O08808
Gene name |
Diaph1 (Diap1) |
Protein name |
Protein diaphanous homolog 1 |
Names |
Diaphanous-related formin-1, DRF1, p140mDIA, mDIA1 |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:13367 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
PROTEIN DIAPHANOUS (PTHR45691) |
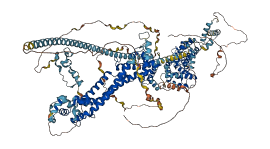
Descriptions
Protein diaphanous homolog 1 (Diaph1, mDia1) is a Rho effector protein involved in the regulation of the actin cytoskeleton and plays a crucial role in cell migration, adhesion, and morphogenesis. Binding of the diaphanous autoregulatory domain (DAD) segment to the diaphanous inhibitory domain (DID) domain inhibits the actin assembly activity of Diaph1. Rho GTPase binding to the N-terminal GTPase-binding domain induces a conformational change in Diaph1 to release its autoinhibited state.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
131-377 (Diaphanous inhibitory, DID domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Partner binding |
Assay |
Deletion assay, Mutagenesis experiment, Structural analysis |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
References
- Lammers M et al. (2005) "The regulation of mDia1 by autoinhibition and its release by Rho*GTP", The EMBO journal, 24, 4176-87
- Otomo T et al. (2010) "Crystal structure of the Formin mDia1 in autoinhibited conformation", PloS one, 5,
- Otomo T et al. (2005) "Structural basis of Rho GTPase-mediated activation of the formin mDia1", Molecular cell, 18, 273-81
- Kitzing TM et al. (2007) "Positive feedback between Dia1, LARG, and RhoA regulates cell morphology and invasion", Genes & development, 21, 1478-83
- Mizuno H et al. (2018) "Helical rotation of the diaphanous-related formin mDia1 generates actin filaments resistant to cofilin", Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 115, E5000-E5007
- Seth A et al. (2006) "Autoinhibition regulates cellular localization and actin assembly activity of the diaphanous-related formins FRLalpha and mDia1", The Journal of cell biology, 174, 701-13
- Lash LL et al. (2013) "Small-molecule intramimics of formin autoinhibition: a new strategy to target the cytoskeletal remodeling machinery in cancer cells", Cancer research, 73, 6793-803
- Deacon SW et al. (2008) "Chemical inhibition through conformational stabilization of Rho GTPase effectors", Handbook of experimental pharmacology, , 431-60
- Orshanskiy IA et al. (2015) "[Molecular Dynamics of N- and C-terminal Interactions during Autoinhibition and Activation of Formin mDial]", Biofizika, 60, 451-6
- Lammers M et al. (2008) "Specificity of interactions between mDia isoforms and Rho proteins", The Journal of biological chemistry, 283, 35236-46
- Copeland SJ et al. (2007) "The diaphanous inhibitory domain/diaphanous autoregulatory domain interaction is able to mediate heterodimerization between mDia1 and mDia2", The Journal of biological chemistry, 282, 30120-30
- Alberts AS (2001) "Identification of a carboxyl-terminal diaphanous-related formin homology protein autoregulatory domain", The Journal of biological chemistry, 276, 2824-30
- Maiti S et al. (2012) "Structure and activity of full-length formin mDia1", Cytoskeleton (Hoboken, N.J.), 69, 393-405
- Gould CJ et al. (2011) "The formin DAD domain plays dual roles in autoinhibition and actin nucleation", Current biology : CB, 21, 384-90
- Goode BL et al. (2007) "Mechanism and function of formins in the control of actin assembly", Annual review of biochemistry, 76, 593-627
- Higgs HN (2005) "Formin proteins: a domain-based approach", Trends in biochemical sciences, 30, 342-53
- Nezami A et al. (2010) "Crystal structure of a complex between amino and carboxy terminal fragments of mDia1: insights into autoinhibition of diaphanous-related formins", PloS one, 5,
- Kovar DR (2006) "Molecular details of formin-mediated actin assembly", Current opinion in cell biology, 18, 11-7
- Li F et al. (2005) "Dissecting requirements for auto-inhibition of actin nucleation by the formin, mDia1", The Journal of biological chemistry, 280, 6986-92
- Copeland JW et al. (2004) "Homo-oligomerization is essential for F-actin assembly by the formin family FH2 domain", The Journal of biological chemistry, 279, 50250-6
- Bai CX et al. (2008) "Activation of TRPP2 through mDia1-dependent voltage gating", The EMBO journal, 27, 1345-56
- Li F et al. (2003) "The mouse Formin mDia1 is a potent actin nucleation factor regulated by autoinhibition", Current biology : CB, 13, 1335-40
Autoinhibited structure
Activated structure

11 structures for O08808
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1V9D | X-ray | 260 A | A/B/C/D | 826-1163 | PDB |
