O35346
Gene name |
Ptk2 |
Protein name |
Focal adhesion kinase 1 |
Names |
FADK 1, Focal adhesion kinase-related nonkinase, FRNK, Protein-tyrosine kinase 2, p125FAK, pp125FAK |
Species |
Rattus norvegicus (Rat) |
KEGG Pathway |
rno:25614 |
EC number |
2.7.10.2: Protein-tyrosine kinases |
Protein Class |
|
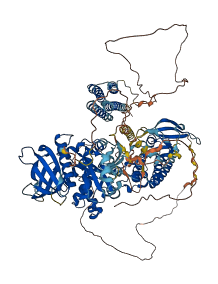
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
422-680 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
PTM |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
563-587 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
422-680 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
References
- Choi I et al. (2016) "LRRK2 Inhibits FAK Activity by Promoting FERM-mediated Autoinhibition of FAK and Recruiting the Tyrosine Phosphatase, SHP-2", Experimental neurobiology, 25, 269-276
- Lietha D et al. (2007) "Structural basis for the autoinhibition of focal adhesion kinase", Cell, 129, 1177-87
- Cai X et al. (2008) "Spatial and temporal regulation of focal adhesion kinase activity in living cells", Molecular and cellular biology, 28, 201-14
- Herzog FA et al. (2017) "Structural Insights How PIP2 Imposes Preferred Binding Orientations of FAK at Lipid Membranes", The journal of physical chemistry. B, 121, 3523-3535
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for O35346
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-O35346-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for O35346
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for O35346 | |||||
No associated diseases with O35346
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.10.2 | Protein-tyrosine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
19 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| apical plasma membrane | The region of the plasma membrane located at the apical end of the cell. |
| basolateral plasma membrane | The region of the plasma membrane that includes the basal end and sides of the cell. Often used in reference to animal polarized epithelial membranes, where the basal membrane is the part attached to the extracellular matrix, or in plant cells, where the basal membrane is defined with respect to the zygotic axis. |
| ciliary basal body | A membrane-tethered, short cylindrical array of microtubules and associated proteins found at the base of a eukaryotic cilium (also called flagellum) that is similar in structure to a centriole and derives from it. The cilium basal body is the site of assembly and remodelling of the cilium and serves as a nucleation site for axoneme growth. As well as anchoring the cilium, it is thought to provide a selective gateway regulating the entry of ciliary proteins and vesicles by intraflagellar transport. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| dendritic spine | A small, membranous protrusion from a dendrite that forms a postsynaptic compartment, typically receiving input from a single presynapse. They function as partially isolated biochemical and an electrical compartments. Spine morphology is variable:they can be thin, stubby, mushroom, or branched, with a continuum of intermediate morphologies. They typically terminate in a bulb shape, linked to the dendritic shaft by a restriction. Spine remodeling is though to be involved in synaptic plasticity. |
| extrinsic component of cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane | The component of a plasma membrane consisting of gene products and protein complexes that are loosely bound to its cytoplasmic surface, but not integrated into the hydrophobic region. |
| focal adhesion | A cell-substrate junction that anchors the cell to the extracellular matrix and that forms a point of termination of actin filaments. In insects focal adhesion has also been referred to as hemi-adherens junction (HAJ). |
| glutamatergic synapse | A synapse that uses glutamate as a neurotransmitter. |
| intercalated disc | A complex cell-cell junction at which myofibrils terminate in cardiomyocytes; mediates mechanical and electrochemical integration between individual cardiomyocytes. The intercalated disc contains regions of tight mechanical attachment (fasciae adherentes and desmosomes) and electrical coupling (gap junctions) between adjacent cells. |
| lamellipodium | A thin sheetlike process extended by the leading edge of a migrating cell or extending cell process; contains a dense meshwork of actin filaments. |
| nuclear body | Extra-nucleolar nuclear domains usually visualized by confocal microscopy and fluorescent antibodies to specific proteins. |
| nucleolus | A small, dense body one or more of which are present in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. It is rich in RNA and protein, is not bounded by a limiting membrane, and is not seen during mitosis. Its prime function is the transcription of the nucleolar DNA into 45S ribosomal-precursor RNA, the processing of this RNA into 5.8S, 18S, and 28S components of ribosomal RNA, and the association of these components with 5S RNA and proteins synthesized outside the nucleolus. This association results in the formation of ribonucleoprotein precursors; these pass into the cytoplasm and mature into the 40S and 60S subunits of the ribosome. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| perinuclear region of cytoplasm | Cytoplasm situated near, or occurring around, the nucleus. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| postsynapse | The part of a synapse that is part of the post-synaptic cell. |
| sarcolemma | The outer membrane of a muscle cell, consisting of the plasma membrane, a covering basement membrane (about 100 nm thick and sometimes common to more than one fiber), and the associated loose network of collagen fibers. |
| stress fiber | A contractile actin filament bundle that consists of short actin filaments with alternating polarity, cross-linked by alpha-actinin and possibly other actin bundling proteins, and with myosin present in a periodic distribution along the fiber. |
15 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| actin binding | Binding to monomeric or multimeric forms of actin, including actin filaments. |
