O00585
Gene name |
CCL21 (SCYA21, UNQ784/PRO1600) |
Protein name |
C-C motif chemokine 21 |
Names |
6Ckine, Beta-chemokine exodus-2, Secondary lymphoid-tissue chemokine, SLC, Small-inducible cytokine A21 |
Species |
Homo sapiens (human) |
KEGG Pathway |
hsa:6366 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
SMALL INDUCIBLE CYTOKINE A (PTHR12015) |
Descriptions
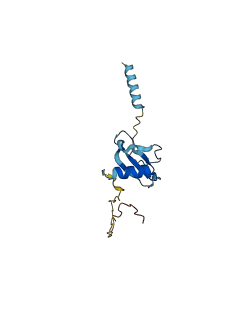
C-C motif chemokine 21 (CCL21) is chemokine that inhibits hemopoiesis and stimulates chemotaxis, and may play a role in mediating homing of lymphocytes to secondary lymphoid organ. CCL21 has an unstructured C-terminus that does not adopt a stable fold. This C-terminal tail of CCL21 makes autoinhibitory contacts with and modulates the structure and function of the CCL21 chemokine domain. CCL21's C-terminus transiently interacts with the chemokine domain of CCL21, thereby providing a putative structural correlate of functional autoinhibition.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
1-79 (Chemokine domain) |
Relief mechanism |
PTM |
Assay |
Deletion assay, Structural analysis |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
References
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure
3 structures for O00585
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2L4N | NMR | - | A | 24-134 | PDB |
| 5EKI | X-ray | 190 A | A/B/C/D/E/F | 24-102 | PDB |
| AF-O00585-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
117 variants for O00585
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
CA373273735 COSM1319603 rs1435524206 |
2 | A>V | haematopoietic_and_lymphoid_tissue [Cosmic] | No |
ClinGen cosmic curated TOPMed |
|
rs376939263 CA5037155 |
4 | S>* | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1413276539 CA373273656 |
6 | A>V | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA192694192 rs779706400 |
7 | L>P | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs766751281 CA5037154 |
8 | S>G | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA192694190 rs901577787 |
8 | S>R | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA373273479 rs1201441537 |
15 | A>T | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1485651001 CA373273461 |
16 | F>L | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA192694183 rs187539558 |
16 | F>S | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes |
|
|
rs372498578 CA192694179 |
17 | G>S | No |
ClinGen ESP TOPMed |
|
|
rs750926648 CA5037152 |
19 | P>H | No |
ClinGen ExAC |
|
|
rs1259222173 CA373273358 |
20 | R>S | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA373273350 rs1212746799 |
21 | T>A | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs768165822 CA373273338 |
21 | T>I | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs768165822 CA5037151 |
21 | T>N | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA373273314 rs1329960763 |
22 | Q>H | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1332010028 CA373273292 |
23 | G>S | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA373272501 rs1433326878 |
24 | S>R | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA373272480 rs1435356127 |
25 | D>Y | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA373272391 rs1323280490 |
29 | Q>* | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs768083949 CA5037134 |
29 | Q>H | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA5037135 rs750836820 |
29 | Q>L | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs753133670 CA192693980 |
30 | D>Y | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA373272202 rs1164366610 |
36 | S>G | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs762419173 CA5037133 |
38 | R>K | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1371709137 CA373272121 COSM1314790 |
39 | K>N | urinary_tract [Cosmic] | No |
ClinGen cosmic curated gnomAD |
| TCGA novel | 39 | K>R | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
| TCGA novel | 40 | I>F | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
|
rs142482921 CA5037130 |
42 | A>S | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs142482921 CA373272080 |
42 | A>T | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA373272044 rs969995486 |
43 | K>N | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1435390901 CA373272066 |
43 | K>Q | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs865854292 CA192693934 |
44 | V>I | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs1453433779 CA373271981 |
46 | R>C | Variant assessed as Somatic; 0.0 impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No |
ClinGen NCI-TCGA gnomAD |
|
rs1453433779 CA373271977 |
46 | R>G | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA5037129 rs776318372 |
46 | R>H | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1195160505 CA373271946 |
47 | S>G | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA5037127 rs760414514 |
49 | R>Q | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA5037128 rs765979271 |
49 | R>W | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs539376444 CA5037124 |
53 | P>R | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs771921191 CA5037125 |
53 | P>S | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA373271768 rs771921191 |
53 | P>T | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA5037123 rs774203687 |
56 | G>D | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs780269897 CA5037120 |
59 | I>N | No |
ClinGen ExAC |
|
|
CA5037121 rs749355595 COSM1108516 |
59 | I>V | Variant assessed as Somatic; 0.0 impact. endometrium [NCI-TCGA, Cosmic] | No |
ClinGen cosmic curated ExAC NCI-TCGA gnomAD |
|
rs1371156951 CA373271610 |
60 | P>L | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA192693815 rs201778181 |
60 | P>S | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA373271554 rs1170851787 |
62 | I>N | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA373271275 rs1283173183 |
66 | P>L | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs753313552 CA5037095 |
66 | P>S | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs753313552 CA5037096 |
66 | P>T | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA5037092 rs750044894 |
