase binding | Binding to a protein kinase, any enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a protein substrate. |
| protein-containing complex binding | Binding to a macromolecular complex. |
11 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| chemical synaptic transmission | The vesicular release of classical neurotransmitter molecules from a presynapse, across a chemical synapse, the subsequent activation of neurotransmitter receptors at the postsynapse of a target cell (neuron, muscle, or secretory cell) and the effects of this activation on the postsynaptic membrane potential and ionic composition of the postsynaptic cytosol. This process encompasses both spontaneous and evoked release of neurotransmitter and all parts of synaptic vesicle exocytosis. Evoked transmission starts with the arrival of an action potential at the presynapse. |
| establishment of localization in cell | Any process, occuring in a cell, that localizes a substance or cellular component. This may occur via movement, tethering or selective degradation. |
| gamma-aminobutyric acid secretion | The regulated release of gamma-aminobutyric acid by a cell or a tissue. The gamma-aminobutyric acid is the principal inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain but is also found in several extraneural tissues. |
| glutamate secretion | The controlled release of glutamate by a cell. The glutamate is the most abundant excitatory neurotransmitter in the nervous system. |
| in utero embryonic development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the embryo in the uterus over time, from formation of the zygote in the oviduct, to birth. An example of this process is found in Mus musculus. |
| intracellular protein transport | The directed movement of proteins in a cell, including the movement of proteins between specific compartments or structures within a cell, such as organelles of a eukaryotic cell. |
| locomotory behavior | The specific movement from place to place of an organism in response to external or internal stimuli. Locomotion of a whole organism in a manner dependent upon some combination of that organism's internal state and external conditions. |
| multicellular organism growth | The increase in size or mass of an entire multicellular organism, as opposed to cell growth. |
| presynaptic modulation of chemical synaptic transmission | Any process, acting in the presynapse that results in modulation of chemical synaptic transmission. |
| regulation of gene expression | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product (protein or RNA). |
| synaptic vesicle exocytosis | Fusion of intracellular membrane-bounded vesicles with the pre-synaptic membrane of the neuronal cell resulting in release of neurotransmitter into the synaptic cleft. |
8 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q99767 | APBA2 | Amyloid-beta A4 precursor protein-binding family A member 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q02410 | APBA1 | Amyloid-beta A4 precursor protein-binding family A member 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P98084 | Apba2 | Amyloid-beta A4 precursor protein-binding family A member 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| B2RUJ5 | Apba1 | Amyloid-beta A4 precursor protein-binding family A member 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| O35431 | Apba2 | Amyloid-beta A4 precursor protein-binding family A member 2 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q4KLN0 | Sdcbp2 | Syntenin-2 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q9JI92 | Sdcbp | Syntenin-1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| O17583 | lin-10 | Protein lin-10 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MNHLEGSAEV | EVADEAPGGE | VNESVEADLE | HPEVEEEQQP | SPPPPAGHAP | EDHRAHPAPP |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| PPPPPQEEEE | ERGECLARSA | STESGFHNHT | DTAEGDVLAA | ARDGYEAERA | QDADDESAYA |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| VQYRPEAEEY | TEQAEAEHAE | AAQRRALPNH | LHFHSLEHEE | AMNAAYSGYV | YTHRLFHRAE |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| DEPYAEPYAD | YGGLQEHVYE | EIGDAPELEA | RDGLRLYERE | RDEAAAYRQE | ALGARLHHYD |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| ERSDGESDSP | EKEAEFAPYP | RMDSYEQEED | IDQIVAEVKQ | SMSSQSLDKA | AEDMPEAEQD |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| LERAPTPGGG | HPDSPGLPAP | AGQQQRVVGT | PGGSEVGQRY | SKEKRDAISL | AIKDIKEAIE |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| EVKTRTIRSP | YTPDEPKEPI | WVMRQDISPT | RDCDDQRPVD | GDSPSPGSSS | PLGAESSITP |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| LHPGDPTEAS | TNKESRKSLA | SFPTYVEVPG | PCDPEDLIDG | IIFAANYLGS | TQLLSDKTPS |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| KNVRMMQAQE | AVSRIKTAQK | LAKSRKKAPE | GESQPMTEVD | LFISTQRIKV | LNADTQEPMM |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| DHPLRTISYI | ADIGNIVVLM | ARRRMPRSNS | QENVEASHPS | QDAKRQYKMI | CHVFESEDAQ |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| LIAQSIGQAF | SVAYQEFLRA | NGINPEDLSQ | KEYSDLLNTQ | DMYNDDLIHF | SKSENCKDVF |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| IEKQKGEILG | VVIVESGWGS | ILPTVIIANM | MHGGPAEKSG | KLNIGDQIMS | INGTSLVGLP |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| LSTCQSIIKG | LKNQSRVKLN | IVRCPPVTTV | LIRRPDLRYQ | LGFSVQNGII | CSLMRGGIAE |
| 790 | 800 | 810 | 820 | 830 | |
| RGGVRVGHRI | IEINGQSVVA | TPHEKIVHIL | SNAVGEIHMK | TMPAAMYRLL | TAQEQPVYI |