O08561
Gene name |
Pi4kb (Pik4cb) |
Protein name |
Phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase beta |
Names |
PI4K-beta, PI4Kbeta, PtdIns 4-kinase beta |
Species |
Rattus norvegicus (Rat) |
KEGG Pathway |
rno:81747 |
EC number |
2.7.1.67: Phosphotransferases with an alcohol group as acceptor |
Protein Class |
|
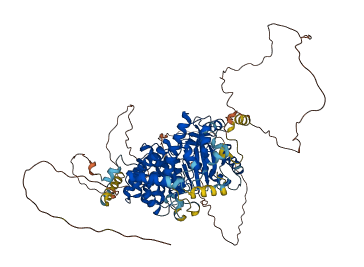
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
689-711 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
529-816 (Catalytic domain of Type III Phosphoinositide 4-kinase beta) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for O08561
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-O08561-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for O08561
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for O08561 | |||||
No associated diseases with O08561
4 regional properties for O08561
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Phosphatidylinositol 3-/4-kinase, catalytic domain | 535 - 814 | IPR000403 |
| domain | Phosphoinositide 3-kinase, accessory (PIK) domain | 61 - 242 | IPR001263 |
| conserved_site | Phosphatidylinositol 3/4-kinase, conserved site | 563 - 577 | IPR018936-1 |
| conserved_site | Phosphatidylinositol 3/4-kinase, conserved site | 656 - 676 | IPR018936-2 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.1.67 | Phosphotransferases with an alcohol group as acceptor |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
8 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| Golgi apparatus | A membrane-bound cytoplasmic organelle of the endomembrane system that further processes the core oligosaccharides (e.g. N-glycans) added to proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum and packages them into membrane-bound vesicles. The Golgi apparatus operates at the intersection of the secretory, lysosomal, and endocytic pathways. |
| Golgi membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding any of the compartments of the Golgi apparatus. |
| membrane | A lipid bilayer along with all the proteins and protein complexes embedded in it an attached to it. |
| mitochondrial outer membrane | The outer, i.e. cytoplasm-facing, lipid bilayer of the mitochondrial envelope. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| rough endoplasmic reticulum membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding the rough endoplasmic reticulum. |
4 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| 1-phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: 1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol + ATP = 1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol 4-phosphate + ADP + 2 H(+). |
| 14-3-3 protein binding | Binding to a 14-3-3 protein. A 14-3-3 protein is any of a large family of approximately 30kDa acidic proteins which exist primarily as homo- and heterodimers within all eukaryotic cells, and have been implicated in the modulation of distinct biological processes by binding to specific phosphorylated sites on diverse target proteins, thereby forcing conformational changes or influencing interactions between their targets and other molecules. Each 14-3-3 protein sequence can be roughly divided into three sections: a divergent amino terminus, the conserved core region and a divergent carboxy-terminus. The conserved middle core region of the 14-3-3s encodes an amphipathic groove that forms the main functional domain, a cradle for interacting with client proteins. |
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| phosphatidylinositol kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + a phosphatidylinositol = ADP + a phosphatidylinositol phosphate. |
5 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| lysosome organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of a lysosome. A lysosome is a cytoplasmic, membrane-bounded organelle that is found in most animal cells and that contains a variety of hydrolases. |
| phosphatidylinositol phosphate biosynthetic process | The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of phosphatidylinositol phosphate. |
| phosphatidylinositol-mediated signaling | The series of molecular signals in which a cell uses a phosphatidylinositol-mediated signaling to convert a signal into a response. Phosphatidylinositols include phosphatidylinositol (PtdIns) and its phosphorylated derivatives. |
| phosphorylation | The process of introducing a phosphate group into a molecule, usually with the formation of a phosphoric ester, a phosphoric anhydride or a phosphoric amide. |
| signal transduction | The cellular process in which a signal is conveyed to trigger a change in the activity or state of a cell. Signal transduction begins with reception of a signal (e.g. a ligand binding to a receptor or receptor activation by a stimulus such as light), or for signal transduction in the absence of ligand, signal-withdrawal or the activity of a constitutively active receptor. Signal transduction ends with regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. regulation of transcription or regulation of a metabolic process. Signal transduction covers signaling from receptors located on the surface of the cell and signaling via molecules located within the cell. For signaling between cells, signal transduction is restricted to events at and within the receiving cell. |
8 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P39104 | PIK1 | Phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase PIK1 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) | PR |
| O02810 | PI4KB | Phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase beta | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| Q9UBF8 | PI4KB | Phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase beta | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q8BKC8 | Pi4kb | Phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase beta | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| O08662 | Pi4ka | Phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase alpha | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q9Z1L0 | Pik3cb | Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit beta isoform | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| A4IID4 | pi4kb | Phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase beta | Xenopus tropicalis (Western clawed frog) (Silurana tropicalis) | PR |
| Q49GP3 | pi4kb | Phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase beta | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MGDMVVEPAT | LKPTSEPTPS | PSGNNGGSLL | SVITEGVGEL | SVIDPEVAQK | ACQEVLEKVK |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| LLHGGVAISS | KGSPLELVNG | DGVDNEIRCL | DDPPTEIREE | EDEMEPGVVS | GTAKGTRRRR |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| QNNSAKQSWL | LRLFESKLFD | ISMAISYLYN | SKEPGVQAYI | GNRLFCFRNE | DVDFYLPQLL |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| NMYIHMDEDV | GDAIKPYIVH | RCRQSINFSL | QCALLLGAYS | SDMHISTQRH | SRGTKLRKLI |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| LSDELKPAHR | KRELPTLSPA | PDTGLSPSKR | THQRSKSDAT | ASISLSSNLK | RTASNPKVEN |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| EDEELSSSTE | SIDNSFSSPV | RLAPEREFIK | SLMAIGKRLA | TLPTKEQKTQ | RLISELSLLN |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| HKLPARVWLP | TAGFDHHVVR | VPHTQAVVLN | SKDKAPYLIY | VEVLECENFD | TTNVPARIPE |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| NRIRSTRSVE | NLPECGITHE | QRAGSFSTVP | NYDNDDEAWS | VDDIGELQVE | LPEVHTNSCD |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| NISQFSVDSI | TSQESKEPVF | IAAGDIRRRL | SEQLAHTPTA | FKRDPEDPSA | VALKEPWQEK |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| VRRIREGSPY | GHLPNWRLLS | VIVKCGDDLR | QELLAFQVLK | QLQSIWEQER | VPLWIKPYKI |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| LVISADSGMI | EPVVNAVSIH | QVKKQSQLSL | LDYFLQEHGS | YTTEAFLSAQ | RNFVQSCAGY |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| CLVCYLLQVK | DRHNGNILLD | AEGHIIHIDF | GFILSSSPRN | LGFETSAFKL | TTEFVDVMGG |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| LNGDMFNYYK | MLMLQGLIAA | RKHMDKVVQI | VEIMQQGSQL | PCFHGSSTIR | NLKERFHMSM |
| 790 | 800 | 810 | |||
| TEEQLQLLVE | QMVDGSMRSI | TTKLYDGFQY | LTNGIM |