67 | R>C | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs34598986 CA5037090 |
67 | R>H | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs34598986 CA5037091 |
67 | R>L | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs764022594 CA5037088 |
68 | K>N | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA373271198 rs1437686948 |
68 | K>R | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA5037087 rs762798553 |
69 | R>C | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA5037086 rs775560130 COSM1247596 |
69 | R>H | oesophagus [Cosmic] | No |
ClinGen cosmic curated ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
rs762798553 CA373271180 |
69 | R>S | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA5037085 rs769975656 |
72 | A>E | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1359922266 CA373271097 |
72 | A>T | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1390934171 CA373271064 |
74 | L>I | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs759733358 CA5037084 |
75 | C>R | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA5037083 rs776954599 |
75 | C>S | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA373271013 rs1268054875 |
76 | A>T | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA192693454 rs956153540 |
76 | A>V | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA373270965 rs1473024111 |
78 | P>S | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs778006557 CA373270884 |
80 | E>D | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs778006557 CA5037080 |
80 | E>D | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1451078274 CA373270854 |
82 | W>* | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA373270829 rs1182863895 |
83 | V>A | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
| TCGA novel | 87 | M>K | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
|
COSM379761 CA5037079 rs772545076 |
88 | Q>* | lung [Cosmic] | No |
ClinGen cosmic curated ExAC TOPMed |
|
CA192693400 rs772545076 |
88 | Q>K | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed |
|
|
CA192693374 rs939141004 |
89 | H>Q | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA5037077 rs748581651 |
89 | H>R | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA373270673 rs1334728950 |
90 | L>V | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA5037074 rs755580810 |
92 | K>R | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA5037073 rs749954967 |
93 | T>A | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1391448419 CA373270544 |
95 | S>F | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1161356955 CA373270562 |
95 | S>T | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1391448419 CA373270558 |
95 | S>Y | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA373270504 rs1408399469 |
97 | Q>R | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA192693334 rs915935603 |
99 | P>L | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1336150097 CA373270386 |
101 | Q>H | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs751296236 CA5037070 |
103 | C>R | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs762857659 CA5037068 |
104 | R>S | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA373270274 rs1166542420 |
105 | K>* | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA373270233 rs1450916503 |
106 | D>E | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs752548751 CA5037067 |
107 | R>M | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs752548751 CA373270212 |
107 | R>T | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA373270198 rs1564116483 |
108 | G>E | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
| rs777471870 | 109 | A>P | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
|
CA5037066 rs759642265 |
109 | A>S | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA5037065 rs759642265 |
109 | A>T | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs776864576 CA5037063 |
110 | S>F | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA373270096 rs1322924992 |
111 | K>N | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA5037062 rs771211630 |
111 | K>R | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs760793347 CA5037061 |
113 | G>R | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA373270007 rs1257922234 |
114 | K>R | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA373269805 rs772291642 |
121 | G>A | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
COSM1624932 CA5037060 rs773531936 |
121 | G>S | liver [Cosmic] | No |
ClinGen cosmic curated ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
rs772291642 CA5037059 |
121 | G>V | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA373269712 rs368229543 |
124 | R>G | No |
ClinGen ESP TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs779340021 CA5037056 |
124 | R>K | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA373269596 rs1219925355 |
124 | R>S | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs754971604 CA5037044 |
126 | E>K | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs148496138 CA5037042 COSM1734322 |
127 | R>Q | pancreas [Cosmic] | No |
ClinGen cosmic curated 1000Genomes ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
rs1370944166 CA373269500 |
128 | S>* | Variant assessed as Somatic; 0.0 impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No |
ClinGen NCI-TCGA gnomAD |
|
rs576393548 CA5037041 |
129 | Q>E | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1191474871 CA373269479 |
129 | Q>R | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA5037040 rs374347595 |
130 | T>I | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA373269431 rs1360588383 |
131 | P>S | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1301405103 CA373269415 |
132 | K>E | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs767802042 CA5037039 |
132 | K>N | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA192693140 rs1007358262 |
133 | G>R | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs762022123 CA5037038 |
134 | P>S | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
No associated diseases with O00585
