O18334
Gene name |
Rab6 |
Protein name |
Ras-related protein Rab6 |
Names |
Protein warthog |
Species |
Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) |
KEGG Pathway |
dme:Dmel_CG6601 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
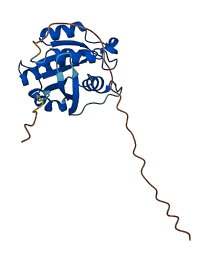
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

2 structures for O18334
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2Y8E | X-ray | 139 A | A/B | 1-177 | PDB |
| AF-O18334-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for O18334
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for O18334 | |||||
No associated diseases with O18334
1 regional properties for O18334
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Small GTP-binding protein domain | 12 - 168 | IPR005225 |
Functions
10 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| anchoring junction | A cell junction that mechanically attaches a cell (and its cytoskeleton) to neighboring cells or to the extracellular matrix. |
| autophagosome | A double-membrane-bounded compartment that engulfs endogenous cellular material as well as invading microorganisms to target them to the lytic vacuole/lysosome for degradation as part of macroautophagy. |
| cytoplasmic vesicle | A vesicle found in the cytoplasm of a cell. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| Golgi apparatus | A membrane-bound cytoplasmic organelle of the endomembrane system that further processes the core oligosaccharides (e.g. N-glycans) added to proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum and packages them into membrane-bound vesicles. The Golgi apparatus operates at the intersection of the secretory, lysosomal, and endocytic pathways. |
| Golgi membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding any of the compartments of the Golgi apparatus. |
| lysosome | A small lytic vacuole that has cell cycle-independent morphology found in most animal cells and that contains a variety of hydrolases, most of which have their maximal activities in the pH range 5-6. The contained enzymes display latency if properly isolated. About 40 different lysosomal hydrolases are known and lysosomes have a great variety of morphologies and functions. |
| neuronal cell body | The portion of a neuron that includes the nucleus, but excludes cell projections such as axons and dendrites. |
| perikaryon | The portion of the cell soma (neuronal cell body) that excludes the nucleus. |
| synapse | The junction between an axon of one neuron and a dendrite of another neuron, a muscle fiber or a glial cell. As the axon approaches the synapse it enlarges into a specialized structure, the presynaptic terminal bouton, which contains mitochondria and synaptic vesicles. At the tip of the terminal bouton is the presynaptic membrane; facing it, and separated from it by a minute cleft (the synaptic cleft) is a specialized area of membrane on the receiving cell, known as the postsynaptic membrane. In response to the arrival of nerve impulses, the presynaptic terminal bouton secretes molecules of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft. These diffuse across the cleft and transmit the signal to the postsynaptic membrane. |
3 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| actin binding | Binding to monomeric or multimeric forms of actin, including actin filaments. |
| GTP binding | Binding to GTP, guanosine triphosphate. |
| GTPase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: GTP + H2O = GDP + H+ + phosphate. |
18 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| axon guidance | The chemotaxis process that directs the migration of an axon growth cone to a specific target site in response to a combination of attractive and repulsive cues. |
| compound eye morphogenesis | The morphogenetic process in which the anatomical structures of the compound eye are generated and organized. The adult compound eye is a precise assembly of 700-800 ommatidia. Each ommatidium is composed of 20 cells, identified by cell type and position. An example of compound eye morphogenesis is found in Drosophila melanogaster. |
| defense response to fungus | Reactions triggered in response to the presence of a fungus that act to protect the cell or organism. |
| exocytosis | A process of secretion by a cell that results in the release of intracellular molecules (e.g. hormones, matrix proteins) contained within a membrane-bounded vesicle. Exocytosis can occur either by full fusion, when the vesicle collapses into the plasma membrane, or by a kiss-and-run mechanism that involves the formation of a transient contact, a pore, between a granule (for exemple of chromaffin cells) and the plasma membrane. The latter process most of the time leads to only partial secretion of the granule content. Exocytosis begins with steps that prepare vesicles for fusion with the membrane (tethering and docking) and ends when molecules are secreted from the cell. |
| germarium-derived egg chamber formation | Construction of a stage-1 egg chamber in the anterior part of the germarium, from the progeny of germ-line and somatic stem cells. An example of this is found in Drosophila melanogaster. |