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| identical protein binding | Binding to an identical protein or proteins. |
| integrin binding | Binding to an integrin. |
| JUN kinase binding | Binding to JUN kinase, an enzyme that catalyzes the phosphorylation and activation of members of the JUN family. |
| non-membrane spanning protein tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + protein L-tyrosine = ADP + protein L-tyrosine phosphate by a non-membrane spanning protein. |
| phosphatase binding | Binding to a phosphatase. |
| phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase binding | Binding to a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, any enzyme that catalyzes the addition of a phosphate group to an inositol lipid at the 3' position of the inositol ring. |
| protein kinase binding | Binding to a protein kinase, any enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a protein substrate. |
| protein phosphatase binding | Binding to a protein phosphatase. |
| protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + a protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate; ATP + a protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate; and ATP + a protein tyrosine = ADP + protein tyrosine phosphate. |
| protein tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + a protein tyrosine = ADP + protein tyrosine phosphate. |
| protein-containing complex binding | Binding to a macromolecular complex. |
| SH2 domain binding | Binding to a SH2 domain (Src homology 2) of a protein, a protein domain of about 100 amino-acid residues and belonging to the alpha + beta domain class. |
| signaling receptor binding | Binding to one or more specific sites on a receptor molecule, a macromolecule that undergoes combination with a hormone, neurotransmitter, drug or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell function. |
73 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| angiogenesis | Blood vessel formation when new vessels emerge from the proliferation of pre-existing blood vessels. |
| blood vessel development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a blood vessel over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The blood vessel is the vasculature carrying blood. |
| cell differentiation | The process in which relatively unspecialized cells, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cells, acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate and its subsequent development to the mature state. |
| cell migration | The controlled self-propelled movement of a cell from one site to a destination guided by molecular cues. Cell migration is a central process in the development and maintenance of multicellular organisms. |
| cellular chloride ion homeostasis | Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady state of chloride ions at the level of a cell. |
| cellular response to transforming growth factor beta stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a transforming growth factor beta stimulus. |
| central nervous system neuron axonogenesis | Generation of a long process from a neuron whose cell body resides in the central nervous system. The process carries efferent (outgoing) action potentials from the cell body towards target cells. |
| endothelial cell migration | The orderly movement of an endothelial cell into the extracellular matrix to form an endothelium. |
| ephrin receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by ephrin binding to its receptor, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by binding of a ligand to the tyrosine kinase receptor EGFR (ERBB1) on the surface of a cell. The pathway ends with regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| extracellular matrix organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of an extracellular matrix. |
| fat cell differentiation | The process in which a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of an adipocyte, an animal connective tissue cell specialized for the synthesis and storage of fat. |
| growth hormone receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals generated as a consequence of growth hormone receptor binding to its physiological ligand. |
| innate immune response | Innate immune responses are defense responses mediated by germline encoded components that directly recognize components of potential pathogens. |
| integrin-mediated signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by an extracellular ligand binding to an integrin on the surface of a target cell, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| JNK cascade | An intracellular protein kinase cascade containing at least a JNK (a MAPK), a JNKK (a MAPKK) and a JUN3K (a MAP3K). The cascade can also contain an additional tier: the upstream MAP4K. The kinases in each tier phosphorylate and activate the kinases in the downstream tier to transmit a signal within a cell. |
| MAPK cascade | An intracellular protein kinase cascade containing at least a MAPK, a MAPKK and a MAP3K. The cascade can also contain an additional tiers: the upstream MAP4K. The kinases in each tier phosphorylate and activate the kinase in the downstream tier to transmit a signal within a cell. |
| microtubule cytoskeleton organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures comprising microtubules and their associated proteins. |
| negative regulation of anoikis | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of anoikis. |
| negative regulation of apoptotic process | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cell death by apoptotic process. |
| negative regulation of autophagy | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of autophagy. Autophagy is the process in which cells digest parts of their own cytoplasm. |
| negative regulation of axonogenesis | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of axonogenesis. |
| negative regulation of cell migration | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cell migration. |