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | ||
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | PTHR12015 | SMALL INDUCIBLE CYTOKINE A |
| PANTHER Subfamily | PTHR12015:SF72 | C-C MOTIF CHEMOKINE 21 |
| PANTHER Protein Class | cytokine | |
| PANTHER Pathway Category |
Inflammation mediated by chemokine and cytokine signaling pathway CHK |
|
2 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| extracellular region | The space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite. |
| extracellular space | That part of a multicellular organism outside the cells proper, usually taken to be outside the plasma membranes, and occupied by fluid. |
4 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| CCR chemokine receptor binding | Binding to a CCR chemokine receptor. |
| CCR7 chemokine receptor binding | Binding to a CCR7 chemokine receptor. |
| chemokine activity | The function of a family of small chemotactic cytokines; their name is derived from their ability to induce directed chemotaxis in nearby responsive cells. All chemokines possess a number of conserved cysteine residues involved in intramolecular disulfide bond formation. Some chemokines are considered pro-inflammatory and can be induced during an immune response to recruit cells of the immune system to a site of infection, while others are considered homeostatic and are involved in controlling the migration of cells during normal processes of tissue maintenance or development. Chemokines are found in all vertebrates, some viruses and some bacteria. |
| chemokine receptor binding | Binding to a chemokine receptor. |
51 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| activation of GTPase activity | Any process that initiates the activity of an inactive GTPase through the replacement of GDP by GTP. |
| antimicrobial humoral immune response mediated by antimicrobial peptide | An immune response against microbes mediated by anti-microbial peptides in body fluid. |
| cell chemotaxis | The directed movement of a motile cell guided by a specific chemical concentration gradient. Movement may be towards a higher concentration (positive chemotaxis) or towards a lower concentration (negative chemotaxis). |
| cell maturation | A developmental process, independent of morphogenetic (shape) change, that is required for a cell to attain its fully functional state. |
| cell-cell signaling | Any process that mediates the transfer of information from one cell to another. This process includes signal transduction in the receiving cell and, where applicable, release of a ligand and any processes that actively facilitate its transport and presentation to the receiving cell. Examples include signaling via soluble ligands, via cell adhesion molecules and via gap junctions. |
| cellular response to chemokine | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a chemokine stimulus. |
| cellular response to interleukin-1 | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an interleukin-1 stimulus. |
| cellular response to tumor necrosis factor | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a tumor necrosis factor stimulus. |
| cellular response to type II interferon | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an interferon-gamma stimulus. Interferon gamma is the only member of the type II interferon found so far. |
| chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 21 signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by the binding of the C-C chemokine CCL21 to its receptor on the surface of a target cell, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| chemokine-mediated signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by a chemokine binding to its receptor on the surface of a target cell, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| dendritic cell chemotaxis | The movement of a dendritic cell in response to an external stimulus. |
| dendritic cell dendrite assembly | Formation of dendrites, branched cellular projections (or cytoplasmic extension) that are extended from the surface of a dendritic immune cell, and which enable the cell to sample luminal pathogens and increase the surface area for antigen presentation to T cells. |
| eosinophil chemotaxis | The movement of an eosinophil in response to an external stimulus. |
| establishment of T cell polarity | The directed orientation of T cell signaling molecules and associated membrane rafts towards a chemokine gradient or a contact point with antigen presenting cell. |
| G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by a ligand binding to its receptor, in which the activated receptor promotes the exchange of GDP for GTP on the alpha-subunit of an associated heterotrimeric G-protein complex. The GTP-bound activated alpha-G-protein then dissociates from the beta- and gamma-subunits to further transmit the signal within the cell. The pathway begins with receptor-ligand interaction, and ends with regulation of a downstream cellular process. The pathway can start from the plasma membrane, Golgi or nuclear membrane. |
| immune response | Any immune system process that functions in the calibrated response of an organism to a potential internal or invasive threat. |
| immunological synapse formation | The formation of an area of close contact between a lymphocyte (T-, B-, or natural killer cell) and a target cell through the clustering of particular signaling and adhesion molecules and their associated membrane rafts on both the lymphocyte and target cell, which facilitates activation of the lymphocyte, transfer of membrane from the target cell to the lymphocyte, and in some situations killing of the target cell through release of secretory granules and/or death-pathway ligand-receptor interaction. |
| inflammatory response | The immediate defensive reaction (by vertebrate tissue) to infection or injury caused by chemical or physical agents. The process is characterized by local vasodilation, extravasation of plasma into intercellular spaces and accumulation of white blood cells and macrophages. |