| intra-Golgi vesicle-mediated transport | The directed movement of substances within the Golgi, mediated by small transport vesicles. These either fuse with the cis-Golgi or with each other to form the membrane stacks known as the cis-Golgi reticulum (network). |
| intracellular protein transport | The directed movement of proteins in a cell, including the movement of proteins between specific compartments or structures within a cell, such as organelles of a eukaryotic cell. |
| oocyte microtubule cytoskeleton polarization | Establishment and maintenance of a specific axis of polarity of the oocyte microtubule network. The axis is set so that the minus and plus ends of the microtubules of the mid stage oocyte are positioned along the anterior cortex and at the posterior pole, respectively. An example of this is found in Drosophila melanogaster. |
| phototransduction | The sequence of reactions within a cell required to convert absorbed photons into a molecular signal. |
| pole plasm oskar mRNA localization | Any process in which oskar mRNA is transported to, or maintained in, the oocyte pole plasm. |
| protein targeting to Golgi apparatus | The process of targeting specific proteins to the Golgi apparatus. Usually requires an organelle-specific protein sequence motif or a protein modification (for example a palmitoylation). |
| R7 cell development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the R7 photoreceptor over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The R7 photoreceptor is the last photoreceptor to develop in the ommatidium. |
| Rab protein signal transduction | The series of molecular signals within the cell that are mediated by a member of the Rab family of proteins switching to a GTP-bound active state. |
| receptor recycling | The process that results in the return of receptor molecules to an active state and an active cellular location after they have been stimulated by a ligand. An active state is when the receptor is ready to receive a signal. |
| regulation of postsynaptic membrane potential | Any process that modulates the potential difference across a post-synaptic membrane. |
| retrograde transport, endosome to Golgi | The directed movement of membrane-bounded vesicles from endosomes back to the trans-Golgi network where they are recycled for further rounds of transport. |
| retrograde vesicle-mediated transport, Golgi to endoplasmic reticulum | The directed movement of substances from the Golgi back to the endoplasmic reticulum, mediated by vesicles bearing specific protein coats such as COPI or COG. |
| vesicle-mediated transport | A cellular transport process in which transported substances are moved in membrane-bounded vesicles; transported substances are enclosed in the vesicle lumen or located in the vesicle membrane. The process begins with a step that directs a substance to the forming vesicle, and includes vesicle budding and coating. Vesicles are then targeted to, and fuse with, an acceptor membrane. |
17 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A6QR46 | RAB6B | Ras-related protein Rab-6B | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| Q1KME6 | RAB6A | Ras-related protein Rab-6A | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | PR |
| O95755 | RAB36 | Ras-related protein Rab-36 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9BZG1 | RAB34 | Ras-related protein Rab-34 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9NRW1 | RAB6B | Ras-related protein Rab-6B | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q5JT25 | RAB41 | Ras-related protein Rab-41 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P20340 | RAB6A | Ras-related protein Rab-6A | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q8CAM5 | Rab36 | Ras-related protein Rab-36 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P61294 | Rab6b | Ras-related protein Rab-6B | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P35279 | Rab6a | Ras-related protein Rab-6A | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9WVB1 | Rab6a | Ras-related protein Rab-6A | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P34213 | rab-6.1 | Ras-related protein rab-6.1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| Q22782 | rab-6.2 | Ras-related protein rab-6.2 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| O80501 | RABH1B | Ras-related protein RABH1b | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9LFT9 | RABH1E | Ras-related protein RABH1e | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9SMR4 | RABH1C | Ras-related protein RABH1c | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9LV79 | RABH1A | Ras-related protein RABH1a | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MSSGDFGNPL | RKFKLVFLGE | QSVGKTSLIT | RFMYDSFDNT | YQATIGIDFL | SKTMYLEDRT |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| VRLQLWDTAG | QERFRSLIPS | YIRDSTVAVV | VYDITNTNSF | HQTSKWIDDV | RTERGSDVII |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| MLVGNKTDLS | DKRQVSTEEG | ERKAKELNVM | FIETSAKAGY | NVKQLFRRVA | AALPGMDSTE |
| 190 | 200 | ||||
| NKPSEDMQEV | VLKDSPNETK | DPEGGCAC |