| 1Z2C | X-ray | 300 A | B/D | 69-451 | PDB |
| 2BAP | X-ray | 330 A | PDB | ||
| 2BNX | X-ray | 240 A | A/B | 131-516 | PDB |
| 2F31 | X-ray | 210 A | PDB | ||
| 2V8F | X-ray | 110 A | C | 635-655 | PDB |
| 3EG5 | X-ray | 270 A | B/D | 69-451 | PDB |
| 3O4X | X-ray | 320 A | PDB | ||
| 3OBV | X-ray | 275 A | PDB | ||
| 4UWX | X-ray | 165 A | A/B | 135-369 | PDB |
| AF-O08808-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
10 variants for O08808
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs1132489998 | 93 | D>Y | No | Ensembl | |
| rs1133959615 | 94 | M>I | No | Ensembl | |
| rs235054169 | 602 | S>P | No | Ensembl | |
| rs217471489 | 604 | P>S | No | Ensembl | |
| rs252727994 | 631 | G>V | No | Ensembl | |
| rs580167898 | 645 | A>T | No | Ensembl | |
| rs586033558 | 646 | S>A | No | Ensembl | |
| rs238272030 | 792 | N>D | No | Ensembl | |
| rs31757019 | 955 | N>S | No | Ensembl | |
| rs212584221 | 1013 | D>H | No | Ensembl |
No associated diseases with O08808
5 regional properties for O08808
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Formin, FH3 domain | 265 - 457 | IPR010472 |
| domain | Formin, GTPase-binding domain | 75 - 259 | IPR010473 |
| domain | Diaphanous autoregulatory (DAD) domain | 1177 - 1205 | IPR014767 |
| domain | Rho GTPase-binding/formin homology 3 (GBD/FH3) domain | 75 - 440 | IPR014768 |
| domain | Formin, FH2 domain | 752 - 1197 | IPR015425 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | ||
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | PTHR45691 | PROTEIN DIAPHANOUS |
| PANTHER Subfamily | PTHR45691:SF4 | PROTEIN DIAPHANOUS HOMOLOG 1 |
| PANTHER Protein Class | cytoskeletal protein | |
| PANTHER Pathway Category |
Cytoskeletal regulation by Rho GTPase mDia |
|
7 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| brush border | The dense covering of microvilli on the apical surface of an epithelial cell in tissues such as the intestine, kidney, and choroid plexus; the microvilli aid absorption by increasing the surface area of the cell. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| microtubule organizing center | An intracellular structure that can catalyze gamma-tubulin-dependent microtubule nucleation and that can anchor microtubules by interacting with their minus ends, plus ends or sides. |
| mitotic spindle | A spindle that forms as part of mitosis. Mitotic and meiotic spindles contain distinctive complements of proteins associated with microtubules. |
| neuron projection | A prolongation or process extending from a nerve cell, e.g. an axon or dendrite. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| ruffle membrane | The portion of the plasma membrane surrounding a ruffle. |
5 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| actin binding | Binding to monomeric or multimeric forms of actin, including actin filaments. |
| identical protein binding | Binding to an identical protein or proteins. |
| profilin binding | Binding to profilin, an actin-binding protein that forms a complex with G-actin and prevents it from polymerizing to form F-actin. |
| small GTPase binding | Binding to a small monomeric GTPase. |
| transmembrane transporter binding | Binding to a transmembrane transporter, a protein or protein complex that enables the transfer of a substance, usually a specific substance or a group of related substances, from one side of a membrane to the other. |
13 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| actin cytoskeleton organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures comprising actin filaments and their associated proteins. |
| actin filament polymerization | Assembly of actin filaments by the addition of actin monomers to a filament. |
| brain development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the brain over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Brain development begins with patterning events in the neural tube and ends with the mature structure that is the center of thought and emotion. The brain is responsible for the coordination and control of bodily activities and the interpretation of information from the senses (sight, hearing, smell, etc.). |
| cellular response to histamine | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a histamine stimulus. Histamine, the biogenic amine 2-(1H-imidazol-4-yl)ethanamine, is involved in local immune responses as well as regulating physiological function in the gut and acting as a neurotransmitter. |
| cytoskeleton organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures. |
| neuron projection development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron projection over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A neuron projection is any process extending from a neural cell, such as axons or dendrites (collectively called neurites). |
