F1M7Y5
Gene name |
Prkci (Pkcl) |
Protein name |
Protein kinase C iota type |
Names |
EC 2.7.11.13 , Atypical protein kinase C-lambda/iota , aPKC-lambda/iota , nPKC-iota |
Species |
Rattus norvegicus (Rat) |
KEGG Pathway |
rno:84006 |
EC number |
2.7.11.13: Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
Protein Class |
|
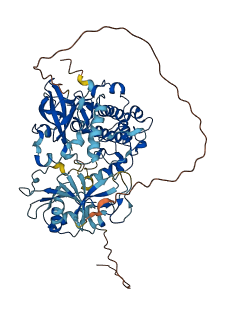
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
233-596 (Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, Atypical Protein Kinase C iota) |
Relief mechanism |
Ligand binding |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
395-418 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
233-596 (Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, Atypical Protein Kinase C iota) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
395-418 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
233-596 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
References
- Yeon JH et al. (2016) "Systems-wide Identification of cis-Regulatory Elements in Proteins", Cell systems, 2, 89-100
- Ivey RA et al. (2014) "Requirements for pseudosubstrate arginine residues during autoinhibition and phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-(PO₄)₃-dependent activation of atypical PKC", The Journal of biological chemistry, 289, 25021-30
- Huang X et al. (2003) "Crystal structure of an inactive Akt2 kinase domain", Structure (London, England : 1993), 11, 21-30
- Truebestein L et al. (2021) "Structure of autoinhibited Akt1 reveals mechanism of PIP(3)-mediated activation", Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 118,
- Lučić I et al. (2018) "Conformational sampling of membranes by Akt controls its activation and inactivation", Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 115, E3940-E3949
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for F1M7Y5
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-F1M7Y5-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for F1M7Y5
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for F1M7Y5 | |||||
No associated diseases with F1M7Y5
14 regional properties for F1M7Y5
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | PB1 domain | 25 - 107 | IPR000270 |
| domain | Protein kinase domain | 254 - 522 | IPR000719 |
| domain | AGC-kinase, C-terminal | 523 - 594 | IPR000961 |
| domain | Protein kinase C-like, phorbol ester/diacylglycerol-binding domain | 140 - 192 | IPR002219 |
| active_site | Serine/threonine-protein kinase, active site | 374 - 386 | IPR008271 |
| binding_site | Protein kinase, ATP binding site | 260 - 287 | IPR017441 |
| domain | Protein kinase, C-terminal | 546 - 584 | IPR017892 |
| domain | Diacylglycerol/phorbol-ester binding | 138 - 152 | IPR020454-1 |
| domain | Diacylglycerol/phorbol-ester binding | 154 - 163 | IPR020454-2 |
| domain | Diacylglycerol/phorbol-ester binding | 167 - 178 | IPR020454-3 |
| domain | Diacylglycerol/phorbol-ester binding | 179 - 191 | IPR020454-4 |
| domain | Atypical protein kinase C iota type, catalytic domain | 233 - 596 | IPR034661 |
| domain | Protein kinase C, PB1 domain | 26 - 108 | IPR034877 |
| domain | PB1-like domain | 25 - 108 | IPR053793 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.11.13 | Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
15 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| apical part of cell | The region of a polarized cell that forms a tip or is distal to a base. For example, in a polarized epithelial cell, the apical region has an exposed surface and lies opposite to the basal lamina that separates the epithelium from other tissue. |
| apical plasma membrane | The region of the plasma membrane located at the apical end of the cell. |
| brush border | The dense covering of microvilli on the apical surface of an epithelial cell in tissues such as the intestine, kidney, and choroid plexus; the microvilli aid absorption by increasing the surface area of the cell. |
| cell leading edge | The area of a motile cell closest to the direction of movement. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| endosome | A vacuole to which materials ingested by endocytosis are delivered. |
| glutamatergic synapse | A synapse that uses glutamate as a neurotransmitter. |
| Golgi membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding any of the compartments of the Golgi apparatus. |
| intercellular bridge | A direct connection between the cytoplasm of two cells that is formed following the completion of cleavage furrow ingression during cell division. They are usually present only briefly prior to completion of cytokinesis. However, in some cases, such as the bridges between germ cells during their development, they become stabilised. |
| microtubule cytoskeleton | The part of the cytoskeleton (the internal framework of a cell) composed of microtubules and associated proteins. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| PAR polarity complex | A protein kinase complex that is required for the establishment of a cell polarity axis during the cell division cycle. Binds directly to activated CDC42 GTPase and is required for orchestrating a cellular gradient of CDC42. In S. cerevisiae components are |
| Schaffer collateral - CA1 synapse | A synapse between the Schaffer collateral axon of a CA3 pyramidal cell and a CA1 pyramidal cell. |
| Schmidt-Lanterman incisure | Regions within compact myelin in which the cytoplasmic faces of the enveloping myelin sheath are not tightly juxtaposed, and include cytoplasm from the cell responsible for making the myelin. Schmidt-Lanterman incisures occur in the compact myelin internode, while lateral loops are analogous structures found in the paranodal region adjacent to the nodes of Ranvier. |
7 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| diacylglycerol-dependent serine/threonine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction |
| metal ion binding | Binding to a metal ion. |
| phospholipid binding | Binding to a phospholipid, a class of lipids containing phosphoric acid as a mono- or diester. |
| protein kinase activity | Catalysis of the phosphorylation of an amino acid residue in a protein, usually according to the reaction |
| protein serine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions |
| protein serine/threonine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions |
21 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| actin filament organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures comprising actin filaments. Includes processes that control the spatial distribution of actin filaments, such as organizing filaments into meshworks, bundles, or other structures, as by cross-linking. |
| cell migration | The controlled self-propelled movement of a cell from one site to a destination guided by molecular cues. |