| negative regulation of cell-cell adhesion | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the rate or extent of cell adhesion to another cell. |
| negative regulation of organ growth | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of growth of an organ of an organism. |
| negative regulation of synapse assembly | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of synapse assembly, the aggregation, arrangement and bonding together of a set of components to form a synapse. |
| neuron migration | The characteristic movement of an immature neuron from germinal zones to specific positions where they will reside as they mature. |
| nuclear migration | The directed movement of the nucleus to a specific location within a cell. |
| peptidyl-tyrosine autophosphorylation | The phosphorylation by a protein of one or more of its own tyrosine amino acid residues, or a tyrosine residue on an identical protein. |
| peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation | The phosphorylation of peptidyl-tyrosine to form peptidyl-O4'-phospho-L-tyrosine. |
| positive regulation of cardiac muscle hypertrophy | Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of the enlargement or overgrowth of all or part of the heart due to an increase in size (not length) of individual cardiac muscle fibers, without cell division. |
| positive regulation of cell adhesion | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell adhesion. |
| positive regulation of cell growth | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, extent or direction of cell growth. |
| positive regulation of cell migration | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell migration. |
| positive regulation of cell population proliferation | Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of cell proliferation. |
| positive regulation of fibroblast migration | Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of fibroblast cell migration. Fibroblast cell migration is accomplished by extension and retraction of a pseudopodium. |
| positive regulation of glial cell proliferation | Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of glial cell proliferation. |
| positive regulation of macrophage chemotaxis | Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of macrophage chemotaxis. Macrophage chemotaxis is the movement of a macrophage in response to an external stimulus. |
| positive regulation of macrophage proliferation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of macrophage proliferation. |
| positive regulation of phagocytosis | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of phagocytosis. |
| positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction mediated by the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase cascade. |
| positive regulation of protein kinase activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of protein kinase activity. |
| positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of protein kinase B signaling, a series of reactions mediated by the intracellular serine/threonine kinase protein kinase B. |
| positive regulation of protein phosphorylation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of addition of phosphate groups to amino acids within a protein. |
| positive regulation of smooth muscle cell migration | Any process that activates, maintains or increases the frequency, rate or extent of smooth muscle cell migration. |
| positive regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation | Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of smooth muscle cell proliferation. |
| positive regulation of synaptic transmission | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of synaptic transmission, the process of communication from a neuron to a target (neuron, muscle, or secretory cell) across a synapse. |
| positive regulation of ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process. |
| positive regulation of wound healing | Any process that increases the rate, frequency, or extent of the series of events that restore integrity to a damaged tissue, following an injury. |
| protein autophosphorylation | The phosphorylation by a protein of one or more of its own amino acid residues (cis-autophosphorylation), or residues on an identical protein (trans-autophosphorylation). |
| protein phosphorylation | The process of introducing a phosphate group on to a protein. |
| regulation of cell adhesion | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of attachment of a cell to another cell or to the extracellular matrix. |
| regulation of cell adhesion mediated by integrin | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of cell adhesion mediated by integrin. |
| regulation of cell population proliferation | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell proliferation. |
| regulation of cell shape | Any process that modulates the surface configuration of a cell. |
| regulation of epithelial cell migration | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of epithelial cell migration. |
| regulation of focal adhesion assembly | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of focal adhesion formation, the establishment and maturation of focal adhesions. |
| regulation of osteoblast differentiation | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of osteoblast differentiation. |
| regulation of protein phosphorylation | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of addition of phosphate groups into an amino acid in a protein. |
| regulation of substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading. |
| response to arsenic-containing substance | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an arsenic stimulus from compounds containing arsenic, including arsenates, arsenites, and arsenides. |
| response to estradiol | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of stimulus by estradiol, a C18 steroid hormone hydroxylated at C3 and C17 that acts as a potent estrogen. |
| response to glucose | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a glucose stimulus. |