| positive regulation of cell migration | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell migration. |
| protein localization to microtubule | A process in which a protein is transported to, or maintained at, a microtubule. |
| regulation of cell shape | Any process that modulates the surface configuration of a cell. |
| regulation of cytoskeleton organization | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures. |
| regulation of microtubule-based process | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any cellular process that depends upon or alters the microtubule cytoskeleton. |
| regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the release into the cytosolic compartment of calcium ions sequestered in the endoplasmic reticulum or mitochondria. |
| sensory perception of sound | The series of events required for an organism to receive an auditory stimulus, convert it to a molecular signal, and recognize and characterize the signal. Sonic stimuli are detected in the form of vibrations and are processed to form a sound. |
8 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P48608 | dia | Protein diaphanous | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | EV |
| O60879 | DIAPH2 | Protein diaphanous homolog 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q9NSV4 | DIAPH3 | Protein diaphanous homolog 3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| O60610 | DIAPH1 | Protein diaphanous homolog 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| O70566 | Diaph2 | Protein diaphanous homolog 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q9Z207 | Diaph3 | Protein diaphanous homolog 3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| F1LVW7 | Diaph3 | Protein diaphanous homolog 3 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| F1M775 | Diaph1 | Protein diaphanous homolog 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MEPSGGGLGP | GRGTRDKKKG | RSPDELPATG | GDGGKHKKFL | ERFTSMRIKK | EKEKPNSAHR |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| NSSASYGDDP | TAQSLQDISD | EQVLVLFEQM | LVDMNLNEEK | QQPLREKDIV | IKREMVSQYL |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| HTSKAGMNQK | ESSRSAMMYI | QELRSGLRDM | HLLSCLESLR | VSLNNNPVSW | VQTFGAEGLA |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| SLLDILKRLH | DEKEETSGNY | DSRNQHEIIR | CLKAFMNNKF | GIKTMLETEE | GILLLVRAMD |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| PAVPNMMIDA | AKLLSALCIL | PQPEDMNERV | LEAMTERAEM | DEVERFQPLL | DGLKSGTSIA |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| LKVGCLQLIN | ALITPAEELD | FRVHIRSELM | RLGLHQVLQE | LREIENEDMK | VQLCVFDEQG |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| DEDFFDLKGR | LDDIRMEMDD | FGEVFQIILN | TVKDSKAEPH | FLSILQHLLL | VRNDYEARPQ |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| YYKLIEECVS | QIVLHKNGTD | PDFKCRHLQI | DIERLVDQMI | DKTKVEKSEA | KATELEKKLD |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| SELTARHELQ | VEMKKMENDF | EQKLQDLQGE | KDALDSEKQQ | ITAQKQDLEA | EVSKLTGEVA |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| KLSKELEDAK | NEMASLSAVV | VAPSVSSSAA | VPPAPPLPGD | SGTVIPPPPP | PPPLPGGVVP |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| PSPPLPPGTC | IPPPPPLPGG | ACIPPPPQLP | GSAAIPPPPP | LPGVASIPPP | PPLPGATAIP |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| PPPPLPGATA | IPPPPPLPGG | TGIPPPPPPL | PGSVGVPPPP | PLPGGPGLPP | PPPPFPGAPG |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| IPPPPPGMGV | PPPPPFGFGV | PAAPVLPFGL | TPKKVYKPEV | QLRRPNWSKF | VAEDLSQDCF |
| 790 | 800 | 810 | 820 | 830 | 840 |
| WTKVKEDRFE | NNELFAKLTL | AFSAQTKTSK | AKKDQEGGEE | KKSVQKKKVK | ELKVLDSKTA |
| 850 | 860 | 870 | 880 | 890 | 900 |
| QNLSIFLGSF | RMPYQEIKNV | ILEVNEAVLT | ESMIQNLIKQ | MPEPEQLKML | SELKEEYDDL |
| 910 | 920 | 930 | 940 | 950 | 960 |
| AESEQFGVVM | GTVPRLRPRL | NAILFKLQFS | EQVENIKPEI | VSVTAACEEL | RKSENFSSLL |
| 970 | 980 | 990 | 1000 | 1010 | 1020 |
| ELTLLVGNYM | NAGSRNAGAF | GFNISFLCKL | RDTKSADQKM | TLLHFLAELC | ENDHPEVLKF |
| 1030 | 1040 | 1050 | 1060 | 1070 | 1080 |
| PDELAHVEKA | SRVSAENLQK | SLDQMKKQIA | DVERDVQNFP | AATDEKDKFV | EKMTSFVKDA |
| 1090 | 1100 | 1110 | 1120 | 1130 | 1140 |
| QEQYNKLRMM | HSNMETLYKE | LGDYFVFDPK | KLSVEEFFMD | LHNFRNMFLQ | AVKENQKRRE |
| 1150 | 1160 | 1170 | 1180 | 1190 | 1200 |
| TEEKMRRAKL | AKEKAEKERL | EKQQKREQLI | DMNAEGDETG | VMDSLLEALQ | SGAAFRRKRG |
| 1210 | 1220 | 1230 | 1240 | 1250 | |
| PRQVNRKAGC | AVTSLLASEL | TKDDAMAPGP | VKVPKKSEGV | PTILEEAKEL | VGRAS |