O08816
Gene name |
Wasl |
Protein name |
Actin nucleation-promoting factor WASL |
Names |
Neural Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein, N-WASP |
Species |
Rattus norvegicus (Rat) |
KEGG Pathway |
|
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
SPROUTY-RELATED, EVH1 DOMAIN-CONTAINING PROTEIN FAMILY MEMBER (PTHR11202) |
Descriptions
The neuronal Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome protein (N-WASP) is a key regulator of actin polymerization: it stimulates actin nucleation by the actin related protein 2/3 (Arp2/3) complex in response to upstream inputs. The C-terminal region of N-WASP, known as VCA, serves as the core activity output domain, which can bind and stimulate the de novo actin filament nucleation activity of the Arp2/3/ complex. Two N-terminal regions are required for autoinhibition, a short polybasic (B) motif and an adjacent GTPase binding domain (GBD). In the repressed state, the B motif is postulated to provide a second Arp2/3 complex binding site, whereas the GBD can bind a peptide motif within the VCA output domain. The composite B-GBD module is necessary and sufficient to inhibit VCA activity, because this set of interactions locks the complex in an inactive state. PIP2, which binds to the B motif, and Cdc42, which binds to GBD, act cooperatively to disrupt the autoinhibitory interactions.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
392-501 (C-terminal VCA domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Ligand binding, Partner binding |
Assay |
Deletion assay, Mutagenesis experiment |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
References
- Papayannopoulos V et al. (2005) "A polybasic motif allows N-WASP to act as a sensor of PIP(2) density", Molecular cell, 17, 181-91
- Prehoda KE et al. (2000) "Integration of multiple signals through cooperative regulation of the N-WASP-Arp2/3 complex", Science (New York, N.Y.), 290, 801-6
- Pinyol R et al. (2007) "Regulation of N-WASP and the Arp2/3 complex by Abp1 controls neuronal morphology", PloS one, 2, e400
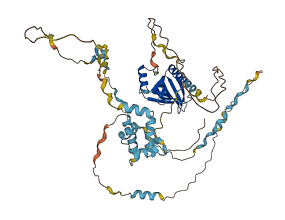
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

3 structures for O08816
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1MKE | NMR | - | A | 26-147 | PDB |
| 2IFS | NMR | - | A | 26-147 | PDB |
| AF-O08816-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for O08816
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for O08816 | |||||
No associated diseases with O08816
8 regional properties for O08816
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Zinc finger, RING-type | 379 - 418 | IPR001841 |
| domain | Adaptor protein Cbl, N-terminal helical | 49 - 173 | IPR003153 |
| domain | Adaptor protein Cbl, EF hand-like | 177 - 260 | IPR014741 |
| domain | Adaptor protein Cbl, SH2-like domain | 254 - 350 | IPR014742 |
| domain | Ubiquitin-associated domain | 863 - 902 | IPR015940 |
| conserved_site | Zinc finger, RING-type, conserved site | 394 - 403 | IPR017907 |
| domain | Zinc finger, C3HC4 RING-type | 379 - 417 | IPR018957 |
| domain | Adaptor protein Cbl, PTB domain | 45 - 349 | IPR024159 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | ||
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | PTHR11202 | SPROUTY-RELATED, EVH1 DOMAIN-CONTAINING PROTEIN FAMILY MEMBER |
| PANTHER Subfamily | PTHR11202:SF36 | NEURAL WISKOTT-ALDRICH SYNDROME PROTEIN |
| PANTHER Protein Class | scaffold/adaptor protein | |
| PANTHER Pathway Category |
Huntington disease N-Wasp Cytoskeletal regulation by Rho GTPase N-WASP |
|
9 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| actin cap | Polarized accumulation of cytoskeletal proteins (including F-actin) and regulatory proteins in a cell. An example of this is the actin cap found in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. |
| cell leading edge | The area of a motile cell closest to the direction of movement. |
| cytoplasmic vesicle | A vesicle found in the cytoplasm of a cell. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| glutamatergic synapse | A synapse that uses glutamate as a neurotransmitter. |
| Golgi membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding any of the compartments of the Golgi apparatus. |
| lamellipodium | A thin sheetlike process extended by the leading edge of a migrating cell or extending cell process; contains a dense meshwork of actin filaments. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| postsynapse | The part of a synapse that is part of the post-synaptic cell. |
3 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| actin binding | Binding to monomeric or multimeric forms of actin, including actin filaments. |
| cytoskeletal protein binding | Binding to a protein component of a cytoskeleton (actin, microtubule, or intermediate filament cytoskeleton). |
| identical protein binding | Binding to an identical protein or proteins. |