| killing of cells of another organism | Any process in an organism that results in the killing of cells of another organism, including in some cases the death of the other organism. Killing here refers to the induction of death in one cell by another cell, not cell-autonomous death due to internal or other environmental conditions. |
| lymphocyte chemotaxis | The directed movement of a lymphocyte in response to an external stimulus. |
| mesangial cell-matrix adhesion | The binding of a mesangial cell to the extracellular matrix via adhesion molecules. A mesangial cell is a cell that encapsulates the capillaries and venules in the kidney. |
| monocyte chemotaxis | The movement of a monocyte in response to an external stimulus. |
| negative regulation of dendritic cell apoptotic process | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of dendritic cell apoptotic process. |
| negative regulation of dendritic cell dendrite assembly | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of dendritic cell dendrite assembly. |
| negative regulation of leukocyte tethering or rolling | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of leukocyte tethering or rolling. |
| neutrophil chemotaxis | The directed movement of a neutrophil cell, the most numerous polymorphonuclear leukocyte found in the blood, in response to an external stimulus, usually an infection or wounding. |
| positive regulation of actin filament polymerization | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of actin polymerization. |
| positive regulation of cell adhesion mediated by integrin | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of cell adhesion mediated by integrin. |
| positive regulation of cell motility | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell motility. |
| positive regulation of cell-matrix adhesion | Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of cell adhesion to an extracellular matrix. |
| positive regulation of chemotaxis | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the directed movement of a motile cell or organism in response to a specific chemical concentration gradient. |
| positive regulation of dendritic cell antigen processing and presentation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of dendritic cell antigen processing and presentation. |
| positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction mediated by the ERK1 and ERK2 cascade. |
| positive regulation of filopodium assembly | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the assembly of a filopodium, a thin, stiff protrusion extended by the leading edge of a motile cell such as a crawling fibroblast or amoeba, or an axonal growth cone. |
| positive regulation of glycoprotein biosynthetic process | Any process that increases the rate, frequency, or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a glycoprotein, a protein that contains covalently bound glycose (i.e. monosaccharide) residues; the glycose occurs most commonly as oligosaccharide or fairly small polysaccharide but occasionally as monosaccharide. |
| positive regulation of GTPase activity | Any process that activates or increases the activity of a GTPase. |
| positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling. |
| positive regulation of JNK cascade | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction mediated by the JNK cascade. |
| positive regulation of myeloid dendritic cell chemotaxis | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of myeloid dendritic cell chemotaxis. |
| positive regulation of neutrophil chemotaxis | Any process that increases the frequency, rate, or extent of neutrophil chemotaxis. Neutrophil chemotaxis is the directed movement of a neutrophil cell, the most numerous polymorphonuclear leukocyte found in the blood, in response to an external stimulus, usually an infection or wounding. |
| positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity. |
| positive regulation of protein kinase activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of protein kinase activity. |
| positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of protein kinase B signaling, a series of reactions mediated by the intracellular serine/threonine kinase protein kinase B. |
| positive regulation of pseudopodium assembly | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the assembly of pseudopodia. |
| positive regulation of receptor-mediated endocytosis | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of receptor mediated endocytosis, the uptake of external materials by cells, utilizing receptors to ensure specificity of transport. |
| positive regulation of T cell chemotaxis | Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of T cell chemotaxis. T cell chemotaxis is the directed movement of a T cell in response to an external stimulus. |
| positive regulation of T cell migration | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of T cell migration. |
| release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol | The process in which calcium ions sequestered in the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus or mitochondria are released into the cytosolic compartment. |
| response to prostaglandin E | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a prostagladin E stimulus. |
| ruffle organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of a ruffle, a projection at the leading edge of a crawling cell. |
4 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P84444 | Ccl21a | C-C motif chemokine 21a | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P86792 | Ccl21b | C-C motif chemokine 21b | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P86793 | Ccl21c | C-C motif chemokine 21c | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q8HYP5 | CCL21 | C-C motif chemokine 21 | Macaca mulatta (Rhesus macaque) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MAQSLALSLL | ILVLAFGIPR | TQGSDGGAQD | CCLKYSQRKI | PAKVVRSYRK | QEPSLGCSIP |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| AILFLPRKRS | QAELCADPKE | LWVQQLMQHL | DKTPSPQKPA | QGCRKDRGAS | KTGKKGKGSK |
| 130 | |||||
| GCKRTERSQT | PKGP |