O04887
Gene name |
PECS-2.1 |
Protein name |
Pectinesterase 2 |
Names |
PE 2, Pectin methylesterase |
Species |
Citrus sinensis (Sweet orange) (Citrus aurantium var sinensis) |
KEGG Pathway |
cit:102577945 |
EC number |
3.1.1.11: Carboxylic ester hydrolases |
Protein Class |
|
Descriptions
(Annotation from UniProt)
The PMEI region may act as an autoinhibitory domain and prevent untimely PME activity during transport.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
202-496 (Pectinesterase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
References
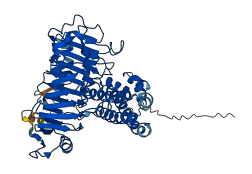
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for O04887
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-O04887-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for O04887
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for O04887 | |||||
No associated diseases with O04887
5 regional properties for O04887
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Pectinesterase, catalytic | 202 - 496 | IPR000070 |
| domain | Pectinesterase inhibitor domain | 1 - 172 | IPR006501 |
| domain | Carbohydrate-binding/sugar hydrolysis domain | 235 - 413 | IPR006633 |
| active_site | Pectinesterase, Tyr active site | 227 - 246 | IPR018040 |
| active_site | Pectinesterase, Asp active site | 344 - 353 | IPR033131 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 3.1.1.11 | Carboxylic ester hydrolases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
1 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| extracellular region | The space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite. |
3 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| aspartyl esterase activity | Catalysis of the hydrolysis of an ester bond by a mechanism involving a catalytically active aspartic acid residue. |
| enzyme inhibitor activity | Binds to and stops, prevents or reduces the activity of an enzyme. |
| pectinesterase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: pectin + n H2O = n methanol + pectate. |
2 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cell wall modification | The series of events leading to chemical and structural alterations of an existing cell wall that can result in loosening, increased extensibility or disassembly. |
| pectin catabolic process | The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of pectin, a polymer containing a backbone of alpha-1,4-linked D-galacturonic acid residues. |
No homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No homologous proteins | ||||
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MALRILITVS | LVLFSLSHTS | FGYSPEEVKS | WCGKTPNPQP | CEYFLTQKTD | VTSIKQDTDF |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| YKISLQLALE | RATTAQSRTY | TLGSKCRNER | EKAAWEDCRE | LYELTVLKLN | QTSNSSPGCT |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| KVDKQTWLST | ALTNLETCRA | SLEDLGVPEY | VLPLLSNNVT | KLISNTLSLN | KVPYNEPSYK |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| DGFPTWVKPG | DRKLLQTTPR | ANIVVAQDGS | GNVKTIQEAV | AAASRAGGSR | YVIYIKAGTY |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| NENIEVKLKN | IMFVGDGIGK | TIITGSKSVG | GGATTFKSAT | VAVVGDNFIA | RDITIRNTAG |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| PNNHQAVALR | SGSDLSVFYR | CSFEGYQDTL | YVHSQRQFYR | ECDIYGTVDF | IFGNAAVVLQ |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| NCNIFARKPP | NRTNTLTAQG | RTDPNQSTGI | IIHNCRVTAA | SDLKPVQSSV | KTFLGRPWKQ |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| YSRTVYIKTF | LDSLINPAGW | MEWSGDFALN | TLYYAEYMNT | GPGSSTANRV | KWRGYHVLTS |
| 490 | 500 | ||||
| PSQVSQFTVG | NFIAGNSWLP | ATNVPFTSGL |