23 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| actin cytoskeleton organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures comprising actin filaments and their associated proteins. |
| actin filament polymerization | Assembly of actin filaments by the addition of actin monomers to a filament. |
| cell division | The process resulting in division and partitioning of components of a cell to form more cells; may or may not be accompanied by the physical separation of a cell into distinct, individually membrane-bounded daughter cells. |
| dendritic spine morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structures of a dendritic spine are generated and organized. A dendritic spine is a protrusion from a dendrite and a specialized subcellular compartment involved in synaptic transmission. |
| membrane invagination | The infolding of a membrane. |
| negative regulation of lymphocyte migration | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of lymphocyte migration. |
| negative regulation of membrane tubulation | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of membrane tubulation. |
| plasma membrane tubulation | A membrane tubulation process occurring in a plasma membrane. |
| positive regulation of chemotaxis | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the directed movement of a motile cell or organism in response to a specific chemical concentration gradient. |
| positive regulation of clathrin-dependent endocytosis | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of clathrin-mediated endocytosis. |
| positive regulation of filopodium assembly | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the assembly of a filopodium, a thin, stiff protrusion extended by the leading edge of a motile cell such as a crawling fibroblast or amoeba, or an axonal growth cone. |
| positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription from an RNA polymerase II promoter. |
| postsynapse organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of a postsynapse. |
| postsynaptic actin cytoskeleton organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures comprising actin filaments and their associated proteins in the postsynaptic actin cytoskeleton. |
| protein-containing complex localization | A localization process that acts on a protein complex; the complex is transported to, or maintained in, a specific location. |
| regulation of cell projection assembly | Any process that modulates the rate, frequency, or extent of cell projection assembly. |
| regulation of postsynapse organization | Any process that modulates the physical form of a postsynapse. |
| regulation of protein localization | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any process in which a protein is transported to, or maintained in, a specific location. |
| response to bacterium | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus from a bacterium. |
| spindle localization | Any process in which is the spindle is transported to, and/or maintained in, a specific location. |
| vesicle budding from membrane | The evagination of a membrane, resulting in formation of a vesicle. |
| vesicle organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of a vesicle. |
| vesicle transport along actin filament | Movement of a vesicle along an actin filament, mediated by motor proteins. |
5 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q95107 | WASL | Actin nucleation-promoting factor WASL | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| P42768 | WAS | Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| O00401 | WASL | Actin nucleation-promoting factor WASL | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P70315 | Was | Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein homolog | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q91YD9 | Wasl | Actin nucleation-promoting factor WASL | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MSSGQQPPRR | VTNVGSLLLT | PQENESLFSF | LGKKCVTMSS | AVVQLYAADR | NCMWSKKCSG |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| VACLVKDNPQ | RSYFLRIFDI | KDGKLLWEQE | LYNNFVYNSP | RGYFHTFAGD | TCQVALNFAN |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| EEEAKKFRKA | VTDLLGRRQR | KSEKRRDAPN | GPNLPMATVD | IKNPEITTNR | FYSSQVNNIS |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| HTKEKKKGKA | KKKRLTKADI | GTPSNFQHIG | HVGWDPNTGF | DLNNLDPELK | NLFDMCGISE |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| AQLKDRETSK | VIYDFIEKTG | GVEAVKNELR | RQAPPPPPPS | RGGPPPPPPP | PHSSGPPPPP |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| ARGRGAPPPP | PSRAPTAAPP | PPPPSRPGVV | VPPPPPNRMY | PPPPPALPSS | APSGPPPPPP |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| LSMAGSTAPP | PPPPPPPPPG | PPPPPGLPSD | GDHQVPASSG | NKAALLDQIR | EGAQLKKVEQ |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| NSRPVSCSGR | DALLDQIRQG | IQLKSVSDGQ | ESTPPTPAPT | SGIVGALMEV | MQKRSKAIHS |
| 490 | 500 | ||||
| SDEDEDDDDE | EDFQDDDEWE | D |