| cell-cell junction organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of a cell-cell junction. A cell-cell junction is a specialized region of connection between two cells. |
| cellular response to insulin stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an insulin stimulus. Insulin is a polypeptide hormone produced by the islets of Langerhans of the pancreas in mammals, and by the homologous organs of other organisms. |
| establishment of apical/basal cell polarity | The specification and formation of the polarity of a cell along its apical/basal axis. |
| establishment or maintenance of epithelial cell apical/basal polarity | Any cellular process that results in the specification, formation or maintenance of the apicobasal polarity of an epithelial cell. |
| eye photoreceptor cell development | Development of a photoreceptor, a sensory cell in the eye that reacts to the presence of light. They usually contain a pigment that undergoes a chemical change when light is absorbed, thus stimulating a nerve. |
| Golgi vesicle budding | The evagination of the Golgi membrane, resulting in formation of a vesicle. |
| intracellular signal transduction | The process in which a signal is passed on to downstream components within the cell, which become activated themselves to further propagate the signal and finally trigger a change in the function or state of the cell. |
| negative regulation of glial cell apoptotic process | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate, or extent of glial cell apoptotic process. |
| negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cell death by apoptotic process in neurons. |
| phosphorylation | The process of introducing a phosphate group into a molecule, usually with the formation of a phosphoric ester, a phosphoric anhydride or a phosphoric amide. |
| positive regulation of endothelial cell apoptotic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of endothelial cell apoptotic process. |
| positive regulation of glial cell proliferation | Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of glial cell proliferation. |
| positive regulation of glucose import | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the import of the hexose monosaccharide glucose into a cell or organelle. |
| positive regulation of neuron projection development | Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of neuron projection development. Neuron projection development is the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron projection over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A neuron projection is any process extending from a neural cell, such as axons or dendrites (collectively called neurites). |
| positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of activity of the transcription factor NF-kappaB. |
| positive regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of protein localization to plasma membrane. |
| regulation of postsynaptic membrane neurotransmitter receptor levels | Any process that regulates the the local concentration of neurotransmitter receptor at the postsynaptic membrane. |
| response to interleukin-1 | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an interleukin-1 stimulus. |
| response to peptide hormone | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a peptide hormone stimulus. A peptide hormone is any of a class of peptides that are secreted into the blood stream and have endocrine functions in living animals. |
21 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P24583 | PKC1 | Protein kinase C-like 1 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) | SS |
| A1Z9X0 | aPKC | Atypical protein kinase C | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| Q05513 | PRKCZ | Protein kinase C zeta type | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P41743 | PRKCI | Protein kinase C iota type | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q02956 | Prkcz | Protein kinase C zeta type | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q62074 | Prkci | Protein kinase C iota type | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P47196 | Akt1 | RAC-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| O55173 | Pdpk1 | 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P09217 | Prkcz | Protein kinase C zeta type | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q63433 | Pkn1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase N1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q64617 | Prkch | Protein kinase C eta type | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P09215 | Prkcd | Protein kinase C delta type | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P63319 | Prkcg | Protein kinase C gamma type | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P47197 | Akt2 | RAC-beta serine/threonine-protein kinase | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q63484 | Akt3 | RAC-gamma serine/threonine-protein kinase | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| O08874 | Pkn2 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase N2 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P09216 | Prkce | Protein kinase C epsilon type | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P05696 | Prkca | Protein kinase C alpha type | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P68403 | Prkcb | Protein kinase C beta type | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q19266 | pkc-3 | Protein kinase C-like 3 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| Q90XF2 | prkci | Protein kinase C iota type | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MPTQRDSSTM | SHTVACGGGG | DHSHQVRVKA | YYRGDIMITH | FEPSISFEGL | CSEVRDMCSF |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| DNEQPFTMKW | IDEEGDPCTV | SSQLELEEAF | RLYELNKDSE | LLIHVFPCVP | ERPGMPCPGE |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| DKSIYRRGAR | RWRKLYCANG | HTFQAKRFNR | RAHCAICTDR | IWGLGRQGYK | CINCKLLVHK |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| KCHKLVTIEC | GRHSLPPEPM | MPMDQSSMHP | DHTQTVIPYN | PSSHESLDQV | GEEKEAMNTR |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| ESGKASSSLG | LQDFDLLRVI | GRGSYAKVLL | VRLKKTDRIY | AMKVVKKELV | NDDEDIDWVQ |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| TEKHVFEQAS | NHPFLVGLHS | CFQTESRLFF | VIEYVNGGDL | MFHMQRQRKL | PEEHARFYSA |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| EISLALNYLH | ERGIIYRDLK | LDNVLLDSEG | HIKLTDYGMC | KEGLRPGDTT | STFCGTPNYI |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| APEILRGEDY | GFSVDWWALG | VLMFEMMAGR | SPFDIVGSSD | NPDQNTEDYL | FQVILEKQIR |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| IPRSLSVKAA | SVLKSFLNKD | PKERLGCHPQ | TGFADIQGHP | FFRNVDWDMM | EQKQVVPPFK |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | |
| PNISGEFGLD | NFDSQFTNEP | VQLTPDDDDI | VRKIDQSEFE | GFEYINPLLM | SAEECV |