| response to mechanical stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a mechanical stimulus. |
| response to organic cyclic compound | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an organic cyclic compound stimulus. |
| response to organic substance | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an organic substance stimulus. |
| response to organonitrogen compound | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an organonitrogen stimulus. An organonitrogen compound is formally a compound containing at least one carbon-nitrogen bond. |
| response to xenobiotic stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus from a xenobiotic, a compound foreign to the organim exposed to it. It may be synthesized by another organism (like ampicilin) or it can be a synthetic chemical. |
| signal complex assembly | The aggregation, arrangement and bonding together of a set of components to form a complex capable of relaying a signal within a cell. |
| transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by an extracellular ligand binding to a transforming growth factor beta receptor on the surface of a target cell, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by an extracellular ligand binding to a receptor on the surface of the target cell where the receptor possesses tyrosine kinase activity, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| vasculogenesis | The differentiation of endothelial cells from progenitor cells during blood vessel development, and the de novo formation of blood vessels and tubes. |
| vasodilation | An increase in the internal diameter of blood vessels, especially arterioles or capillaries, due to relaxation of smooth muscle cells that line the vessels, and usually resulting in a decrease in blood pressure. |
20 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q00944 | PTK2 | Focal adhesion kinase 1 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | EV |
| Q14289 | PTK2B | Protein-tyrosine kinase 2-beta | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q05397 | PTK2 | Focal adhesion kinase 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q9QVP9 | Ptk2b | Protein-tyrosine kinase 2-beta | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P34152 | Ptk2 | Focal adhesion kinase 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q64725 | Syk | Tyrosine-protein kinase SYK | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q6P6U0 | Fgr | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fgr | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q07014 | Lyn | Tyrosine-protein kinase Lyn | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q62844 | Fyn | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q9WUD9 | Src | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P50545 | Hck | Tyrosine-protein kinase HCK | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| F1LM93 | Yes1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase Yes | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q62662 | Frk | Tyrosine-protein kinase FRK | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P41243 | Matk | Megakaryocyte-associated tyrosine-protein kinase | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P32577 | Csk | Tyrosine-protein kinase CSK | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P70600 | Ptk2b | Protein-tyrosine kinase 2-beta | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q5U2X5 | Tnk2 | Activated CDC42 kinase 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q01621 | Lck | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase LCK | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P09760 | Fer | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fer | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q95YD4 | kin-32 | Inactive tyrosine-protein kinase kin-32 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MAAAYLDPNL | NHTPSSSTKT | HLGTGTERSP | GAMERVLKVF | HYFESSNEPT | TWASIIRHGD |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| ATDVRGIIQK | IVDSHKVKHV | ACYGFRLSHL | RSEEVHWLHV | DMGVSSVREK | YELAHPPEEW |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| KYELRIRYLP | KGFLNQFTED | KPTLNFFYQQ | VKSDYMLEIA | DQVDQDIALK | LGCLEIRRSY |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| WEMRGNALEK | KSNYEVLEKD | VGLKRFFPKS | LLDSVKAKTL | RKLIQQTFRQ | FANLNREESI |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| LKFFEILSPV | YRFDKECFKC | ALGSSWIISV | ELAIGPEEGI | SYLTDKGCNP | THLADFNQVQ |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| TIQYSNSEDK | DRKGMLQLKI | AGAPEPLTVT | APSLTIAENM | ADLIDGYCRL | VNGATQSFII |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| RPQKEGERAL | PSIPKLANNE | KQGMRTHAVS | VSETDDYAEI | IDEEDTYTMP | STRDYEIQRE |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| RIELGRCIGE | GQFGDVHQGV | YLSPENPALA | VAIKTCKNCT | SDSVREKFLQ | EALTMRQFDH |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| PHIVKLIGVI | TENPVWIIME | LCTLGELRSF | LQVRKYSLDL | ASLILYAYQL | STALAYLESK |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| RFVHRDIAAR | NVLVSSNDCV | KLGDFGLSRY | MEDSTYYKAS | KGKLPIKWMA | PESINFRRFT |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| SASDVWMFGV | CMWEILMHGV | KPFQGVKNND | VIGRIENGER | LPMPPNCPPT | LYSLMTKCWA |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| YDPSRRPRFT | ELKAQLSTIL | EEEKVQQEER | MRMESRRQAT | VSWDSGGSDE | APPKPSRPGY |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| PSPRSSEGFY | PSPQHMVQTN | HYQISGYPGS | HGIPAMAGSI | YPGQASLLDQ | TELWNHRPQE |
| 790 | 800 | 810 | 820 | 830 | 840 |
| MSMWQPSVED | SAALDLRGMG | QVLPPHLMEE | RLIRQQQEME | EDQRWLEKEE | RFLKPDVRLS |
| 850 | 860 | 870 | 880 | 890 | 900 |
| RGSIDREDGS | FQGPTGNQHI | YQPVGKPDPA | APPKKPPRPG | APGHLSNLSS | ISSPAESYNE |
| 910 | 920 | 930 | 940 | 950 | 960 |
| GVKPWRLQPQ | EISPPPTANL | DRSNDKVYEN | VTGLVKAVIE | MSSKIQPAPP | EEYVPMVKEV |
| 970 | 980 | 990 | 1000 | 1010 | 1020 |
| GLALRTLLAT | VDETIPILPA | STHREIEMAQ | KLLNSDLGEL | ISKMKLAQQY | VMTSLQQEYK |
| 1030 | 1040 | 1050 | |||
| KQMLTAAHAL | AVDAKNLLDV | IDQARLKMLG | QTRPH |