O09110
Gene name |
Map2k3 (Mkk3, Prkmk3) |
Protein name |
Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 3 |
Names |
MAP kinase kinase 3, MAPKK 3, MAPK/ERK kinase 3, MEK 3 |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:26397 |
EC number |
2.7.12.2: Dual-specificity kinases (those acting on Ser/Thr and Tyr residues) |
Protein Class |
|
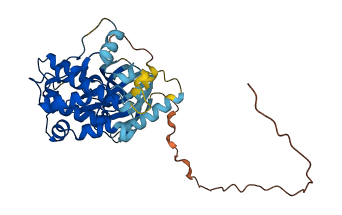
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
207-229 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
64-325 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

2 structures for O09110
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1LEZ | X-ray | 230 A | B | 16-32 | PDB |
| AF-O09110-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
15 variants for O09110
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs212223691 | 6 | A>P | No | EVA | |
| rs243261471 | 7 | S>N | No | EVA | |
| rs3389126637 | 68 | S>T | No | EVA | |
| rs3389165051 | 95 | I>V | No | EVA | |
| rs3389161284 | 106 | R>C | No | EVA | |
| rs3389166092 | 109 | M>R | No | EVA | |
| rs3389138743 | 167 | G>A | No | EVA | |
| rs3389162823 | 179 | H>Y | No | EVA | |
| rs3402402527 | 211 | I>L | No | EVA | |
| rs3389177103 | 247 | V>G | No | EVA | |
| rs3389173481 | 259 | I>V | No | EVA | |
| rs3389163246 | 268 | Y>C | No | EVA | |
| rs3389161346 | 282 | V>M | No | EVA | |
| rs3389161345 | 327 | L>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3389134682 | 333 | T>I | No | EVA |
No associated diseases with O09110
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.12.2 | Dual-specificity kinases (those acting on Ser/Thr and Tyr residues) |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
1 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
6 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| MAP kinase kinase activity | Catalysis of the concomitant phosphorylation of threonine (T) and tyrosine (Y) residues in a Thr-Glu-Tyr (TEY) thiolester sequence in a MAP kinase (MAPK) substrate. |
| protein kinase binding | Binding to a protein kinase, any enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a protein substrate. |
| protein serine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate. |
| protein serine/threonine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate, and ATP + protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate. |
| protein tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + a protein tyrosine = ADP + protein tyrosine phosphate. |
17 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cardiac muscle contraction | Muscle contraction of cardiac muscle tissue. |
| cellular response to lipopolysaccharide | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a lipopolysaccharide stimulus; lipopolysaccharide is a major component of the cell wall of gram-negative bacteria. |
| cellular response to sorbitol | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a sorbitol stimulus. |
| cellular response to vascular endothelial growth factor stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a vascular endothelial growth factor stimulus. |
| heart development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the heart over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The heart is a hollow, muscular organ, which, by contracting rhythmically, keeps up the circulation of the blood. |
| inflammatory response | The immediate defensive reaction (by vertebrate tissue) to infection or injury caused by chemical or physical agents. The process is characterized by local vasodilation, extravasation of plasma into intercellular spaces and accumulation of white blood cells and macrophages. |
| MAPK cascade | An intracellular protein kinase cascade containing at least a MAPK, a MAPKK and a MAP3K. The cascade can also contain an additional tiers: the upstream MAP4K. The kinases in each tier phosphorylate and activate the kinase in the downstream tier to transmit a signal within a cell. |
| negative regulation of hippo signaling | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of hippo signaling. |
| p38MAPK cascade | An intracellular protein kinase cascade containing at least a p38 MAPK, a MAPKK and a MAP3K. The cascade can also contain an additional tier: the upstream MAP4K. The kinases in each tier phosphorylate and activate the kinases in the downstream tier to transmit a signal within a cell. |
| positive regulation of blood vessel endothelial cell migration | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the migration of the endothelial cells of blood vessels. |
| positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cellular DNA-templated transcription. |
| positive regulation of MAPK cascade | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction mediated by the MAPK cascade. |
| positive regulation of nitric-oxide synthase biosynthetic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a nitric oxide synthase enzyme. |
| positive regulation of protein kinase activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of protein kinase activity. |
| positive regulation of protein phosphorylation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of addition of phosphate groups to amino acids within a protein. |
| regulation of cytokine production | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of production of a cytokine. |
| response to ischemia | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a inadequate blood supply. |
15 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q5E9X2 | MAP2K6 | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 6 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | EV |
| P52564 | MAP2K6 | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 6 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P46734 | MAP2K3 | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| O14733 | MAP2K7 | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 7 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P45985 | MAP2K4 | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 4 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q8CE90 | Map2k7 | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 7 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P70236 | Map2k6 | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 6 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| P47809 | Map2k4 | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 4 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| Q9WVS7 | Map2k5 | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 5 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q63932 | Map2k2 | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P31938 | Map2k1 | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| G5EDF7 | sek-1 | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase sek-1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| G5EDT6 | jkk-1 | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase jkk-1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| Q21307 | mek-1 | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase mek-1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| Q9DGE0 | map2k6 | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 6 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MESPAASPPA | SLPQTKGKSK | RKKDLRISCV | SKPPVSNPTP | PRNLDSRTFI | TIGDRNFEVE |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| ADDLVTISEL | GRGAYGVVEK | VRHAQSGTIM | AVKRIRATVN | TQEQKRLLMD | LDINMRTVDC |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| FYTVTFYGAL | FREGDVWICM | ELMDTSLDKF | YRKVLEKNMK | IPEDILGEIA | VSIVRALEHL |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| HSKLSVIHRD | VKPSNVLINK | EGHVKMCDFG | ISGYLVDSVA | KTMDAGCKPY | MAPERINPEL |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| NQKGYNVKSD | VWSLGITMIE | MAILRFPYES | WGTPFQQLKQ | VVEEPSPQLP | ADQFSPEFVD |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | ||
| FTSQCLRKNP | AERMSYLELM | EHPFFTLHKT | KKTDIAAFVK | EILGEDS |